Williams Elements With Generalized Degrees of Freedom for Crack Tip SIFs Analysis Under Crack Surface Distributed Loading
-
摘要:
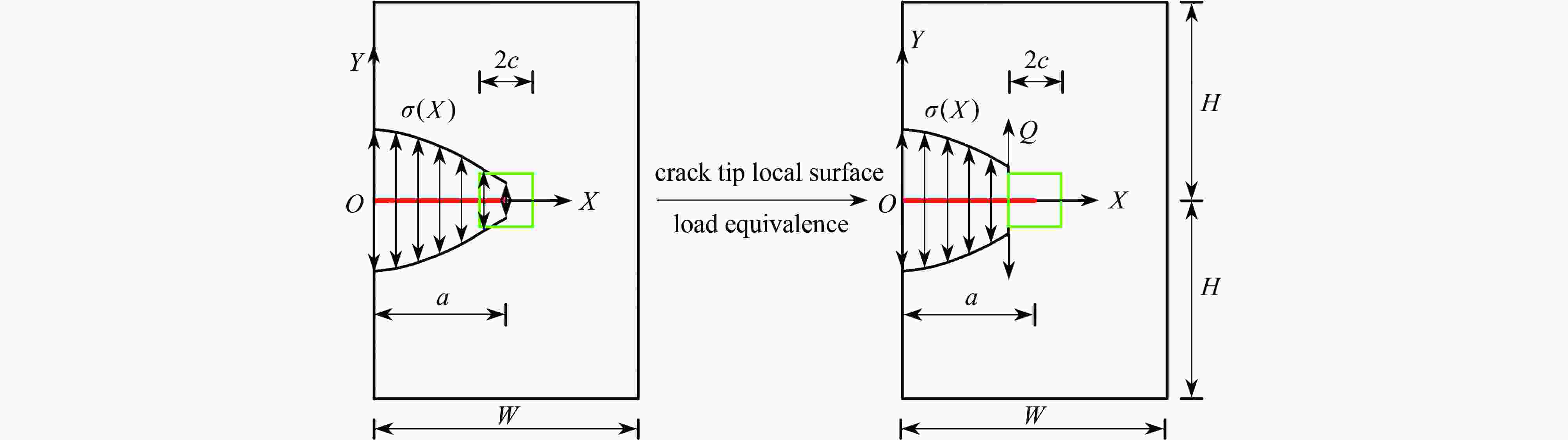
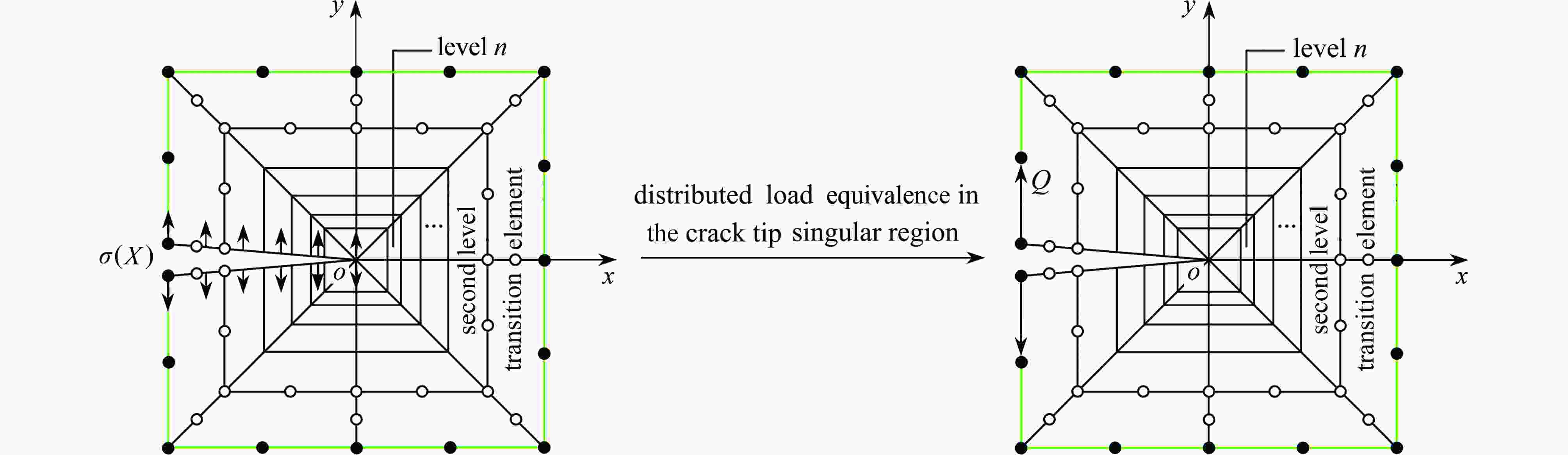
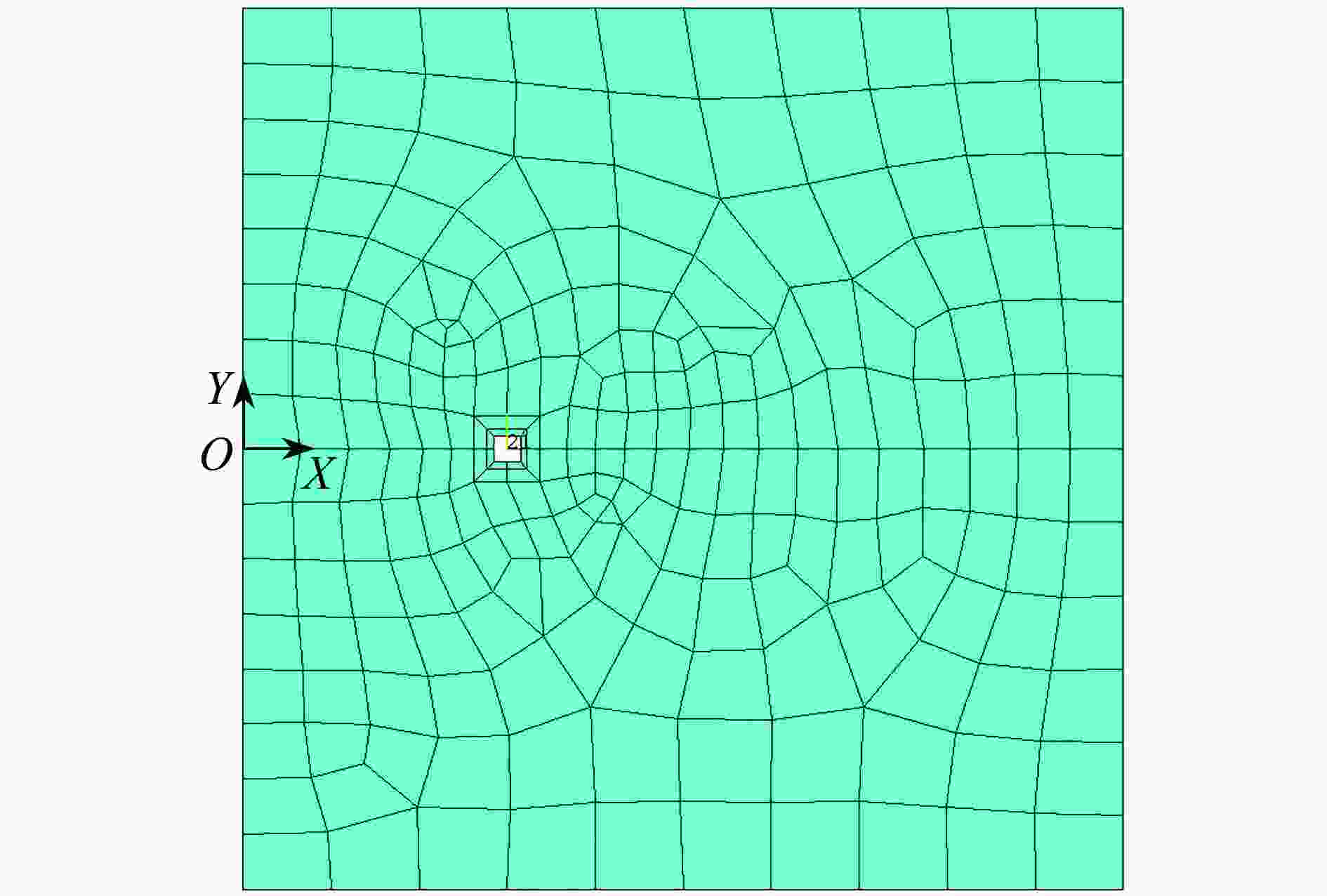
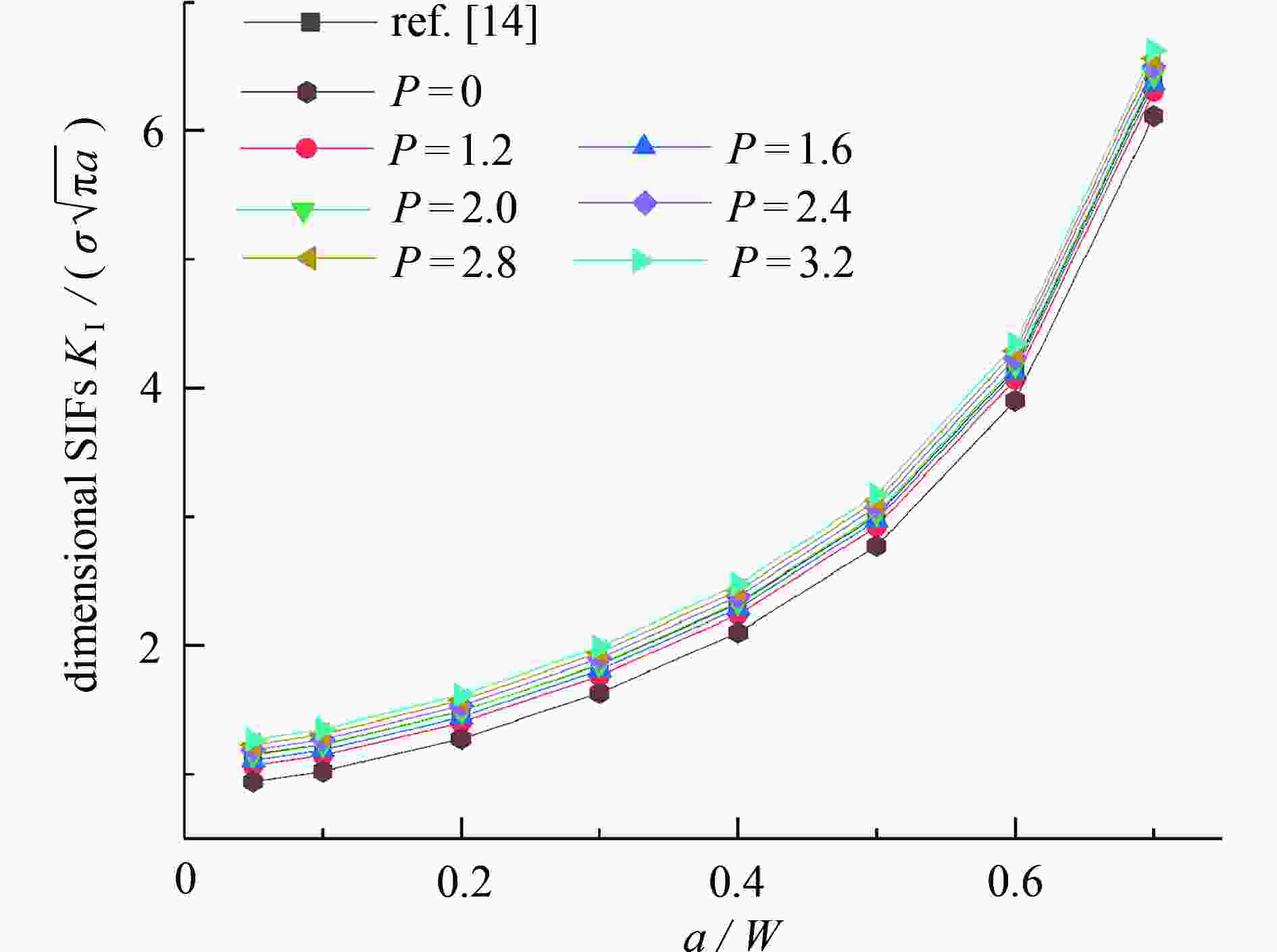
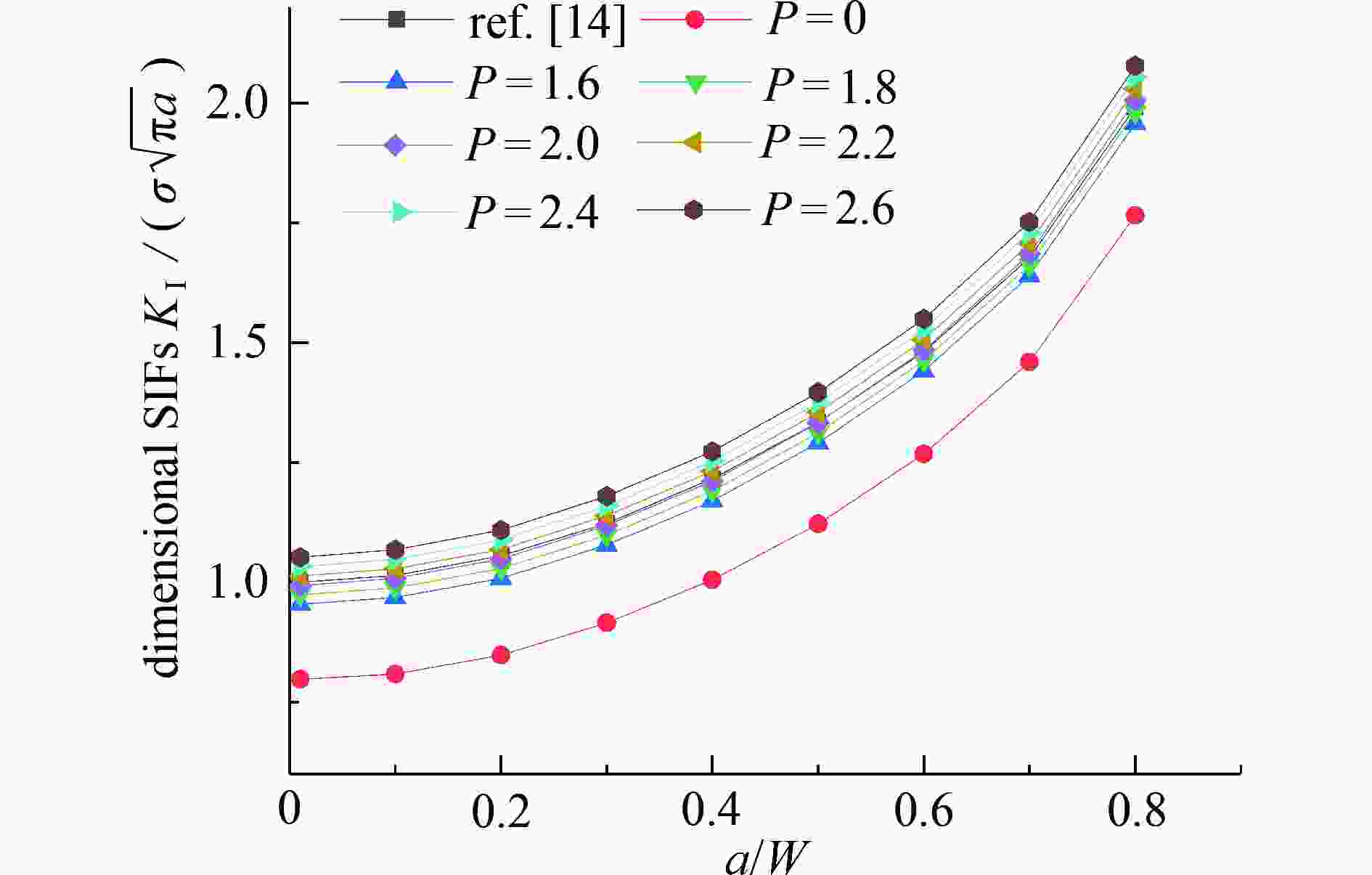
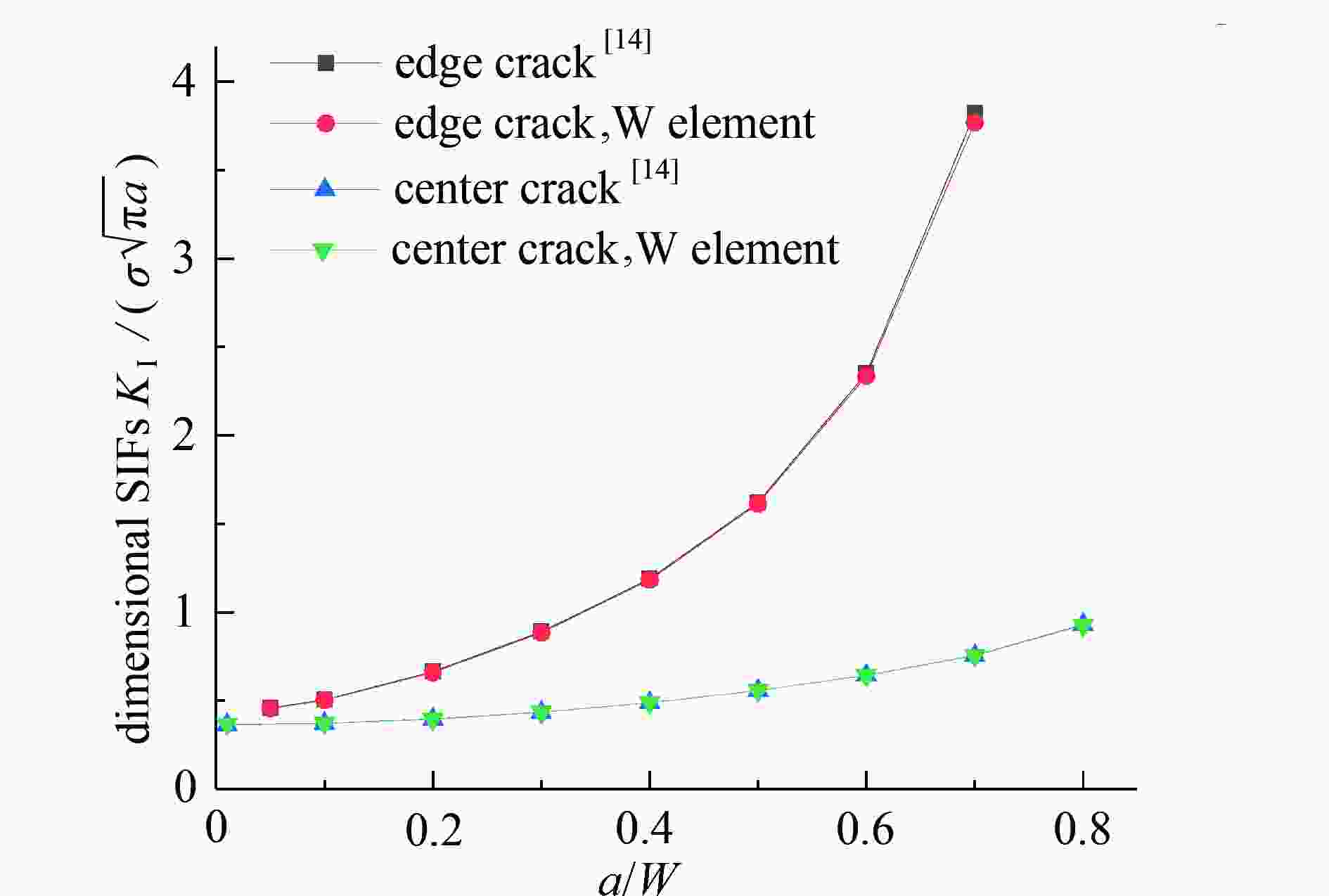
带裂缝服役是工程结构的常态,由于流体侵入到裂缝内部,裂纹面直接受荷,使得裂缝进一步扩展,甚者影响结构的安全性。广义参数Williams单元(简记W单元)在分析断裂问题中,利用Williams级数建立裂尖奇异区的位移场,通过求解广义刚度方程可直接获得应力强度因子(stress intensity factors,SIFs),具有高精高效性;但W单元需满足奇异区内裂纹面自由的边界条件,故在分析裂纹面加载的问题中受限。该文基于SIFs互等,在等效奇异区范围中,将裂纹面的荷载等效为奇异区外围边界裂纹面上的集中力,避免奇异区内裂纹面受荷,故采用W单元即可简便计算。算例分析表明:等效奇异区尺寸取裂纹长度的1/20,等效荷载系数P建议取2.0,W单元计算精度均满足1%的误差限,证明该文在奇异区裂纹面受荷等效处理方法上具有合理性、通用性,克服了W单元在分析裂纹面加载问题的局限性。
-
关键词:
- 裂纹面加载 /
- 荷载等效 /
- 应力强度因子 /
- Williams单元 /
- 广义参数
Abstract:Service with cracks is the normal state of engineering structures. Due to the fluid invading into the crack, the crack surface is loaded directly, which makes the crack further expand, and even affects the safety of the structure. In the analysis of fracture problems, according to the Williams element with generalized degrees of freedom (W element), the Williams series was used to establish the displacement field of the singular zone around the crack tip, and the stress intensity factors (SIFs) can be directly obtained by solving the generalized stiffness equation with high precision and high efficiency. However, the W element needs to satisfy the free boundary condition of the crack surface in the singular zone, so it is limited in the analysis of crack surface loading. Based on the SIFs reciprocity, the loading on the crack surface is equivalent to the concentrated force on the crack surface at the periphery of the equivalent singular zone, so the loading on the crack surface in the singular zone can be avoided, and the W element can be easily used for calculation. The numerical examples show that, the size of the equivalent singular zone is 1/20 of the crack length, the suggested equivalent load coefficient P is 2.0, and the calculation accuracy of the W element meets the error limit of 1%. The equivalent treatment method for the analysis of crack surface loading in the singular zone is reasonable and universal, and overcomes the limitation on the W element in analysis of the loading problem on crack surface.
-
表 1 模型参数(λ=0)
Table 1. Model parameters (λ=0)
a/W $\displaystyle \int_{a - c}^a {\sigma \left( X \right){\text{d} }X}$ P Q 0.05 0.5 1.96 0.982 0.10 0.5 1.98 0.991 0.20 0.5 1.99 0.997 0.30 0.5 1.98 0.988 0.40 0.5 1.93 0.963 0.50 0.5 1.85 0.924 0.60 0.5 1.74 0.869 0.70 0.5 1.60 0.800 -
[1] 刘钧玉, 林皋, 范书立, 等. 裂纹面受荷载作用的应力强度因子的计算[J]. 计算力学学报, 2008, 25(5): 621-626. (LIU Junyu, LIN Gao, FAN Shuli, et al. The calculation of stress intensity factor including the effects of surface tractions[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 2008, 25(5): 621-626.(in Chinese)LIU Junyu, LIN Gao, FAN Shuli, et al. The calculation of stress intensity factor including the effects of surface tractions[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 2008, 25(5): 621-626. (in Chinese)) [2] LIU J Y, LIN G, LI X C, et al. Evaluation of stress intensity factors for multiple cracked circular disks under crack surface tractions with SBFEM[J]. China Ocean Engineering, 2013, 27(3): 417-426. doi: 10.1007/s13344-013-0036-6 [3] ZHONG H, LI C L, LI H J, et al. Stress intensity factors of interfacial crack with arbitrary crack tractions[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2019, 304(5): 052111. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/304/5/052111 [4] 陈白斌, 李建波, 林皋. 无需裂尖增强函数的扩展比例边界有限元法[J]. 水利学报, 2015, 46(4): 489-496, 504. (CHEN Baibin, LI Jianbo, LIN Gao. An extended scaled boundary finite element method without asymptotic enrichment of the crack tip[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2015, 46(4): 489-496, 504.(in Chinese)CHEN Baibin, LI Jianbo, LIN Gao. An extended scaled boundary finite element method without asymptotic enrichment of the crack tip[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2015, 46(4): 489-496, 504. (in Chinese)) [5] 李亚, 易志坚, 王敏, 等. 裂纹面局部均布荷载下Ⅰ型裂纹有限宽板应力强度因子[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2020, 41(10): 1083-1091. (LI Ya, YI Zhijian, WANG Min, et al. The stress intensity factor of a finite-width plate with a mode-Ⅰcenter crack subjected to uniform stress on the crack surface near the crack tip[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2020, 41(10): 1083-1091.(in Chinese)LI Ya, YI Zhijian, WANG Min, et al. The stress intensity factor of a finite-width plate with a mode-Ⅰcenter crack subjected to uniform stress on the crack surface near the crack tip[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2020, 41(10): 1083-1091. (in Chinese)) [6] FETT T, RIZZI G. Weight functions for stress intensity factors and T-stress for oblique cracks in a half-space[J]. International Journal of Fracture, 2005, 132(1): L9-L16. doi: 10.1007/s10704-005-0024-9 [7] LI J, WANG X, TAN C L. Weight functions for the determination of stress intensity factor and T-stress for edge-cracked plates with built-in ends[J]. International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 2004, 81(3): 285-296. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpvp.2003.12.013 [8] WALTERS M C, PAULINO G H, DODDS JR R H. Interaction integral procedures for 3-D curved cracks including surface tractions[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2005, 72(11): 1635-1663. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2005.01.002 [9] MUTHU N, MAITI S K, FALZON B G, et al. A comparison of stress intensity factors obtained through crack closure integral and other approaches using extended element-free Galerkin method[J]. Computational Mechanics, 2013, 52(3): 587-605. doi: 10.1007/s00466-013-0834-y [10] 贾金生, 汪洋, 冯炜, 等. 重力坝高压水劈裂模拟方法与特高重力坝设计准则初步探讨[J]. 水利学报, 2013, 44(2): 127-133. (JIA Jinsheng, WANG Yang, FENG Wei, et al. Simulation method of hydraulic fracturing and discussions on design criteria for super high gravity dams[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2013, 44(2): 127-133.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0559-9350.2013.02.003JIA Jinsheng, WANG Yang, FENG Wei, et al. Simulation method of hydraulic fracturing and discussions on design criteria for super high gravity dams[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2013, 44(2): 127-133. (in Chinese)) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0559-9350.2013.02.003 [11] 唐世斌, 刘向君, 罗江, 等. 水压诱发裂缝拉伸与剪切破裂的理论模型研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2017, 36(9): 2124-2135. (TANG Shibin, LIU Xiangjun, LUO Jiang, et al. Theoretical model for tensile and shear crack initiation at the crack tip in rock subjected to hydraulic pressure[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2017, 36(9): 2124-2135.(in Chinese)TANG Shibin, LIU Xiangjun, LUO Jiang, et al. Theoretical model for tensile and shear crack initiation at the crack tip in rock subjected to hydraulic pressure[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2017, 36(9): 2124-2135. (in Chinese)) [12] 杨绿峰, 徐华, 李冉, 等. 广义参数有限元法计算应力强度因子[J]. 工程力学, 2009, 26(3): 48-54. (YANG Lüfeng, XU Hua, LI Ran, et al. The finite element with generalized coefficients for stress intensity factor[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2009, 26(3): 48-54.(in Chinese)YANG Lufeng, XU Hua, LI Ran, et al. The finite element with generalized coefficients for stress intensity factor[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 2009, 26(3): 48-54. (in Chinese)) [13] 徐华, 邓鹏, 蓝淞耀, 等. 曲线裂纹裂尖SIFs等效分析的广义参数Williams单元确定方法[J]. 工程力学, 2020, 37(6): 34-41. (XU Hua, DENG Peng, LAN Songyao, et al. The determination method of Williams element with generalized degrees of freedom for equivalent analysis of SIFs at the curved crack tip[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2020, 37(6): 34-41.(in Chinese)XU Hua, DENG Peng, LAN Songyao, et al. The determination method of Williams element with generalized degrees of freedom for equivalent analysis of SIFs at the curved crack tip[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2020, 37(6): 34-41. (in Chinese)) [14] 中国航空研究院. 应力强度因子手册[M]. 增订版. 北京: 科学出版社, 1993.Chinese Aeronautical Establishment. Handbook of Stress Intensity Factors[M]. Revised ed. Beijing: Science Press, 1993. (in Chinese) -




 下载:
下载:





 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号