Wave Surface Identification Based on Stereo Vision and Wave Theory: an Initial Attempt
-
摘要:
波高是波浪信息最基本的元素,对波高的精确测量无论是对波浪理论的研究还是数值方法的拓展,都起着指导和验证的作用。文中基于双目立体视觉原理自主搭建了波面光学测量系统,突破了传统测量设备如浪高仪等单点测量的局限性,并将波浪理论融入到数据后处理方法中,对常用的单纯依赖图像的光学测量方法进行了改进。通过在拖曳水池中对单向规则波瞬时波面的识别和重构,并将结果与浪高仪以及理论来波参数进行了对比验证,结果表明该测量系统在大范围波面的测量中误差在1%左右,最后对其在非规则的来波下进行了初步尝试。
Abstract:The wave height is the most basic element of wave information, and accurate measurement of wave heights plays a crucial role in both understanding wave theory and verifying numerical models. An improved optical measurement system was proposed based on the principle of binocular stereo vision, which breaks through the limitations of traditional measurement devices such as wave gauges and other single-point measurements, and improves the commonly used optical measurement method relying solely on images by involving the water wave theory into the data post-processing procedure. Through the identification and reconstruction of the unidirectional regular wave surface in a towing tank and the comparison of the results with the wave gauges and theoretical incoming wave parameters for validation, the research shows that, the measuring system has an error of about 1% in the measurement of a wide-area wave surface. Finally, a preliminary attempt was made on the irregular wave surface identification.
-
Key words:
- wave surface identification /
- stereo vision /
- wave theory
-
引 言
波面的特性如波高、方向、表面坡度等数据的获取,不仅在工程应用上决定了近海岸及近岸结构设计,在机理研究上对理解空气和水界面的动量、质量和传热也起着至关重要的作用[1-2],同时波浪的精确测量在一定程度上也指导和验证了波浪理论的发展及数值模型的建立[3-7],因此如何精确地获取时空连续的波浪数据一直是研究热点。Krogstad和Barstow[8]及Tucker和Pitt[9]对现有的波面测量技术作了比较全面的总结,传统的测量方法一般是基于传感器感应波浪的变化,如浪高仪和浮标等由于测量精度高,已经广泛应用在水波的测量中,然而这类测量仪器存在不可忽略的弊端:1) 单点测量只能获取空间离散点的数据;2) 传感器浸入在测量区域内会干扰表面波的运动[10];3) 为降低干扰,多个测量仪之间须保持一定距离,这就会导致数据在空间上的不连续,从而影响对波浪的分析。
为解决设备对波面的干扰,非接触式测量技术如声学测波仪、雷达[11]、卫星遥感技术[12-14]、激光技术[15]等应运而生。然而随着几十年的研究和应用,上述技术更多应用于海浪观测领域,运行成本高,测量精度受安装和测量环境影响,且短时间内难以替代传统的测量方法。因此,如何精确地获取瞬时的三维波面特性至今仍然是一个亟待解决的问题。随着现代技术的不断发展,近距离波面的光学测量技术取得了显著的进展,其中以立体视觉为基础的测量系统应用最为广泛[16-20]。例如,Gomit等[21]通过分析光在波面的折射、反射等自然特征对自由波面进行了测量;Gomit等[22]、Engelen等[23]、Wang等[24]在波面投射激光图案,通过图案随波动的变化来分析波面的高度;Chatellier等[25]在水面播撒粒子漂浮物、Chabchoub等[26]在水面放置网状漂浮物来获取波面信息,从而对波浪传播、波浪演化等物理问题进行了实验研究。相比于传统的单点测量技术,光学测量的优势在于:1) 能同时获取瞬时波面的三维信息;2) 非浸入式的测量方法对波面无干扰。然而,由于水介质的透光性,以及对光的折射和反射特性,通常需要附加设备来增强光照或者减弱自然光的影响,较高的测量精度同时也意味着更为严苛的测量环境和实验条件。此外,现有的技术通常无法适用于大范围的海面测量,大多数的研究还是局限于实验室、小尺度(<1 m)的范围内。
当实验技术遇到瓶颈时,我们需要通过研究新的数据处理方法或算法来寻求突破。进入21世纪以来,随着计算机运行速度加快,大数据时代的到来,以神经网络为代表的机器学习技术浪潮又一次出现,这为很多相关领域的研究提供了全新的思路,尤其是卷积神经网络在图像处理方面的优异表现更是促进了以光学测量为代表的测量技术的发展[27-31]。同时,数据同化[32]、数据融合等技术的发展不断对传统实验测量方法进行挑战,多学科交叉融合正成为新的研究热点。
因此本文基于立体视觉原理,自主搭建双目测量系统,在实验室条件下对大范围单向规则波面进行了试验测量,该测量系统操作简单、易于实施,无需额外的附加设备,大大降低了实验成本。在波面图像数据处理过程中,本文将波浪理论作为先验知识,实现了瞬时波面的识别和三维空间重构。该方法突破了传统测量设备的单点测量局限性,并改进了以往仅仅依赖图像分析的光学测量方法,理论与试验研究相结合,为波面的光学测量提供了新的思路。
1. 立体视觉测量方法及改进
1.1 测量原理
双目立体视觉技术是机器视觉技术的一种重要形式,相关的开创性工作始于20世纪60年代中期,美国麻省理工学院(MIT)的Roberts[33]在他的博士论文中讨论了从二维图像中提取三维几何信息的可能性,随后MIT及其他人工智能领域的研究者们对这一问题继续开展了研究。到20世纪70年代,Marr[34]从计算机科学的观点出发,融合了数学、心理物理学、神经生理学,首创了视觉计算理论,极大地推动了双目立体视觉技术的发展,到目前为止,立体视觉已成为计算机视觉中非常重要的分支。
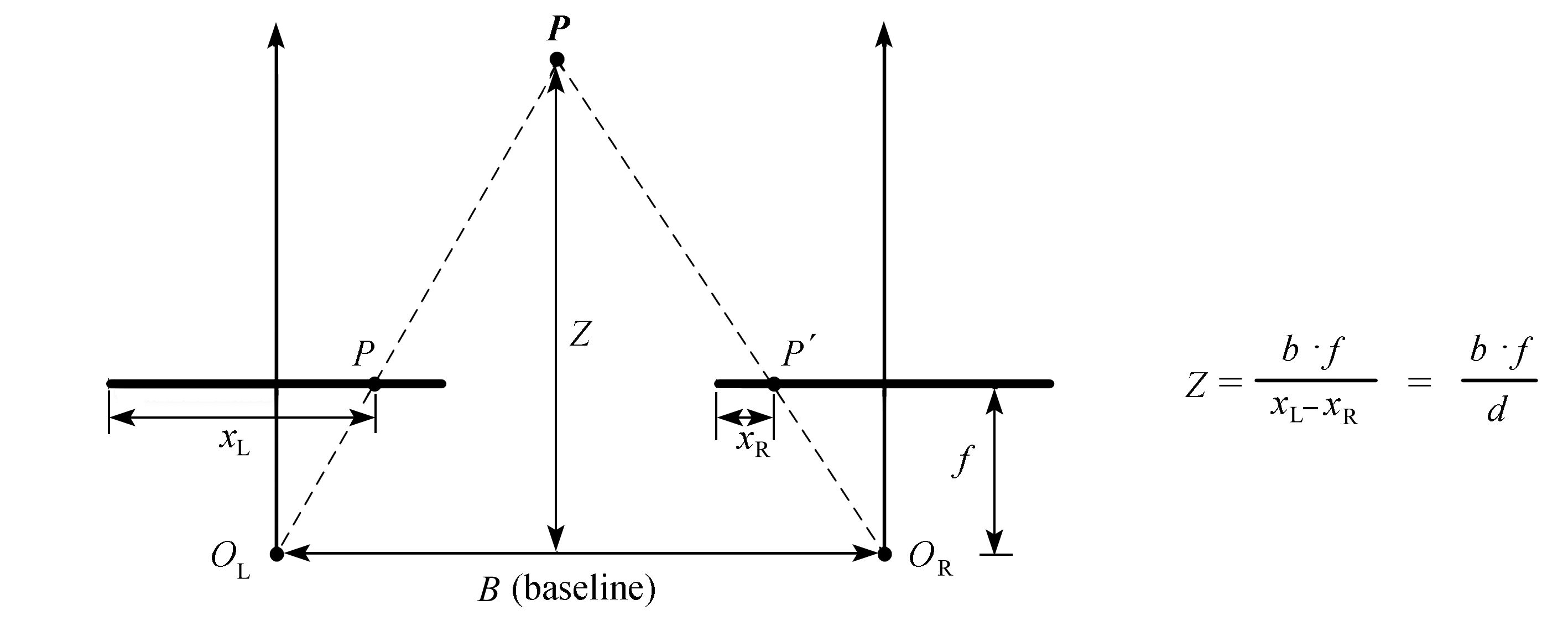
正如人的双眼能够判断物体的远近,双目立体视觉测量也是基于视差原理(图1),根据物体在两个相机上的成像、左右相机的参数及其相对位置,来计算物体离相机的距离,获取该物体的空间三维几何信息。图1中,P,P′分别为P在左右相机的投影,f为相机焦距,xL,xR为P在左右相机上的像素坐标值,B为两个相机光心(OL,OR)之间的距离,Z为物体到相机的距离,d=xL−xR为视差。
该方法涉及到四个坐标系之间的相互转换,即世界坐标系(OW-XWYWZW)、相机坐标系(Oc-XcYcZc)、图像坐标系(xoy)及像素坐标系(u,v)。通过透视投影及仿射变换,可以推导出空间某一点P(XW,YW,ZW)在世界坐标系与像素坐标系之间的转换关系:
$$ {Z}_{{\rm{c}}}\left[\begin{array}{c}u\\ v\\ 1\end{array}\right]=\left[\begin{array}{ccc}{f}_{x}& 0& \begin{array}{cc}{u}_{0}& 0\end{array}\\ 0& {f}_{y}& \begin{array}{cc}{v}_{0}& 0\end{array}\\ 0& 0& \begin{array}{cc}1& 0\end{array}\end{array}\right]\left[\begin{array}{cc}\boldsymbol{R}& \boldsymbol{T}\\ {{\boldsymbol{0}}}& 1\end{array}\right]\left[\begin{array}{c}{X}_{{\rm{W}}}\\ {Y}_{{\rm{W}}}\\ \begin{array}{c}{Z}_{{\rm{W}}}\\ 1\end{array}\end{array}\right] ,$$ (1) 其中
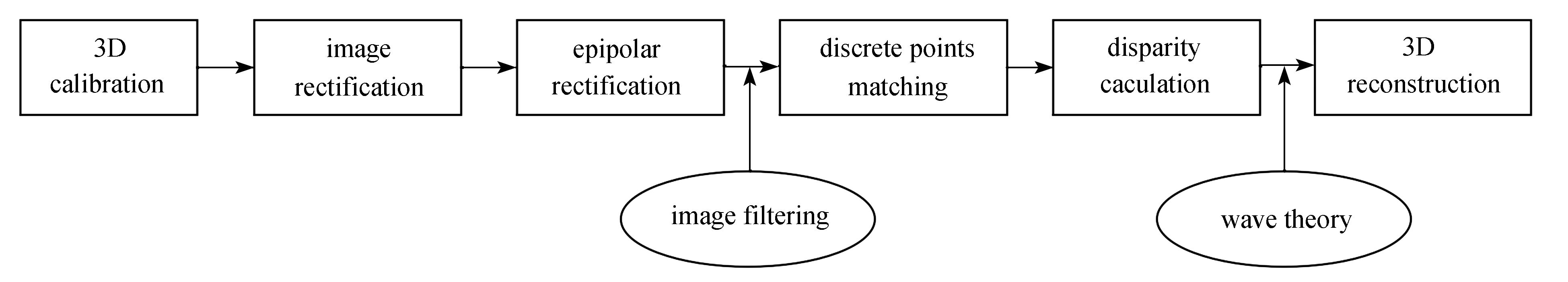
$\left[\begin{array}{cccc}{f}_{x}& 0& {u}_{0}& 0\\ 0&{f}_{y}&{v}_{0}& 0\\ 0& 0& 1& 0 \end{array}\right]$ 为相机内部参数,${f}_{x},{f}_{y}$ 分别为左右相机焦距,${u}_{0},{v}_{0}$ 为像素坐标系原点;$\left[\begin{array}{cc}\boldsymbol{R}& \boldsymbol{T}\\ {{\boldsymbol{0}}}& 1\end{array}\right]$ 为相机外部参数,R为旋转向量,T为平移向量。即:若已知每个相机的内参以及两个相机之间的相对位置,可以从空间点在图像上的像素坐标计算出其空间三维坐标。经典的立体视觉测量系统包含图2所示的几个过程。
其中相机标定及立体匹配过程决定了测量精度。Zhang[35]在2000年提出了单平面棋盘格标定方法,根据标定平面到图像平面的单应性,利用约束条件求解内参矩阵,再基于内参矩阵估算外参矩阵,最后利用最大似然估计法来进行参数优化,提高精度。棋盘格标定法自提出之后,因其方便快捷、易于实施受到了广泛关注和应用,本文中的试验也同样使用该方法来对测量区域进行标定。
双目立体视觉是基于视差原理,因此左右图像中各点的匹配关系至关重要,图像匹配应满足以下几个约束条件:1)极线约束;2)唯一性约束;3)视差连续性约束;4)顺序一致性约束;5)相似性约束。基于以上约束条件,人们提出了几个常用的匹配算法:如SAD (sum of absolute differences) 算法、SSD (sum of squared differences)算法、SGBM(semi-global block matching)算法[36]等,分别在不同类型的图像上都取得了较好的结果,但对于有瑕疵的图像如低纹理、有遮挡、匹配特征不连续等情况,匹配精度会大幅度降低,甚至出现大量误匹配点,直接影响后续的视差计算及三维重构。
1.2 方法改进
由上一小节可知,双目立体视觉是基于视差原理,图像质量的优劣直接决定了测量系统的准确性及精度,而在液体介质的实验测量中,介质的透明特性以及对光的吸收反射等使得界面的测量难度大大提升。因此本文在基于双目立体视觉的基础上,融入波浪理论等物理先验知识,降低了对图像质量的依赖性,摒除了全局 /半全局等对图像要求较高的匹配算法,通过对有限离散点的精准测量来重构规则波的瞬时波面,具体过程如图3所示。
在对图像进行去畸变、极线校正之后,本文中用到的图像滤波方法主要为阈值过滤及膨胀过程,滤掉了图像中灰度值较低会影响匹配的背景噪声,并采用膨胀形态学处理[37]的方式增强了要匹配的白色标识物在图像中的可识别性。
通常讨论的水波问题是理想不可压流体的无旋运动问题,因此服从不可压势流运动的基本控制方程,而该方程组由于1)自由面未知;2)自由面运动学和动力学条件皆为非线性两个原因,求解十分困难,因此在实际应用中往往根据特定的研究问题来对方程组进行简化。
Airy在1845年提出了微幅波理论,即当波动的振幅A远小于波长λ或水深D时,非线性的自由面运动学和动力学条件可以线性化,可以固定在静水面上满足自由面的边界条件。假设水波自由面由
$ y=\eta (x,z,t) $ 表示,z为波浪传播方向,若不考虑初始波的产生且流场中不存在物体,则水波的控制方程及其边界条件可以简化为$$ {\nabla }^{2}\phi =0, \tag{2a}$$ $$ \frac{\partial \phi }{\partial y}=0, \tag{2b}$$ $$ g\frac{\partial \phi }{\partial y} + \frac{{\partial }^{2}\phi }{\partial {t}^{2}}=0 {\text{.}}\tag{2c}$$ 式(2a)为控制方程,式(2b)为水底边界条件(y=−D),式(2c)为自由面边界条件(y=0),
$ \phi $ 为水波速度势,g为重力加速度。对上式进行求解可得Airy波的速度势为$$ \phi =\frac{gA}{\omega }\mathrm{s}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}(kz-\omega t)\frac{\mathrm{cosh}(y + D)}{\mathrm{cosh}(kD)}, $$ (3) 其中A为波幅,波高H=2A,k为波数,ω为圆周频率,当
$ D\to \mathrm{\infty } $ 时,$$ \phi =\frac{gA}{\omega }\mathrm{s}\mathrm{i}\mathrm{n}(kz-\omega t){{\rm{e}}}^{ky} {\text{.}}$$ (4) 由自由面动力学条件,可得Airy波面为
$$ \eta =\left.-\frac{1}{g}\frac{\partial \phi }{\partial t}\right|_{y=0}=A\mathrm{c}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{s}(kz-\omega t) {\text{.}}$$ (5) 上式中有三个参数需要求解,而由色散关系可知k和ω是相互关联的,因此只需要得出A,k或ω的值即可得出Airy波面方程。本文中根据试验条件,满足Airy波的假设,因此将上式的波面方程引入到双目测量系统中,重构出了单向规则波的瞬时波面。
2. 试验工况与结果分析
2.1 试验工况
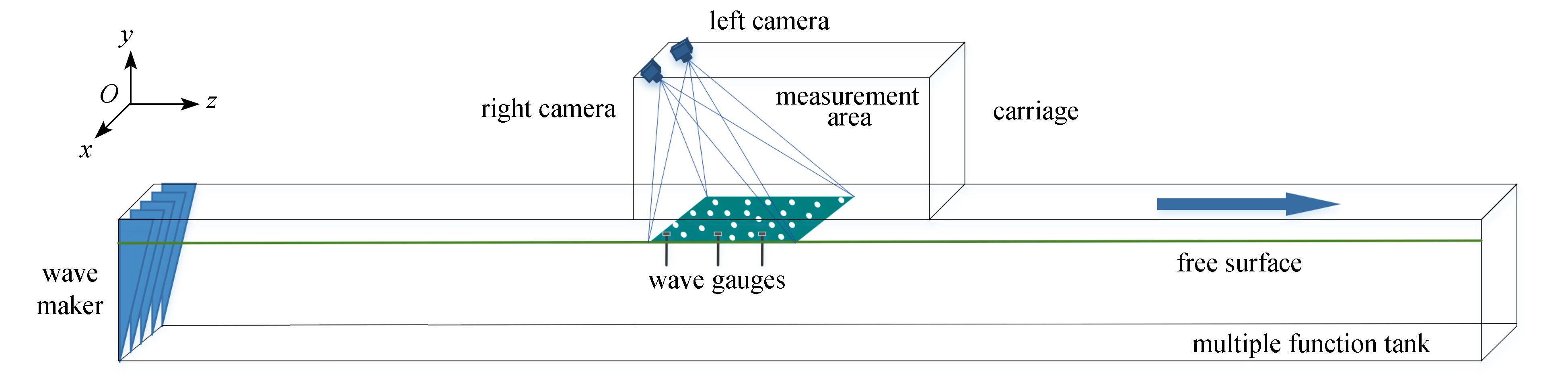
本文中试验在隶属于上海交通大学国家海洋重点实验室的多功能拖曳水池中进行(图4)。水池长300 m,宽16 m,深7.5 m,最高拖曳速度达10 m/s。水池的一端配备了先进的多单元造波系统,采用40片摇板造波,可以生成规则波、不规则波以及斜向波,最大规则波波高0.55 m,满足试验工况所需的要求。消波系统包括位于水池另一端的消波滩、主动消波系统及侧壁消波系统等。试验中测量区域位于距造波机80 m左右处水池中心,既保证了波面的规则性,又避免了水池壁面及回波对测量区域的影响。
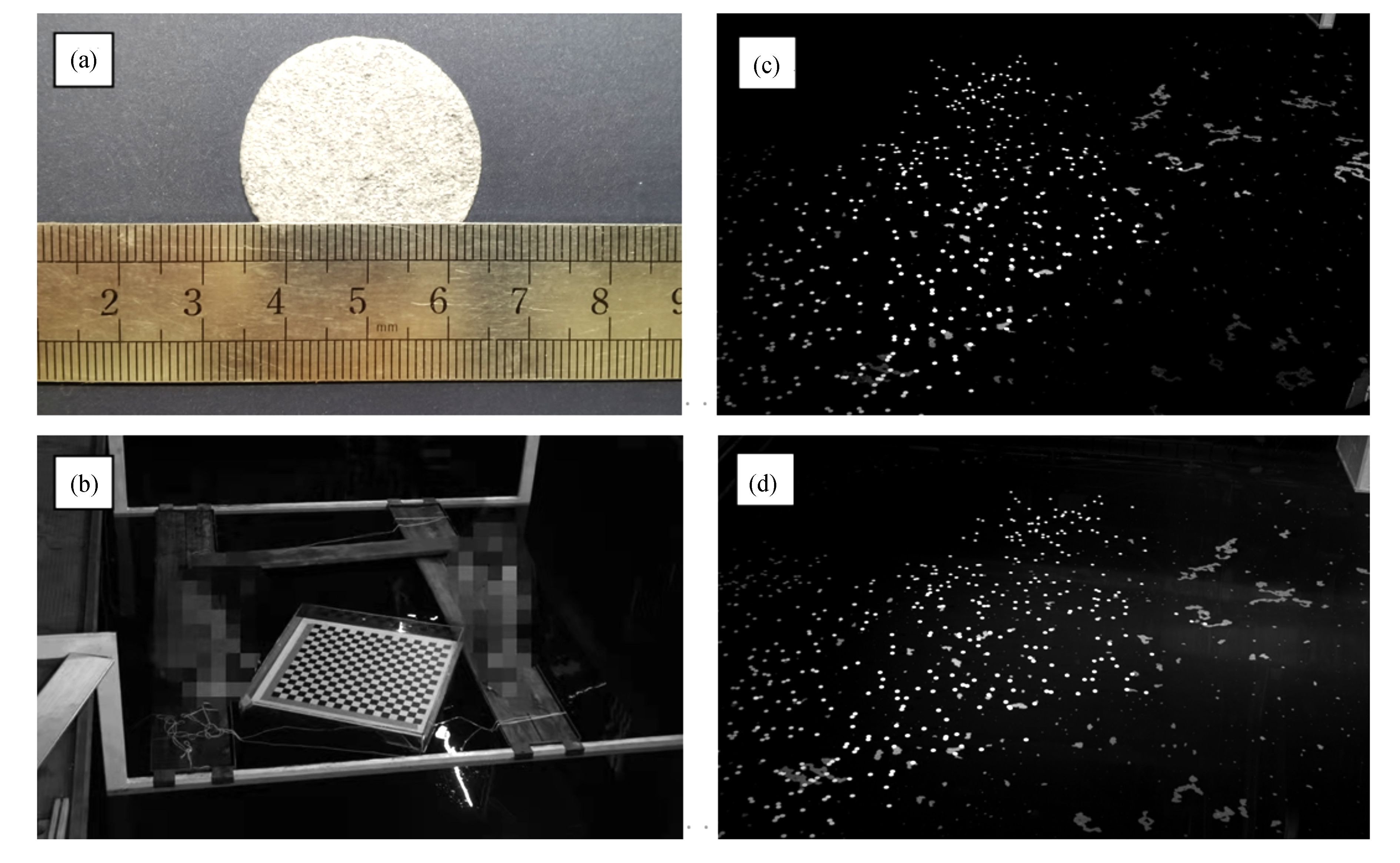
试验装置如图4所示,由于水的透明特性,为了使波面能够在相机成像,试验时在测量区域随机播撒了密度小、吸水性差的聚乙烯泡沫作为标识物(图5(a)所示),直径d =30 cm。试验中所用相机均为Phantom VEO-340L系列高速摄像机,分辨率为2560 pixel × 1600 pixel,像素尺寸为10 μm,试验中拍摄频率设定为50 Hz,每个工况测量时长约为60 s。图5(b)给出了标定过程示例,所使用的标定板尺寸为1 m × 1 m,棋盘格尺寸为45 cm × 45 cm,在测量区域内不断调整标定板位置及角度使其覆盖整个测量区域,以建立标定模型,经过筛选最终用于标定的图像为130对,整个标定的测量区域范围为 x × z ≈3 m × 4 m,x为水池宽度方向,z为波浪传播方向。
在本文试验中,共进行了三个工况:①h=0.08 m,f=0.79 Hz,λ≈2.5 m;②h=0.10 m,f=0.79 Hz,λ≈2.5 m;③h=0.16 m,f=0.63 Hz,λ≈3.9 m(其中h为波高,f为频率,λ为波长)。图5(c)、(d)给出工况①中左右相机拍摄的瞬时图像,可以看出标识物在图像中非常突出、易于识别和提取。随着波浪的传播,标识物会不断的扩散,从而影响整个测量区域波面的重构,因此本文中选取标识物密度较高的工况①为代表来进行结果分析。如装置示意图(图4)所示,试验中还在测量区域内放置了三个浪高仪以验证双目测量系统的试验精度,浪高仪的频率设定为50 Hz。
2.2 试验结果与分析
根据上文所述的张正友标定法[35],本次试验双目测量系统得到的左右相机参数如表1所示(外参参数为右相机相对于左相机的位置),单个相机的标定误差均在0.3个像素以内。如此我们获得了相机标定模型,为了进一步验证其精度,我们将该模型应用于标定图像,对图像中的标定板进行三维重构,计算棋盘格各角点之间的绝对距离,根据已知的棋盘格尺寸(l =45 cm)来验证该模型的测量精度。经过对130对标定图像的处理,得出各角点距离的平均值为43.9387,误差为2.3%,因此可以认为该标定结果满足试验所需。
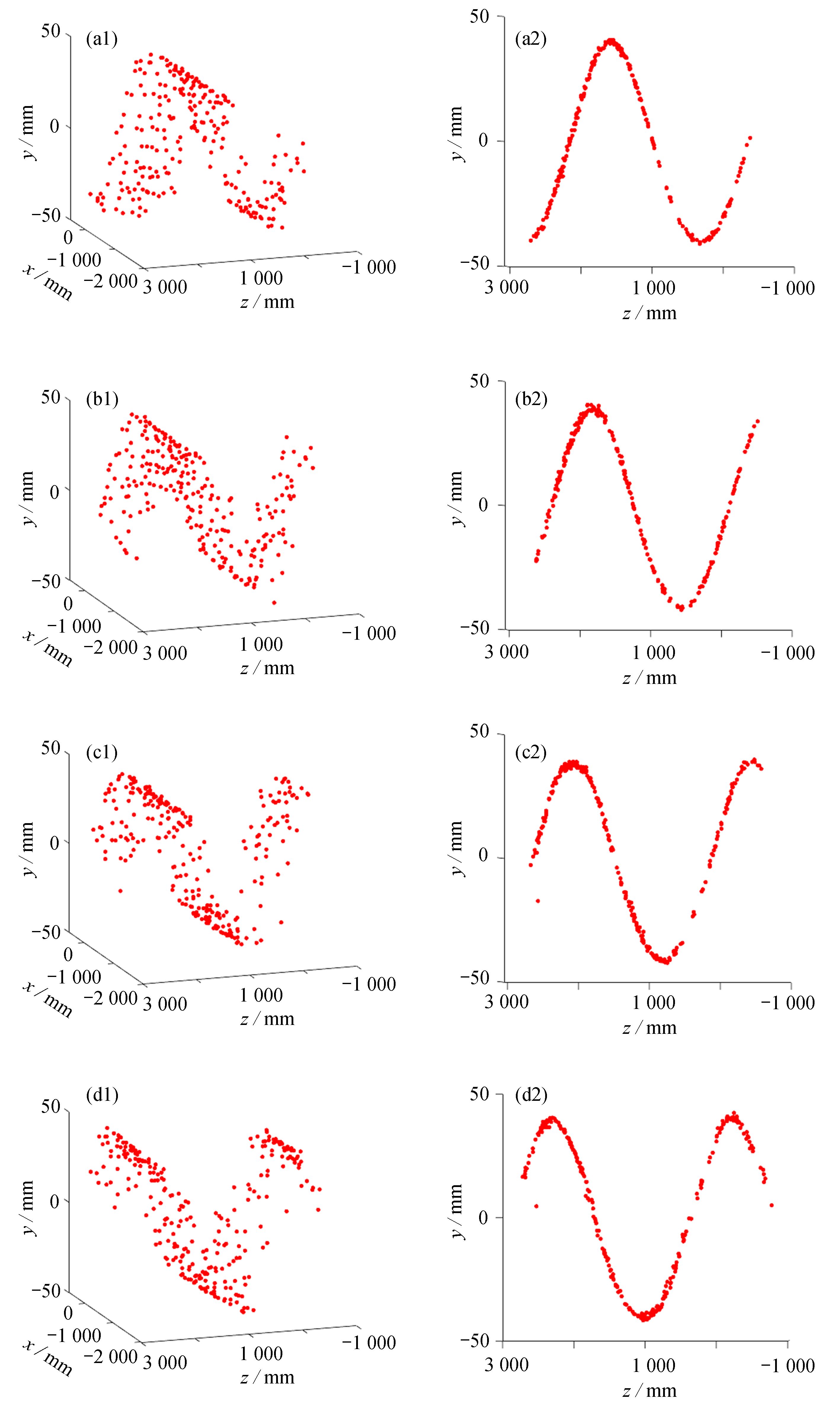
表 1 立体视觉测量系统标定参数Table 1. Calibration parameters of the stereo vision measurement systemintrinsic parameter left camera right camera focal length ( fx, fy) / mm [3937.20908, 3936.40700] T [3925.72662, 3924.51774] T principal point (cx, cy) / pixel [1349.85569, 952.73155] T [1278.88564, 886.81188] T distortion (k1, k2, p1, p2) 0.01 × [−2.593, 32.052, 1.046, 0.321] T 0.01 × [ −2.287, 47.839, 0.656, −0.27] T extrinsic parameter rotation [−0.03702, 0.25002, 0.1387] T translation [−1397.67526, −141.94746, 153.43894] T pixel error / pixel [ 0.20014, 0.23406] T [ 0.13965, 0.21090] T 根据已有的相机标定模型,以及上述的双目测量系统测量原理,对试验图像进行去畸变、极线校正、图像滤波等前期处理之后,便可对左右相机图像进行匹配、计算视差及深度值,最后通过式(1)将像素坐标转换到世界坐标系中。设定第一张图像t=0.02 s,图6给出了几个不同时刻t=20 s, 30 s, 40 s, 50 s时重构出的波面,可以看出数据点虽然比较分散,但仍然有明显的波形特征,且在水池宽度方向(x方向)呈现均一性,因此可以对数据结构进行降维处理,将三维数据拟合降为yoz平面内的二维数据拟合,以规则波的波面曲线方程进行拟合。
由上文可知,对于单向规则波,目标拟合函数为
$$ \eta =A\mathrm{c}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{s}(kz-\theta ), $$ (6) 其中A为波幅,k为波数,
$ \theta $ 为相位。上式属于非线性回归问题,本文中使用的拟合方法为迭代加权最小二乘法(iterative reweighted least squares)[38-39]。最小二乘法是回归分析的一种标准方法,假设一个数据集包含了n个数据点(xi, yi, i=1,2,…,n),其中xi为自变量,yi为观测因变量,模型函数为f (x,β),β包含了m个可调参数。残差
$ {r}_{i}={y}_{i}-f({x}_{i},{\boldsymbol{\beta}} ) $ ,为因变量的观测值与模型预测值之间的差值。标准的最小二乘法通过残差平方和${S}_{S}=\displaystyle{\sum} _{i=1}^{n}{{r}_{i}}^{2}$ 的最小值来寻找模型函数f的最佳参数值。为降低异常值对拟合结果的影响,加权最小二乘法引入了权重函数w,误差估计变为${S}_{w}=\displaystyle{\sum} _{i=1}^{n}{{w}_{i}{r}_{i}}^{2}$ ,本文中选取的权重函数为二次方权重函数(bisquare weights),即赋予每个数据点的权重取决于该点与拟合曲线的距离,在每次迭代中,基于前一次迭代中每个观测值的残差重新计算稳健权重,迭代一直持续到权重收敛为止。主要的计算步骤为:1) 通过加权最小二乘法拟合模型。
2) 计算调整后的残差
$ {r}_{{\rm{adj}}} $ 并对其标准化,$$ {r}_{{\rm{adj}}}=\frac{{r}_{i}}{\sqrt{1-{h}_{i}}}, $$ (7) 其中
$ {h}_{i} $ 为杠杆,通过降低高杠杆数据点的权重来调整残差;然后通过下式对${r}_{{\rm{adj}}}$ 进行标准化:$$ {u}_{i}=\frac{{r}_{{\rm{adj}}}}{Ks}, $$ (8) 其中K=4.685为调谐常数,s=δMAD/0.6745为稳健的标准偏差,δMAD(median absolute deviation)为残差的中位绝对偏差[39]。
3) 计算权重,文中所使用权重函数的表达式为
$$ {w}_{i}=\left\{ \begin{aligned} & {(1-{({u}_{i})}^{2})}^{2},\qquad\; \left|{u}_{i}\right| < 1,\\& 0, \qquad\qquad\qquad \left|{u}_{i}\right|\geqslant 1 {\text{.}} \end{aligned} \right. $$ (9) 4) 若结果收敛则拟合结束,否则返回步骤1)进行下一次迭代。
对全部的2967个时刻的瞬时波面图进行拟合后(见图7),表2给出了波幅A和波数k的统计量,因此我们可以得出波面方程为
表 2 波幅、波数的统计量Table 2. Statistics of the wave amplitude and the wave numberaverage maximum minimum variance standard deviation A/mm 40.2810 41.8385 38.3161 0.2096 0.4578 k 2.4803 2.5928 2.3435 0.0012 0.0351 $$ \eta (z,t)=0.040\;3\mathrm{c}\mathrm{o}\mathrm{s}\left(2.480\;3z-5.04t\right) {\text{.}}$$ (10) 通过对双目立体视觉测量系统所得的波面参数统计分析,得到所测规则波的波幅As=40.2810 mm,波数ks=2.4803,根据微幅波理论,计算得波浪频率为fs=0.7853。试验过程中在测量区域内沿波浪传播方向放置了浪高仪,对浪高仪采集50 s的数据进行统计分析得到波幅Ag,kg以及fg。表3给出了双目系统测量结果、浪高仪统计分析结果和造波机的设定参数的对比以及双目测量系统与其余两者的误差,可以看出三个参数的误差皆在1%左右。
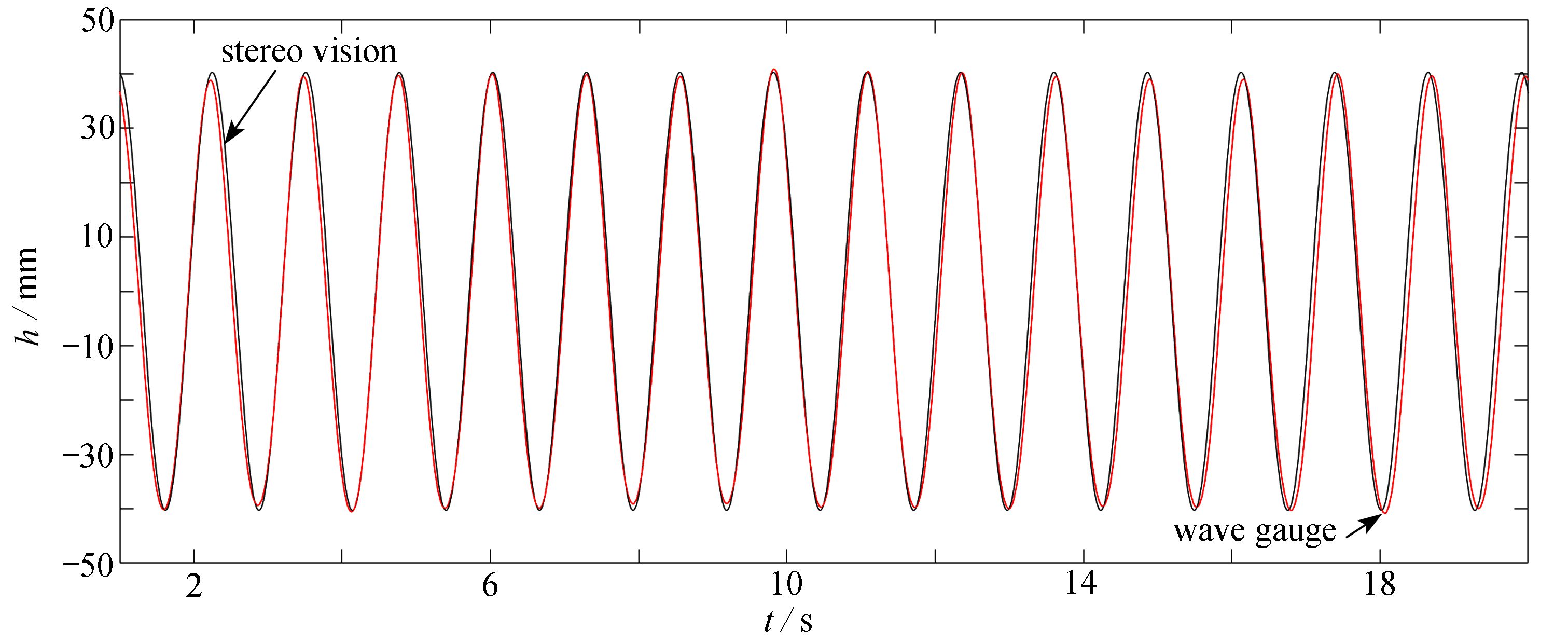
表 3 双目测量、浪高仪测量与造波机输入参数对比Table 3. Comparison of parameters obtained by the stereo vision, the wave gauges and the wave makerparameter stereo vision wave gauge error wave maker error A/mm 40.2810 40.10 0.45% 40 0.70% k 2.4803 2.5112 1.23% 2.5116 1.25% f/Hz 0.7853 0.7899 0.58% 0.79 0.59% 上述结果为统计分析,为了更直观地显示双目测量与浪高仪的对比结果,图8给出了某一空间位置在一段时间内波面高度随时间的变化,可以看到在20 s内,浪高仪测得结果与双目测量结果基本重合,由此进一步验证了该测量系统的可靠性。
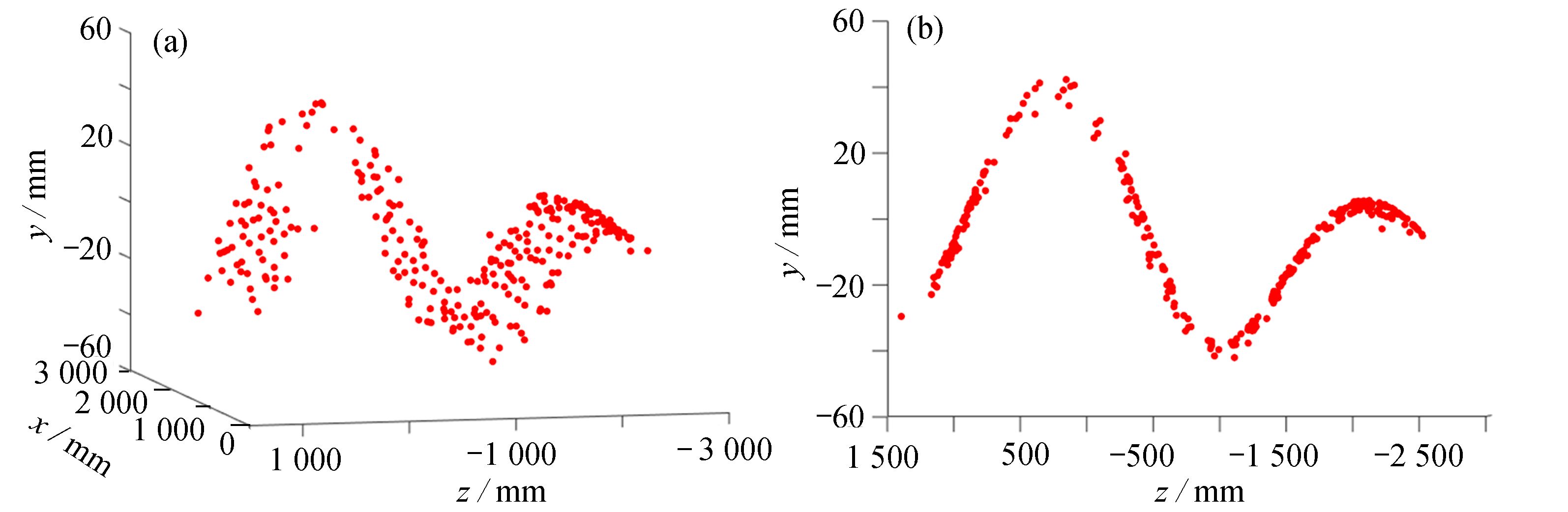
在完成单向规则波工况的试验验证后,我们于近期开展了不规则波的光学测量,图9给出了某一时刻重构出的瞬时波面图。从图中可以看出,虽然有个别匹配点出现错误,但仍然识别出了基本的波形特征,且因为是二维不规则波,在x方向同样呈现出均一性,下一步工作将会对波面进行拟合以验证该方法的适用性,并会融入机器学习、非线性波理论等以将该方法拓展到三维不规则波等更为复杂的工况。
3. 结论与展望
本文基于双目立体视觉理论,自主搭建了测量系统,并对传统的分析和图像处理方法进行了改进,将波浪理论融入数据处理中,在多功能拖曳水池中对规则波进行了试验测量。结果表明,该方法成功提取和重构出了瞬时波面,经过与理论值及浪高仪测量值进行瞬时和统计结果的比较分析,验证了该测量系统的可行性以及数据处理方法的精度。后续将会从测量精度及在复杂工况如二维/三维不规则波的广泛适用性两个角度出发,融入神经网络及机器学习等先进的计算机技术,作进一步的研究工作,以期能够在实验室条件下替代浪高仪作为常用的波面测量技术。
-
表 1 立体视觉测量系统标定参数
Table 1. Calibration parameters of the stereo vision measurement system
intrinsic parameter left camera right camera focal length ( fx, fy) / mm [3937.20908, 3936.40700] T [3925.72662, 3924.51774] T principal point (cx, cy) / pixel [1349.85569, 952.73155] T [1278.88564, 886.81188] T distortion (k1, k2, p1, p2) 0.01 × [−2.593, 32.052, 1.046, 0.321] T 0.01 × [ −2.287, 47.839, 0.656, −0.27] T extrinsic parameter rotation [−0.03702, 0.25002, 0.1387] T translation [−1397.67526, −141.94746, 153.43894] T pixel error / pixel [ 0.20014, 0.23406] T [ 0.13965, 0.21090] T 表 2 波幅、波数的统计量
Table 2. Statistics of the wave amplitude and the wave number
average maximum minimum variance standard deviation A/mm 40.2810 41.8385 38.3161 0.2096 0.4578 k 2.4803 2.5928 2.3435 0.0012 0.0351 表 3 双目测量、浪高仪测量与造波机输入参数对比
Table 3. Comparison of parameters obtained by the stereo vision, the wave gauges and the wave maker
parameter stereo vision wave gauge error wave maker error A/mm 40.2810 40.10 0.45% 40 0.70% k 2.4803 2.5112 1.23% 2.5116 1.25% f/Hz 0.7853 0.7899 0.58% 0.79 0.59% -
[1] THORPE S A. Dynamical processes of transfer at the sea surface[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 1995, 35: 315-352. doi: 10.1016/0079-6611(95)80002-B [2] MELVILLE W K. The role of surface-wave breaking in air-sea interaction[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 1996, 28: 279-321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.fl.28.010196.001431 [3] 王建华, 万德成. 全附体ONRT船模在波浪中自航的数值模拟[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2016, 37(12): 1345-1358WANG Jianhua, WAN Decheng. Investigation of self-propulsion in waves of fully appended ONR tumblehome model[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2016, 37(12): 1345-1358.(in Chinese) [4] 曾维鸿, 傅卓佳, 汤卓超. 水槽动力特性数值模拟的新型局部无网格配点法[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2022, 43(4): 392-400ZENG Weihong, FU Zhuojia, TANG Zhuochao. A novel localized meshless collocation method for numerical simulation of flume dynamic characteristics[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2022, 43(4): 392-400.(in Chinese) [5] 王本龙, 刘桦. 一种适用于非均匀地形的高阶Boussinesq水波模型[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2005, 26(6): 714-722 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0887.2005.06.013WANG Benlong, LIU Hua. Higher order Boussinesq-type equations for water waves on uneven bottom[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2005, 26(6): 714-722.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0887.2005.06.013 [6] 王兆玲, 肖衡. 海洋表面波约化Hamilton方程的新发展: 从小幅波到有限幅波的推广[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2015, 36(11): 1135-1144 doi: 10.3879/j.issn.1000-0887.2015.11.002WANG Zhaoling, XIAO Heng. A new development of reduced Hamiltonian equations for ocean surface waves: an extension from small to finite amplitude[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2015, 36(11): 1135-1144.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3879/j.issn.1000-0887.2015.11.002 [7] 窦依琳, 罗志强. 均匀流中等源强相同浸没深度点源自由面波高数值模拟[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2020, 41(9): 1026-1035DOU Yilin, LUO Zhiqiang. Numerical simulation of free surface wave elevations of point sources with the same source intensity and immersion depth in uniform flow[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2020, 41(9): 1026-1035.(in Chinese) [8] KROGSTAD H E, BARSTOW S F. Recent advances in wave measurement technology[C]//The 9th International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference. Brest, France, 1999: 19-28. [9] TUCKER M J, PITT E G. Waves in Ocean Engineering[M]. UK: Elsevier Ocean Engineering Book Series, 2001: 5, 521. [10] FORRISTALL G Z, BARSTOW S F, KROGSTAD H E, et al. Wave crest sensor intercomparison study: an overview of WACSIS[J]. Journal of Offshore Mechanics and Artic Engineering-Transactions of the ASME, 2004, 126(1): 26-34. doi: 10.1115/1.1641388 [11] PADUAN J D, WASHBURN L. High-frequency radar observations of ocean surface currents[J]. Annual Review of Marine Science, 2013, 5: 115-136. doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-121211-172315 [12] HOLMAN R, HALLER M C. Remote sensing of the nearshore[J]. Annual Review of Marine Science, 2013, 5: 95-113. doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-121211-172408 [13] APEL J R. Satellite sensing of ocean surface dynamics[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 1980, 8: 303-342. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ea.08.050180.001511 [14] PHILLIPS O M. Remote sensing of the sea surface[J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 1988, 20: 89-109. doi: 10.1146/annurev.fl.20.010188.000513 [15] GRUNO A, LIIBUSK A, ELLMANN A, et al. Determining sea surface heights using small footprint airborne laser scanning[C]//Proc SPIE, Remote Sensing of the Ocean, Sea Ice, Coastal Waters, and Large Water Regions. Dresden, Germany, 2013. [16] YAO A, WU C H. An automated image-based technique for tracking sequential surface wave profiles[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2005, 32(2): 157-173. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2004.07.004 [17] 李继磊, 郭晓宇, 王本龙. 基于激光阵列辅助的波面立体视觉测量[J]. 力学季刊, 2017, 38(3): 420-427 doi: 10.15959/j.cnki.0254-0053.2017.03.003LI Jilei, GUO Xiaoyu, WANG Benlong. Stereo photography measurement of wave surface with laser beams[J]. Chinese Quarterly of Mechanics, 2017, 38(3): 420-427.(in Chinese) doi: 10.15959/j.cnki.0254-0053.2017.03.003 [18] 孙鹤泉, 邱大洪, 沈永明, 等. 基于光学折射的波面形态测量[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2006, 4: 609-612SUN Hequan, QIU Dahong, SHEN Yongming, et al. Wave measurement based on light refraction[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2006, 4: 609-612.(in Chinese) [19] DOUXCHAMPS D, DEVRIENDT D, CAPART H, et al. Stereoscopic and velocimetric reconstructions of the free surface topography of antidune flows[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 2005, 39(3): 535-553. doi: 10.1007/s00348-005-0983-7 [20] MOLFETTA M G, BRUNO M F, PRATOLA L, et al. A sterescopic system to measure water waves in laboratories[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(14): 2288. doi: 10.3390/rs12142288 [21] GOMIT G, CHATELLIER L, CALLUAUD D, et al. Free surface measurement by stereo-refraction[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 2013, 54: 1540. doi: 10.1007/s00348-013-1540-4 [22] GOMIT G, ROUSSEAUX G, CHATELLIER L, et al. Spectral analysis of ship waves in deep water from accurate measurements of the free surface elevation by optical methods[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2014, 26(12): 122101. doi: 10.1063/1.4902415 [23] ENGELEN L, CREËLLE S, SCHINDFESSEL L, et al. Spatio-temporal image-based parametric water surface reconstruction: a novel methodology based on refraction[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2018, 29(3): 35302. doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/aa9eb7 [24] WANG Q, LIU H, FANG Y, et al. Experimental study on free-surface deformation and forces on a finite submerged plate induced by a solitary wave[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2020, 32(8): 086601. doi: 10.1063/5.0015903 [25] CHATELLIER L, JARNY S, GIBOUIN F, et al. A parametric PIV/DIC method for the measurement of free surface flows[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 2013, 54: 1488. doi: 10.1007/s00348-013-1488-4 [26] CHABCHOUB A, MOZUMI K, HOFFMANN N, et al. Directional soliton and breather beams[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2019, 116(20): 9759-9763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1821970116 [27] POGGI M, TOSI F, BATSOS K, et al. On the synergies between machine learning and binocular stereo for depth estimation from images: a survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 44(9): 1-20. [28] CHENG X, ZHONG Y, HARANDI M, et al. Hierarchical neural architecture search for deep stereo matching[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2020, 33: 22158-22169. [29] CHENG X, WANG P, YANG R. Learning depth with convolutional spatial propagation network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(10): 2361-2379. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2947374 [30] ŽBONTAR J, LECUN Y. Stereo matching by training a convolutional neural network to compare image patches[J]. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2016, 17: 1-32. [31] 卫志军, 翟钢军, 吴锤结. 气液耦合系统中固有频率的实验研究[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2021, 42(2): 133-141WEI Zhijun, ZHAI Gangjun, WU Chuijie. Experimental investigation of natural frequencies of gas-liquid coupled systems in tanks[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2021, 42(2): 133-141.(in Chinese) [32] STAMMER D, BALMASEDA M, HEIMBACH P, et al. Ocean data assimilation in support of climate applications: status and perspectives[J]. Annual Review of Marine Science, 2016, 8(1): 491-518. doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-122414-034113 [33] ROBERTS L G. Machine perception of three-dimensional solids[D]. PhD Thesis. Cambridge: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1963. [34] MARR D. Vision-a Computational Investigation Into the Human Representation and Processing of Visual Information[M]. Massachusetts: The MIT Press, 2010. [35] ZHANG Z. A flexible new technique for camera calibration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2000, 22(11): 1330-1334. doi: 10.1109/34.888718 [36] HIRSCHMULLER H. Stereo processing by semi-global matching and mutual information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2008, 30(2): 328-341. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2007.1166 [37] GONZALEZ R C, WOODS R E. Digital Image Processing[M]. New Jersey: Prentice Hall, 2002. [38] HOLLAND P W, WELSCH R E. Robust regression using iteratively reweighted least-squares[J]. Communications in Statistics:Theory and Methods, 1977, 6(9): 813-827. [39] DUMOUCHEL W H, O’BRIEN F L. Integrating a robust option into a multiple regression computing environment[C]//Computer Science and Statistics: Proceedings of the 21st Symposium on the Interface. Alexandria, 1989. -






 下载:
下载:


































 下载:
下载:












 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号