A Study on the Vortex-Induced Vibration Mechanism of Cantilever Cylinders Under Gas-Liquid Cross Flows
-
摘要:
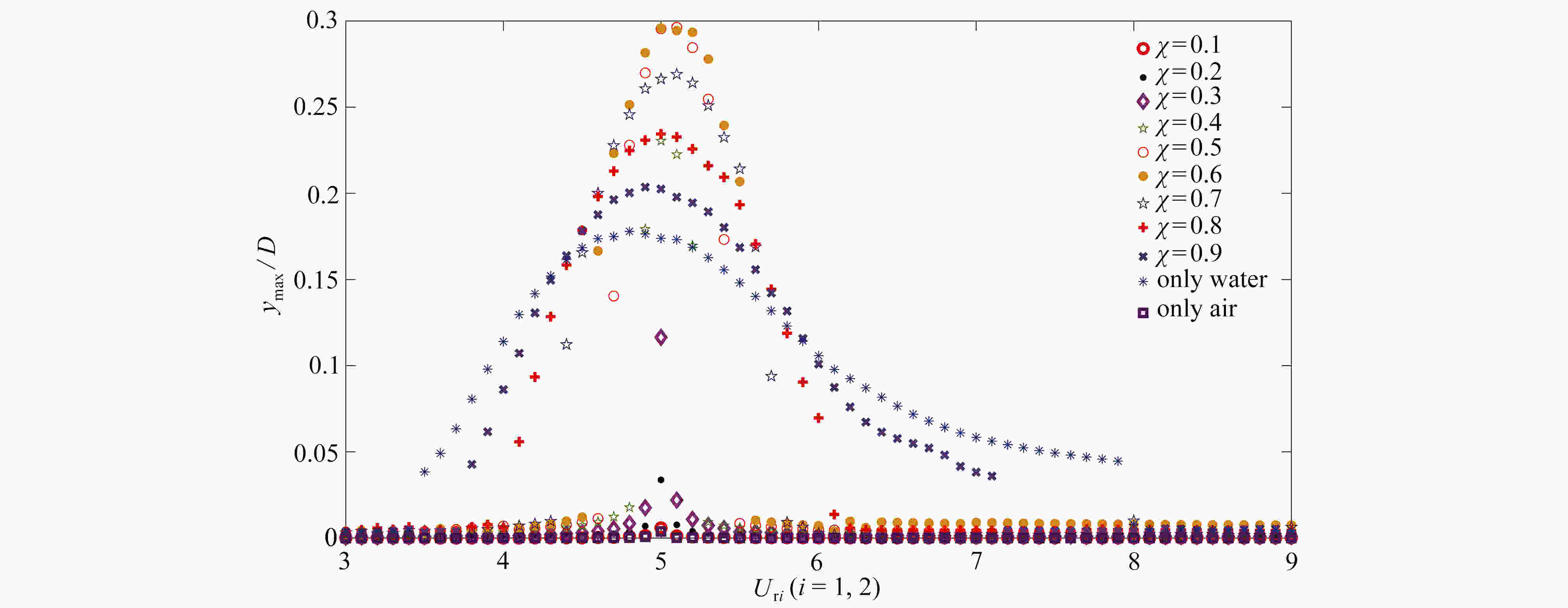
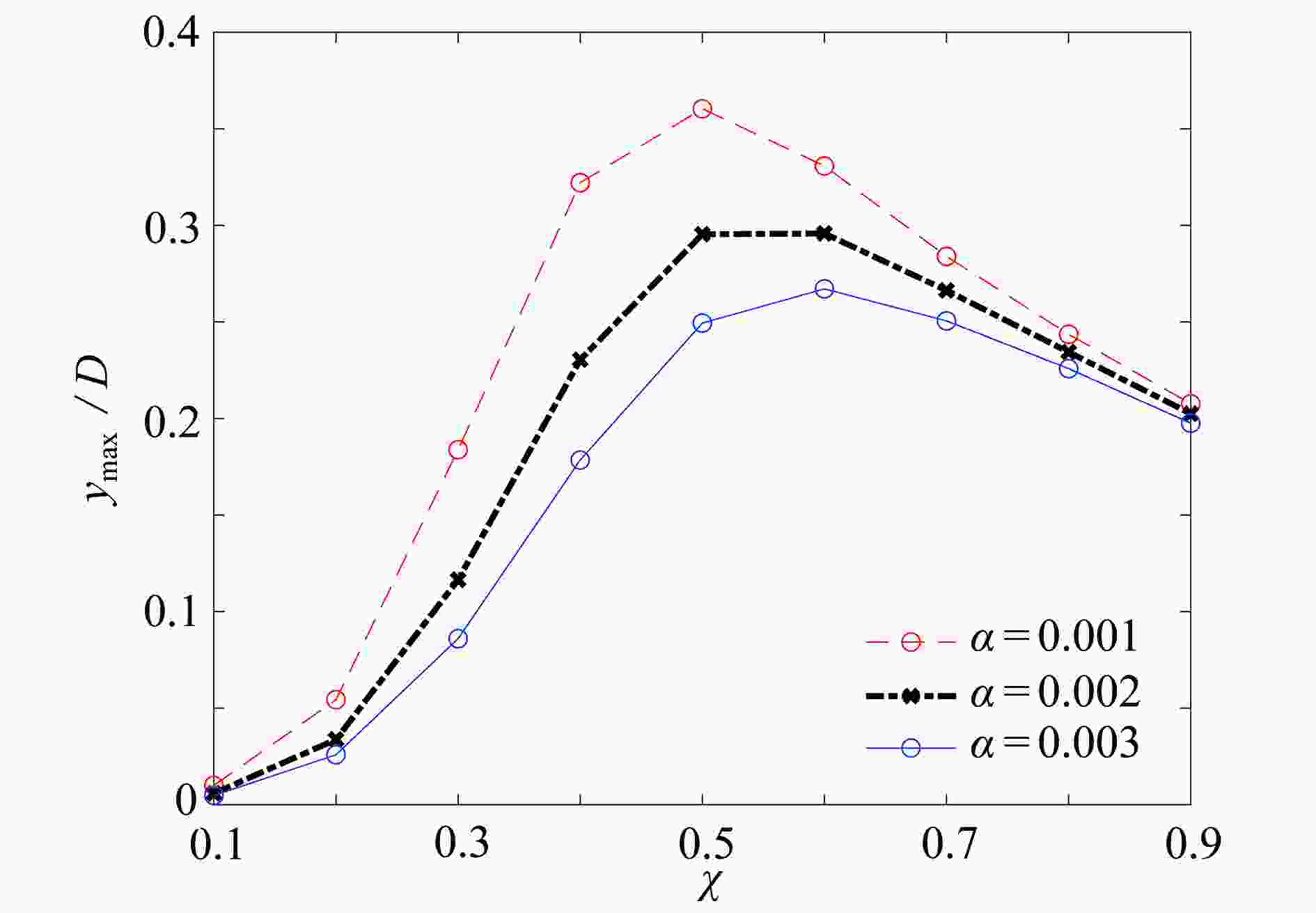
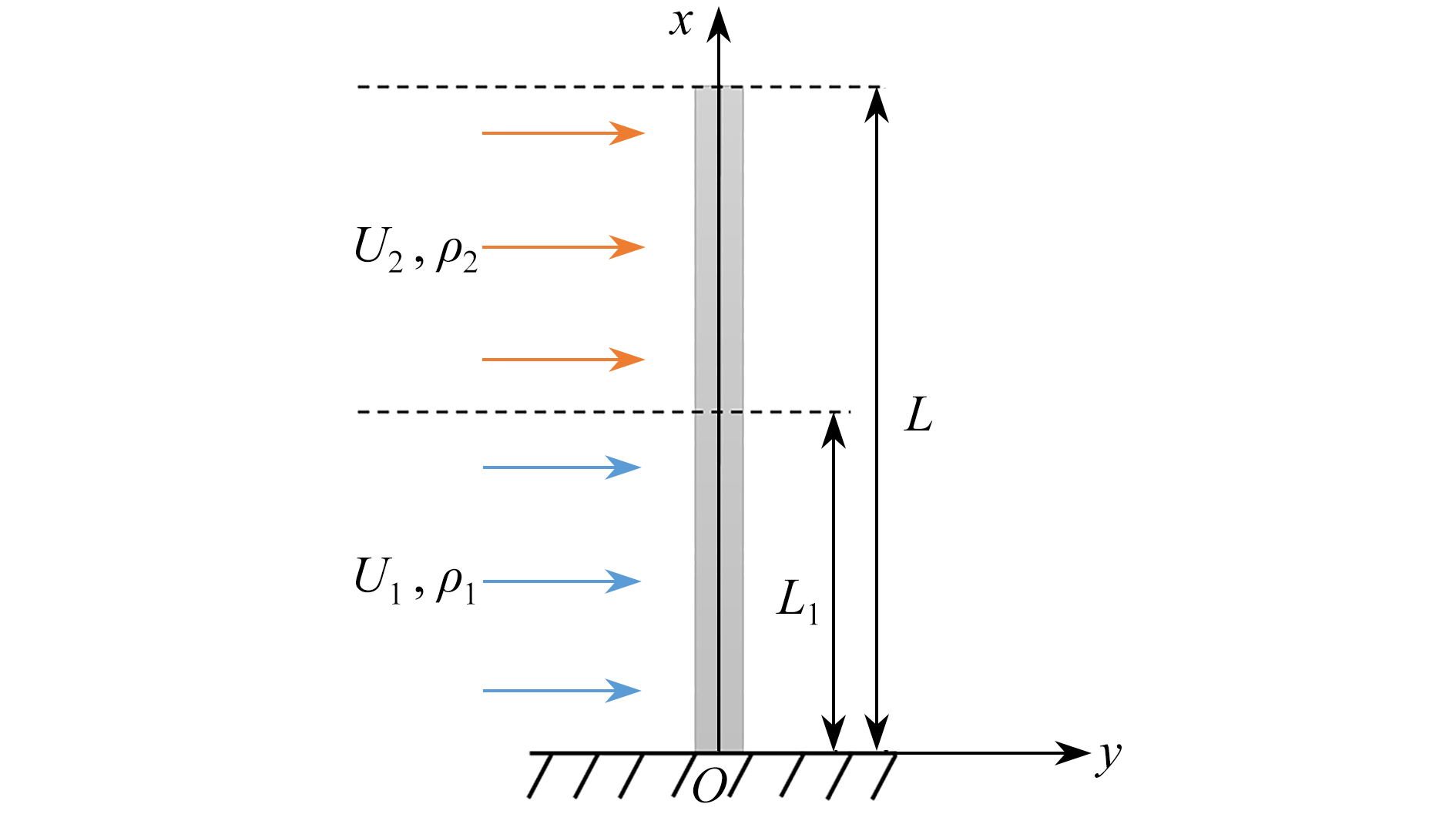
针对潜艇侦查望远镜举升水面时产生的涡激振动现象,该文建立了悬臂柱体结构受气-液两种不同横向流作用下的涡激振动理论模型。研究了两种流体不同的分布比和密度比对柱体结构涡激振动行为的影响规律。基于Galerkin法和Runge-Kutta法,得到了柱体结构涡激振动响应的数值结果。研究表明,柱体结构的涡激振动锁频区随着流体分布比的增大而增大,自由端最大幅值随着流体分布比的增大先增大后减小。当分布比为0.5附近时,振幅出现极大值,该极大值随着流体密度比的减小呈现明显的增大趋势。此外,柱体的动力学行为随着流体分布比的变化呈现出周期和多周期等振动模式。该研究可为潜艇侦查望远镜结构的设计与分析提供理论指导意义。
Abstract:Aimed at vortex-induced vibration (VIV) of the submarine reconnaissance telescope lifting above the water surface, a theoretical model for VIV of a cantilever cylinder under the actions of two different cross flows, i.e. gas and liquid, was established. The effects of parameters such as the distribution ratio and the density ratio for these two fluids on VIV responses of the cylinder were studied. Based on the Galerkin technique and the Runge-Kutta algorithm, numerical results of the cylinder vibration responses were obtained. The results show that, the increase of the distribution ratio can widen the lock-in range of the cylinder. The peak amplitude of the cylinder increases first and then decreases with the distribution ratio. The amplitude reaches the maximum value with a distribution ratio of 0.5, and this maximum value will increase with the decrease of the density ratio. In addition, single-period and multi-period motions will occur with the change of the fluid distribution ratio. The present research provides a theoretical guidance for the design and analysis of the submarine reconnaissance telescope.
-
Key words:
- vortex-induced vibration /
- cantilever cylinder /
- lock-in /
- cross flow
-
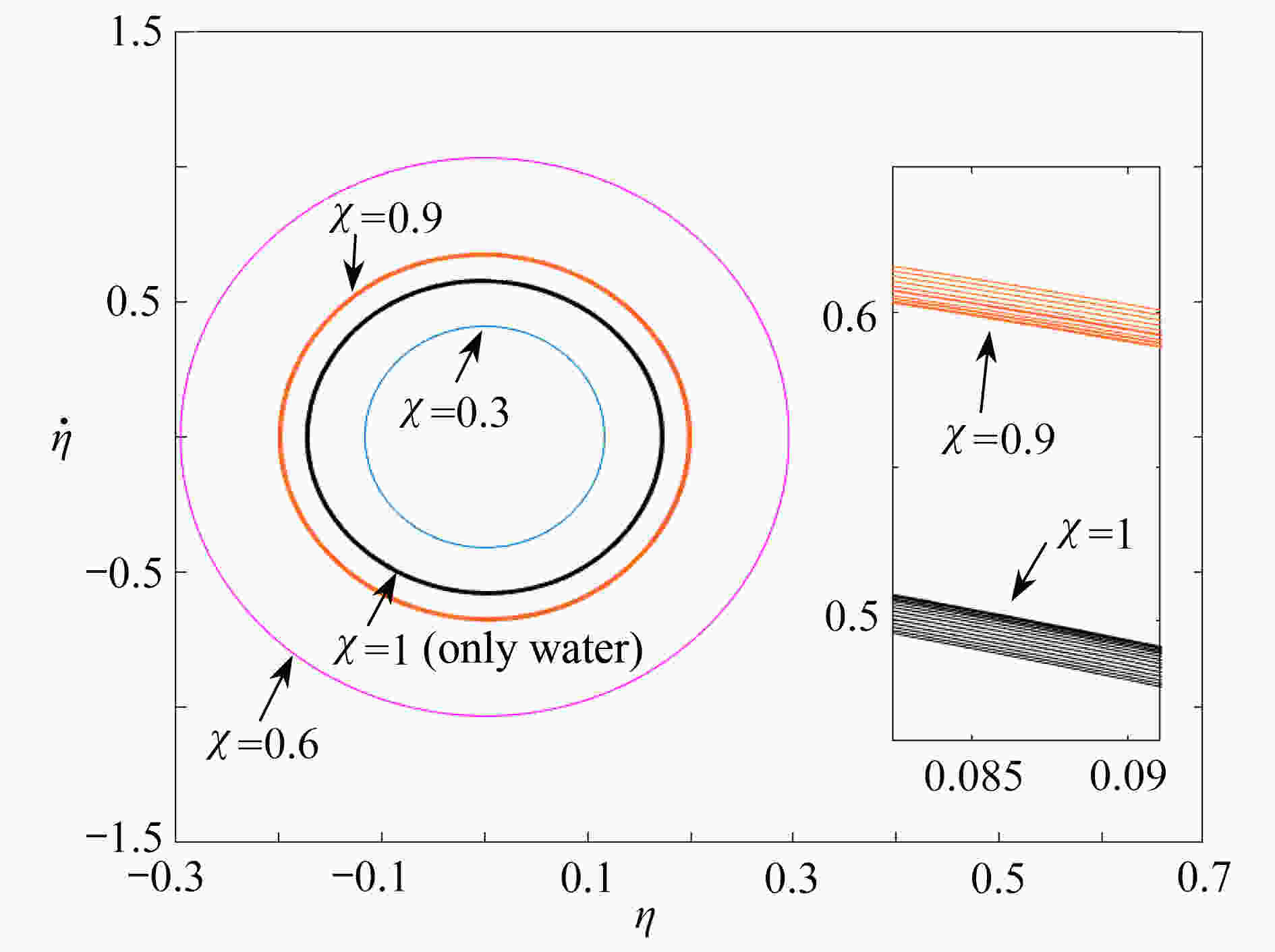
图 2 不同模态截断数N下的圆柱体自由端振幅:(a)仅有水作用的情况,
${U_{{\rm{r}}1}} = 5$ ;(b) 空气和水共同作用的情况,${U_{{\rm{r}}1}} = {U_{{\rm{r}}2}} = 5$ 注 为了解释图中的颜色,读者可以参考本文的电子网页版本,后同。
Figure 2. Amplitudes at the cylinder’s free end for different Galerkin truncation number N values: (a) only water case,
${U_{{\rm{r}}1}} = 5$ ; (b) air-water case,${U_{{\rm{r}}1}} = {U_{{\rm{r}}2}} = 5$ -
[1] LANGRE E. Frequency lock-in is caused by coupled-mode flutter[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2006, 22(6/7): 783-791. [2] BRIKA D, LANEVILLE A. Vortex-induced vibrations of a long flexible circular cylinder[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1993, 250: 481-508. doi: 10.1017/S0022112093001533 [3] ZHOU C Y, SO R M C, LAM K. Vortex-induced vibrations of an elastic circular cylinder[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 1999, 13(2): 165-189. doi: 10.1006/jfls.1998.0195 [4] 孙云卿, 吴志强, 章国齐, 等. 海洋立管双模态动力学分岔分析[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2020, 41(5): 480-490. (SUN Yunqing, WU Zhiqiang, ZHANG Guoqi, et al. Bifurcation analysis of dual-mode dynamics for marine risers[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2020, 41(5): 480-490.(in Chinese) [5] BISHOP R E D, HASSAN A. The lift and drag forces on a circular cylinder oscillating in a flowing fluid[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1964, 277(1368): 51-75. [6] GRIFFIN O M, SKOP R A, KOOPMANN G H. The vortex-excited resonant vibrations of circular cylinders[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1973, 31(2): 235-249. doi: 10.1016/S0022-460X(73)80377-3 [7] SKOP R, GRIFFIN O. On a theory for the vortex-excited oscillations of flexible cylindrical structures[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1975, 41(3): 263-274. doi: 10.1016/S0022-460X(75)80173-8 [8] SKOP R A, BALASUBRAMANIAN S. A new twist on an old model for vortex-excited vibration[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 1997, 11(4): 395-412. doi: 10.1006/jfls.1997.0085 [9] FACCHINETTI M L, LANGRE E, BIOLLEY F. Coupling of structure and wake oscillators in vortex-induced vibrations[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2004, 19(2): 123-140. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2003.12.004 [10] VIOLETTE R, LANGRE E, SZYDLOWSKI J. Computation of vortex-induced vibrations of long structures using a wake oscillator model: comparison with DNS and experiments[J]. Computers & Structures, 2007, 85(11/14): 1134-1141. [11] PAÏDOUSSIS M P, SEMLER C. Nonlinear dynamics of a fluid-conveying cantilevered pipe with an intermediate spring support[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 1993, 7(3): 269-298. doi: 10.1006/jfls.1993.1017 [12] MUNIR A, ZHAO M, WU H, et al. Numerical investigation of the effect of plane boundary on two-degree-of-freedom of vortex-induced vibration of a circular cylinder in oscillatory flow[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2018, 148: 17-32. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2017.11.022 [13] YANG W, AI Z, ZHANG X D, et al. Nonlinear three-dimensional dynamics of a marine viscoelastic riser subjected to uniform flow[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2018, 149: 38-52. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2017.12.004 [14] GE Fei, LONG Xu, WANG Lei, et al. Flow-induced vibrations of long circular cylinders modeled by coupled nonlinear oscillators[J]. Science in China (Series G) : Physics, Mechanics and Astronomy, 2009, 52(7): 1086-1093. doi: 10.1007/s11433-009-0128-8 [15] GABBAI R D, BENAROYA H. An overview of modeling and experiments of vortex-induced vibration of circular cylinders[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2005, 282(3/5): 575-616. [16] BLEVINS R. Flow-Induced Vibrations[M]. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold, 1990. [17] KEBER M, WIERCIGROCH M. Dynamics of a vertical riser with weak structural nonlinearity excited by wakes[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2008, 315(3): 685-699. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2008.03.023 [18] DAI Huliang, WANG Lin, QIAN Qin, et al. Vortex-induced vibrations of pipes conveying fluid in the subcritical and supercritical regimes[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2013, 39: 322-334. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2013.02.015 -





 下载:
下载:





















 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号