Influence of Multiple Micro Cracks on the Damage Behavior of a Macro-Crack Tip
-
摘要:
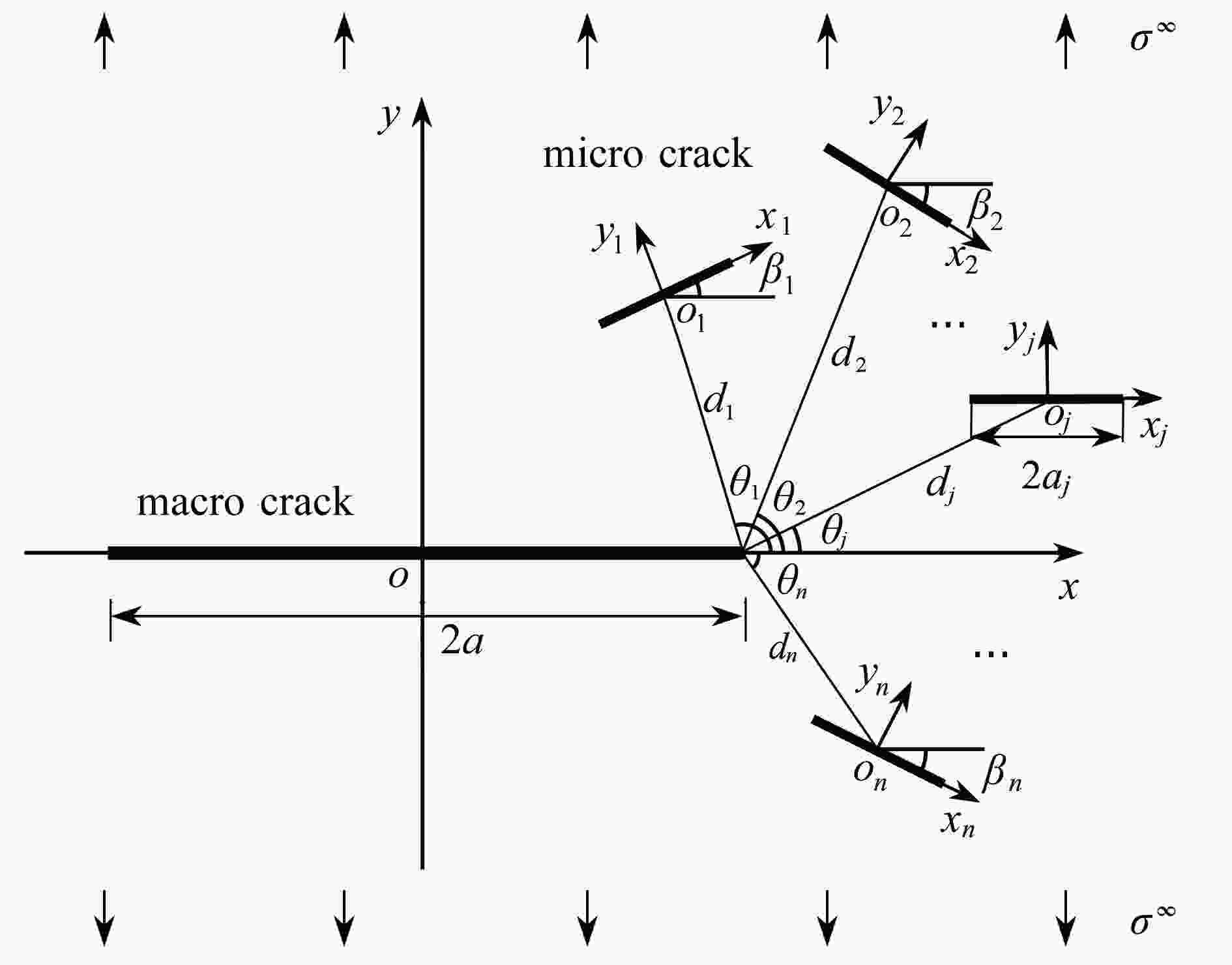
在单轴拉伸荷载作用下,运用Muskhelishvili复变函数法和逐步递推法对无限大平面内含一个主裂纹和多个任意分布的微裂纹问题进行求解,得到了裂纹尖端的应力场和应力强度因子K。在此基础上,结合损伤力学,重新定义了单轴拉伸条件下主裂纹和微裂纹尖端的损伤参量D,分析了不同的损伤区形式对主裂纹尖端损伤的影响。结果表明,正向链式和反向链式分布的微裂纹均对主裂纹尖端损伤有增强作用,并且主裂纹尖端的损伤参量随微裂纹的倾斜角度和裂纹间距的减小而增大。当微裂纹的倾斜角度较小时,主裂纹和微裂纹尖端损伤均有增强作用,并且主裂纹尖端损伤的增强作用随着微裂纹的长度增加而增大。在连续损伤区内,均匀分布的微裂纹对主裂纹尖端损伤的增强作用随着微裂纹的数量增加而逐渐增大。
Abstract:The solution of an infinite plane containing a macro crack and a cluster of micro cracks under uniaxial tensile load was presented based on Muskhelishvili’s complex function method and the stepwise recursive method. The stress field and stress intensity factor K were obtained. Combined with the damage mechanics, damage parameter D of the macro-crack tip and the micro-crack tip under uniaxial tension was redefined, and the influence of different damage zone forms on the damage of the crack tip was analyzed. The results show that, both the chain-distribution and the reverse-chain-distribution micro cracks have an amplifying effect on the macro crack growth, and the damage parameter increases with the decrease of the inclination angle of the micro crack and the reduction of the distance between the macro crack and the micro cracks. For a relatively small inclination angle of the micro crack, the damage parameters of the macro crack and the micro crack heightens, and the damage parameter of the macro crack increases with the micro-crack length. For evenly distributed micro cracks in the continuous damage zone, the micro cracks have an amplifying effect on the macro-crack growth, and the damage parameter of the macro crack increases with the micro-crack number.
-
Key words:
- micro-crack /
- macro-crack /
- micro-crack configuration /
- damage zone /
- damage parameter
-
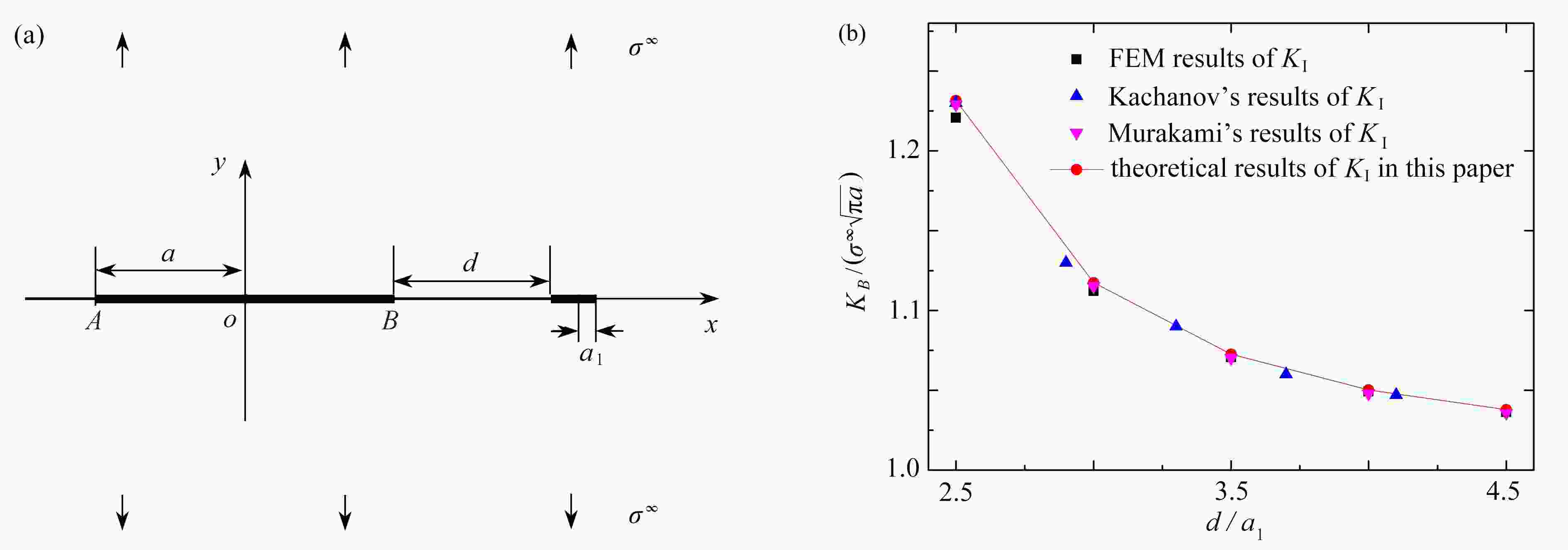
图 6 共线微裂纹对主裂纹尖端应力强度因子的影响:(a) 无限大平面内的共线裂纹;(b) 裂纹尖端B点的应力强度因子随裂纹间距的变化
Figure 6. Influence of the collinear micro crack on the stress intensity factor of the macro crack tip: (a) a collinear micro crack and a macro crack in an infinite plane; (b)
${{{K_B}} / ({{\sigma ^\infty }\sqrt {{\text{π}}{\text{a}}} }})$ vs.$ {d / {{a_1}}} $ for$ {a / {{a_1}}} = 1 $ under tensile load表 1 主裂纹尖端到微裂纹中心的距离 dk/a (k=1, 2, ···, 7)
Table 1. The distance dk/a (k=1, 2, ···, 7) between the macro crack and each micro crack
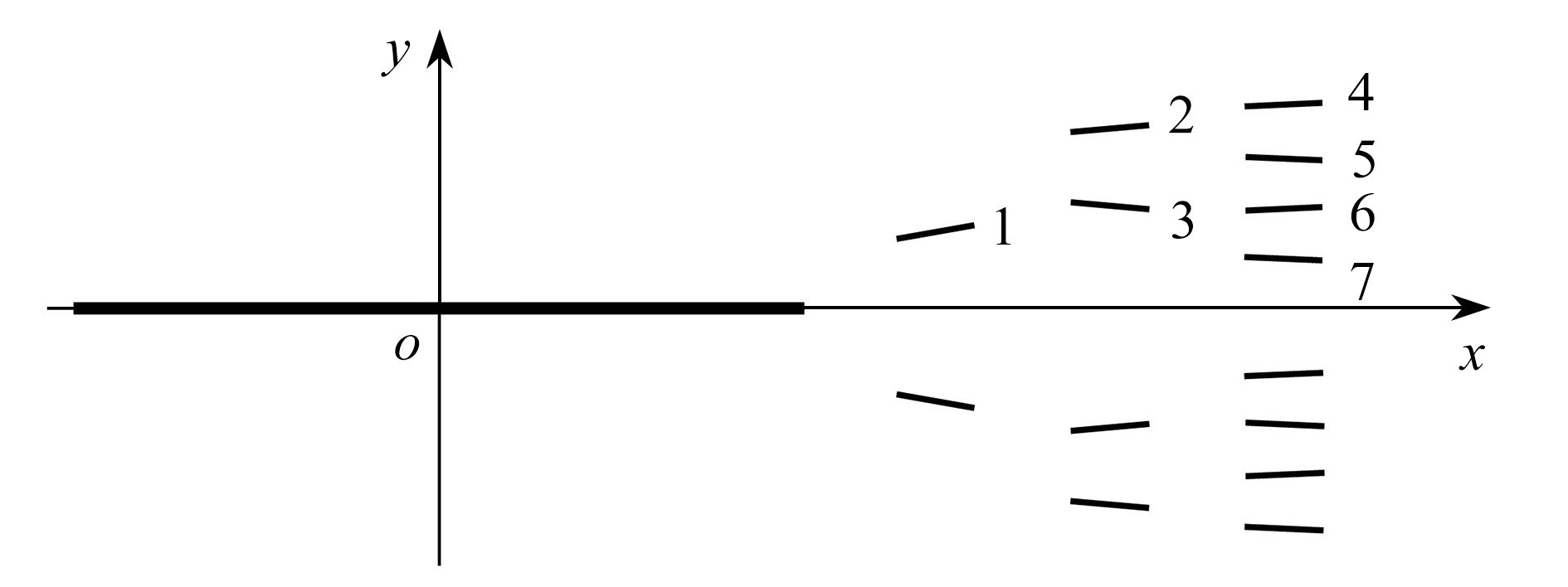
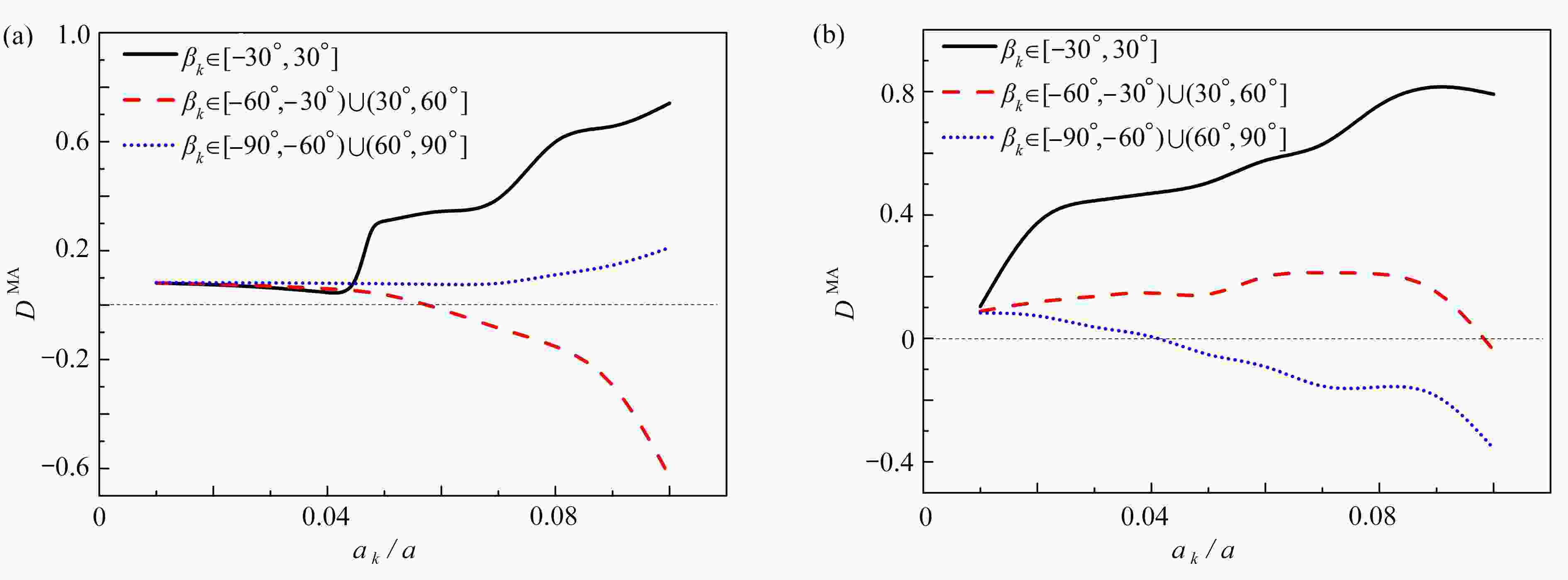
d1/a d2,3/a=d1/a + 0.3 d4,5,6,7/a=d1/a + 0.6 0.2 0.5 0.8 0.3 0.6 0.9 0.4 0.7 1 0.5 0.8 1.1 表 2 微裂纹的倾斜角度βk (k=1, 2, ···, 7)
Table 2. The inclination angle βk (k=1, 2, ···, 7) of each micro crack
$ {\beta _1}/{(^ \circ }) $ $ ({\beta _2} = {{{\beta _1}} /2}) /{(^ \circ }) $ $ ({\beta _3} = {{ - {\beta _1}} / 2}) /{(^ \circ }) $ $ ({\beta _4} = {{{\beta _1}} / 4}) /{(^ \circ }) $ $ ({\beta _5} = {{ - {\beta _1}} / 4}) /{(^ \circ }) $ $ ({\beta _6} = {{{\beta _1}} / 4}) /{(^ \circ }) $ $ ({\beta _7} = {{ - {\beta _1}} / 4}) /{(^ \circ }) $ 10 5 −5 2.5 −2.5 2.5 −2.5 20 10 −10 5 −5 5 −5 30 15 −15 7.5 −7.5 7.5 −7.5 40 20 −20 10 −10 10 −10 50 25 −25 12.5 −12.5 12.5 −12.5 表 3 主裂纹尖端到微裂纹中心的距离 dk/a (k=1, 2, ···, 7)
Table 3. The distance dk/a (k=1, 2, ···, 7) between the macro crack and each micro crack
d1,2,3,4/a=d1/a d5,6/a=d1/a + 0.3 d7/a=d1/a + 0.6 0.2 0.5 0.8 0.3 0.6 0.9 0.4 0.7 1 0.5 0.8 1.1 表 4 微裂纹的倾斜角度 βk (k=1, 2, ···, 7)
Table 4. The inclination angle βk (k=1, 2, ···, 7) of each micro crack
β1/$(^ \circ ) $ (β2=−β1)/$(^ \circ ) $ (β3=β1)/$(^ \circ ) $ (β4=−β1)/$(^ \circ ) $ (β5=2β1)/$(^ \circ ) $ (β6=−2β1)/(°) (β7=4β1)/$(^ \circ ) $ 2.5 −2.5 2.5 −2.5 5 −5 10 5 −5 5 −5 10 −10 20 7.5 −7.5 7.5 −7.5 15 −15 30 10 −10 10 −10 20 −20 40 12.5 −12.5 12.5 −12.5 25 −25 50 -
[1] LI X T, LI X, JIANG X Y. Influence of a micro-crack on the finite macro-crack[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2017, 177: 95-103. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2017.03.037 [2] GONG S X, HORII H. General solution to the problem of micro-cracks near the tip of a main crack[J]. Journal of the Mechanics & Physics of Solids, 1989, 37(1): 27-46. [3] GONG S X, MEGUID S A. Microdefect interacting with a main crack: a general treatment[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 1992, 34(12): 933-945. doi: 10.1016/0020-7403(92)90063-M [4] GONG S X. On the main crack-microcrack interaction under mode Ⅲ loading[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 1995, 51(5): 753-762. doi: 10.1016/0013-7944(94)00318-C [5] PETROVA V E, TAMUZS V, ROMALIS N. A survey of macro-microcrack interaction problems[J]. Applied Mechanics Reviews, 2000, 53(5): 117-146. doi: 10.1115/1.3097344 [6] PETROVA V E. Interaction between a main crack and inclusions of a given orientation[J]. Mechanics of Composite Materials, 1988, 24(3): 288-294. doi: 10.1007/BF00606598 [7] PETROVA V E. Modified model of macro-microcrack interaction[J]. Theoretical & Applied Fracture Mechanics, 1999, 32(2): 111-117. [8] LI X T, LI X, YANG H D, et al. Effect of micro-cracks on plastic zone ahead of the macro-crack tip[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2017, 52(1): 1-14. doi: 10.1007/s10853-016-0371-0 [9] 夏晓舟, 章青, 乔丕忠, 等. 裂纹间作用机制探讨及微裂纹区对主裂纹的作用效应研究[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2010, 31(1): 61-70 doi: 10.3879/j.issn.1000-0887.2010.01.007XIA Xiaozhou, ZHANG Qing, QIAO Pizhong, et al. Interaction between cracks and effect of micro-crack zone on main crack tip[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2010, 31(1): 61-70.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3879/j.issn.1000-0887.2010.01.007 [10] 李亚, 易志坚, 王敏, 等. 裂纹面局部均布荷载下Ⅰ型裂纹有限宽板应力强度因子[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2020, 41(10): 1083-1091LI Ya, YI Zhijian, WANG Min, et al. The stress intensity factor of a finite width plate with a mode-Ⅰ center crack subjected to uniform stress on the crack surface near the crack tip[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2020, 41(10): 1083-1091.(in Chinese) [11] CHESSA J, SMOLINSKI P, BELYTSCHKO T. The extended finite element method (XFEM) for solidification problems[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2002, 53(8): 1959-1977. doi: 10.1002/nme.386 [12] SOH A K, YANG C H. Numerical modeling of interactions between a macro-crack and a cluster of micro-defects[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2004, 71(2): 193-217. doi: 10.1016/S0013-7944(03)00097-3 [13] OUINAS D, BOUIADJRA B B, BENDERDOUCHE N, et al. Numerical modelling of the interaction macro-multimicrocracks in a plate under tensile stress[J]. Journal of Computational Science, 2011, 2(2): 153-164. doi: 10.1016/j.jocs.2010.12.009 [14] KACHANOV L. Time of the rupture process under creep conditions[J]. Doklady Akademii Nauk SSSR, 1958, 8: 26-31. [15] RABOTNOV Y N, LECKIE F A, PRAGER W. Creep problems in structural members[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1970, 37(1): 249-250. [16] LEMAITRE J. A continuous damage mechanics model for ductile fracture[J]. Transactions of the ASME Journal of Engineering Materials and Technology, 1985, 107(1): 83-89. doi: 10.1115/1.3225775 [17] MUSKHELISHVILI N I. Some Basic Problems of the Mathematical Theory of Elasticity[M]. Berlin: Springer Science & Business Media , 1977. [18] 范天佑. 断裂理论基础[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003.FAN Tianyou. The Theory of Fracture Mechanics[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2003. (in Chinese) [19] KRAJCINOVIC D. Constitutive equations for damaging materials[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1983, 50(2): 355-360. doi: 10.1115/1.3167044 [20] CHOW C L, WANG J. An anisotropic theory of elasticity for continuum damage mechanics[J]. International Journal of Fracture, 1987, 33(1): 3-16. doi: 10.1007/BF00034895 [21] TANAKA K. Fatigue crack propagation from a crack inclined to the cyclic tensile axis[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 1974, 6(3): 493-507. doi: 10.1016/0013-7944(74)90007-1 [22] KACHANOV M. Elastic solids with many cracks and related problems[J]. Advances in Applied Mechanics, 1993, 30: 259-445. [23] MURAKAMI Y, KEER L M. Stress intensity factors handbook[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1993, 60(4): 1063-1063. doi: 10.1115/1.2900983 [24] 冯西桥. 脆性材料的细观损伤理论和损伤结构的安定分析[D]. 博士学位论文. 北京: 清华大学, 1995.FENG Xiqiao. Micro-failure theory for brittle materials and shakedown analysis of structures with damage[D]. PhD Thesis. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 1995. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载:













 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号