The Inverse Source Problem for a Class of Stochastic Convection-Diffusion Equations
-
摘要:
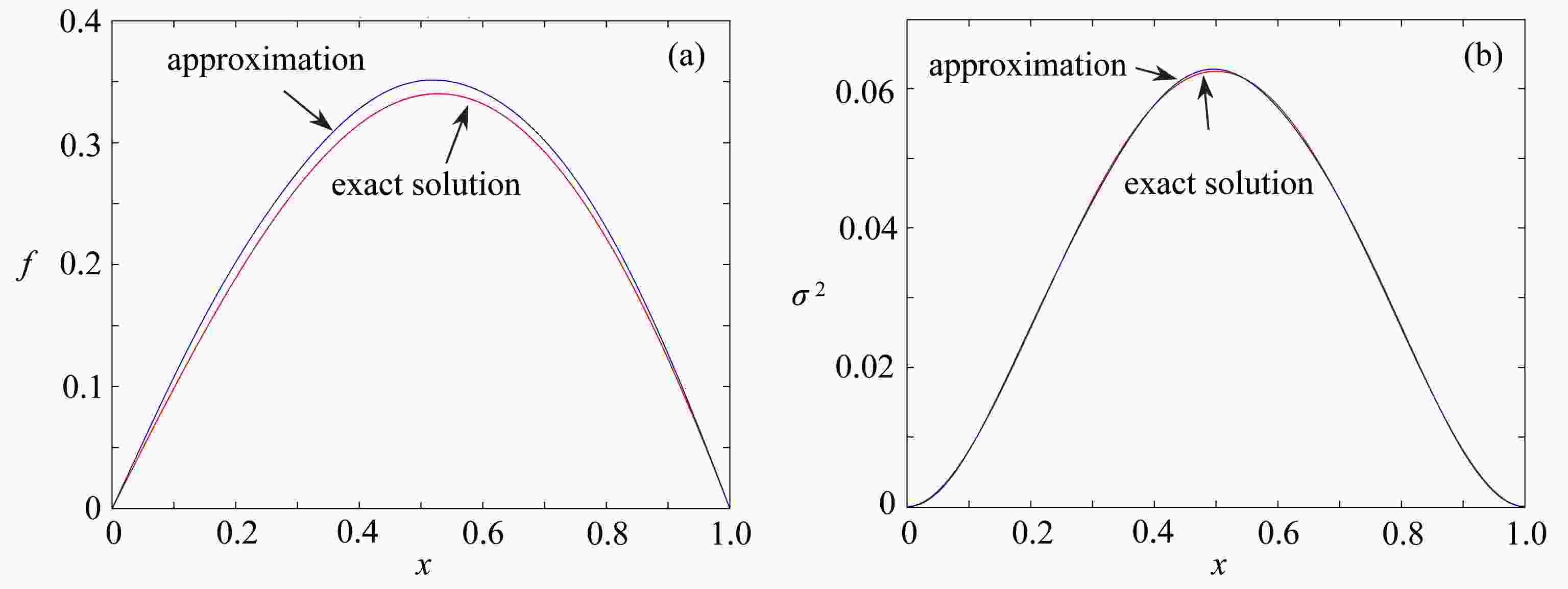
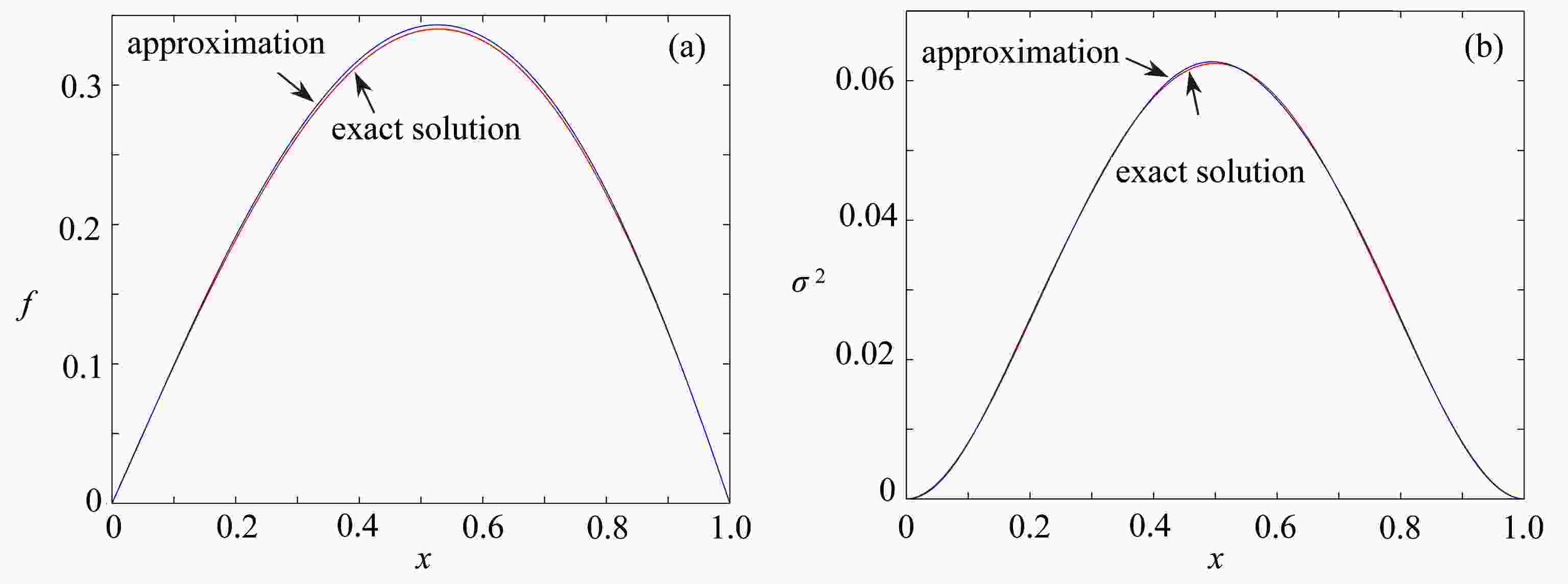
考虑了一类由分数阶Brown运动驱动的随机对流扩散方程的源项反演问题。正问题部分首先利用分离变量法,得出了方程的温和解,进一步在期望的意义下,讨论了正问题的适定性。反问题部分研究了由终止时刻的随机数据来反演随机源项的部分统计量,并证明了相应的唯一性和不稳定性。最后进行了一些数值模拟,验证了相应的理论结果。
-
关键词:
- 随机对流扩散方程 /
- 反源问题 /
- 分数阶Brown运动 /
- 唯一性 /
- 不适定性
Abstract:The inverse source problem for a class of stochastic convection-diffusion equations driven by the fractional Brownian motion with the Hurst index, was considered. The direct problem is to study the solution to the stochastic convection-diffusion equation. The inverse problem is to determine the statistical properties of the source from the expectation and covariance of the final-time data. The direct problem is well-posed. The uniqueness and instability of the inverse source problem was proved. Some numerical simulation examples verify the theoretical analysis.
-
-
[1] 李晓晓, 郭亨贞, 万诗敏, 等. 一类对流-扩散方程热源识别反问题[J]. 兰州理工大学学报, 2012, 38(3): 147-149 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5196.2012.03.034LI Xiaoxiao, GUO Hengzhen, WAN Shimin, et al. A class of inverse problem of identification of heat source term in convection-diffusion equation[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University of Technology, 2012, 38(3): 147-149.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5196.2012.03.034 [2] 贾现正, 张大利, 李功胜, 等. 空间-时间分数阶变系数对流扩散方程微分阶数的数值反演[J]. 计算数学, 2014, 36(2): 113-132 doi: 10.12286/jssx.2014.2.113JIA Xianzheng, ZHANG Dali, LI Gongsheng, et al. Numerical inversion of the fractional orders in the space-time fractional advection-diffusion equation with variable coefficients[J]. Mathematica Numerica Sinica, 2014, 36(2): 113-132.(in Chinese) doi: 10.12286/jssx.2014.2.113 [3] FURATI K M, IYIOLA O S, KIRANE M. An inverse problem for a generalized fractional diffusion[J]. Applied Mathmatics and Computation, 2014, 249: 24-31. doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2014.10.046 [4] AMMARI H, BAO G, FLEMING J L. An inverse source problem for Maxwell’s equations in magnetoencephalography[J]. SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, 2002, 62(4): 1369-1382. doi: 10.1137/S0036139900373927 [5] ANASTASIO M A, ZHANG J, MODGIL D, et al. Application of inverse source concepts to photoacoustic tomography[J]. Inverse Problems, 2007, 23(6): S21-S35. doi: 10.1088/0266-5611/23/6/S03 [6] DEVANEY A J. Inverse source and scattering problems in ultrasonics[J]. IEEE Transaction on Sonics and Ultrasonics, 1983, 30(6): 355-363. doi: 10.1109/T-SU.1983.31440 [7] MARENGO E A, DEVANEY A J. The inverse source problem of electromagnetics: linear inversion formulation and minimum energy solution[J]. IEEE Transaction on Antennas and Propagation, 1999, 47(2): 410-412. doi: 10.1109/8.761085 [8] MARENGO E A, KHODJA M R, BOUCHERIF A. Inverse source problem in nonhomogeneous background media, Ⅱ: vector formulation and antenna substrate performance characterization[J]. SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, 2008, 69(1): 81-110. doi: 10.1137/070689875 [9] LÜ Q. Carleman estimate for stochastic parabolic equations and inverse stochastic parabolic problems[J]. Inverse Problems, 2012, 28(4): 045008. doi: 10.1088/0266-5611/28/4/045008 [10] CHEN S L, WANG Z W, CHEN G L. Cauchy problem of non-homogenous stochastic heat equation and application to inverse random source problem[J]. Inverse Problems and Imaging, 2021, 15(4): 619-639. [11] TUAN N H, NANE E. Inverse source problem for time-fractional diffusion with discrete random noise[J]. Statistics and Probability Letters, 2017, 120: 126-134. doi: 10.1016/j.spl.2016.09.026 [12] NIU P P, HELIN T, ZHANG Z D. An inverse random source problem in a stochastic fractional diffusion equation[J]. Inverse Problems, 2020, 36(4): 045002. doi: 10.1088/1361-6420/ab532c [13] LIU C. Reconstruction of the time-dependent source term in stochastic fractional diffusion equation[J]. Inverse Problems and Imaging, 2020, 14(6): 1001-1024. doi: 10.3934/ipi.2020053 [14] FU S B, ZHANG Z D. Application of the generalized multiscale finite element method in an inverse random source problem[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2021, 429: 110032. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2020.110032 [15] GONG Y X, LI P J, WANG X, et al. Numerical solution of an inverse random source problem for the time fractional diffusion equation via PhaseLift[J]. Inverse Problems, 2021, 37: 045001. doi: 10.1088/1361-6420/abe6f0 [16] LI P J, WANG X. An inverse random source problem for Maxwell’s equations[J]. SIAM Journal on Multiscale Modeling and Simulation, 2021, 19(1): 25-45. doi: 10.1137/20M1331342 [17] LI P J, WANG X. An inverse random source problem for the one-dimensional Helmholtz equation with attenuation[J]. Inverse Problems, 2021, 37(1): 015009. doi: 10.1088/1361-6420/abcd43 [18] FENG X L, LI P J, WANG X. An inverse random source problem for the time fractional diffusion equation driven by a fractional Brownian motion[J]. Inverse Problems, 2020, 36(4): 045008. doi: 10.1088/1361-6420/ab6503 [19] NIE D X, DENG W H. An inverse random source problem for the time-space fractional diffusion equation driven by fractional Brownian motion[EB/OL]. (2021-06-02)[2022-02-12]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.00917. [20] NIE D X, DENG W H. A unified convergence analysis for the fractional diffusion equation driven by fractional Gaussion noise with Hurst index H∈(0, 1)[J]. SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis, 2022, 60(3): 1548-1573. doi: 10.1137/21M1422616 -












 下载:
下载:
























 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号