Dynamics of a Diffusion Malaria Model With Vector-Bias
-
摘要:
为了探讨季节性、蚊子叮咬的偏好性和人类的扩散对疟疾传播的影响,该文提出了一个部分退化的周期反应扩散模型。利用动力系统的持续性理论,研究了模型关于基本再生数
\begin{document}$ \mathcal{R}_0 $\end{document} 的阈值动力学。即当
$ \mathcal{R}_0<1 $ 时,疾病灭绝;而当
$ \mathcal{R}_0>1 $ 时,疾病一致持续,且会发生季节性的流行。数值上发现了忽略空间异质性和蚊子叮咬的偏好性会低估疾病传染的风险。
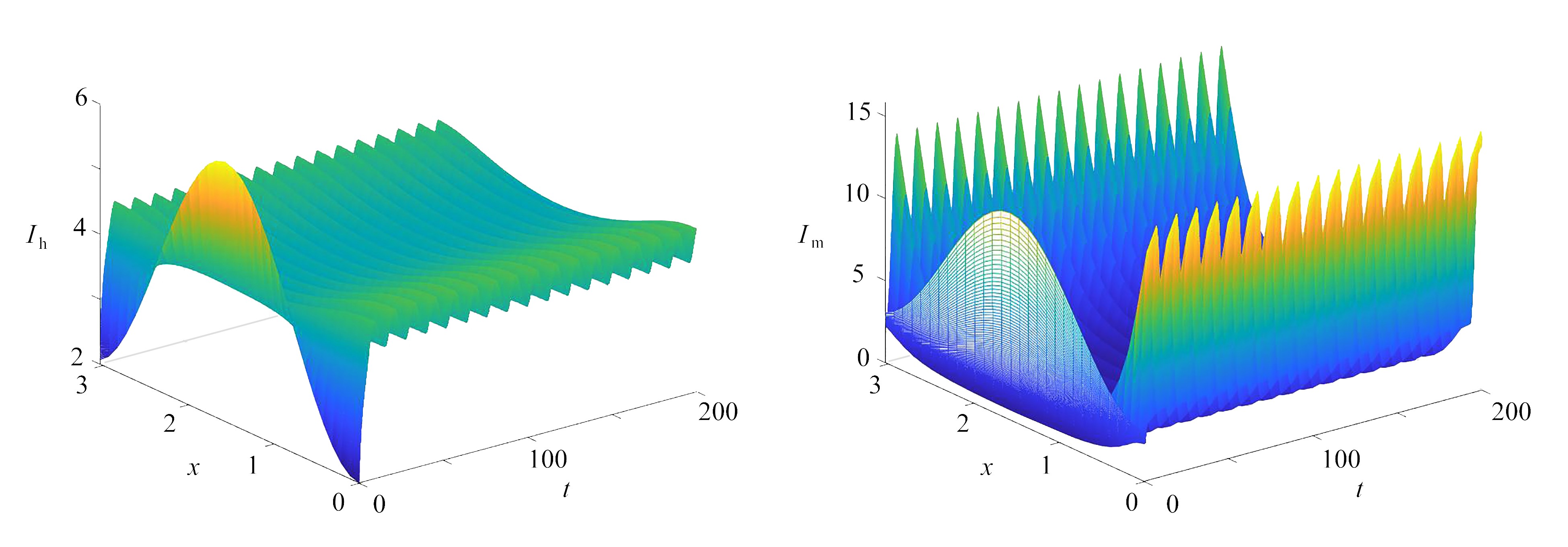
Abstract:In order to explore the combined effects of seasonality, vector-bias and human diffusion on malaria transmission, a partially degenerate periodic reaction-diffusion model was considered. With the persistence theory for dynamical systems, the threshold dynamics for the system was established in terms of basic reproduction number
\begin{document}$\mathcal{R}_0$\end{document} . That is, the disease will go extinct if
$\mathcal{R}_0<1$ , while the disease will be uniformly persistent and break out seasonally for
$\mathcal{R}_0>1$ . Numerical results show that, the neglect of spatial heterogeneity and vector-bias will lead to underestimation of the risk of disease spread.
-
Key words:
- malaria model /
- threshold dynamics /
- seasonality /
- vector-bias /
- spatial heterogeneity
-
-
[1] World Health Organization (WHO). 世界疟疾报告2022[EB/OL]. [2022-04-13]. https://www.who.int/zh/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/malaria. [2] 贾尚春, 邹铮, 徐伏牛. 全球气候变暖对疟疾传播的潜在影响[J]. 中国寄生虫病防治杂志, 2004, 17(1): 63-64 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5234.2004.01.020JIA Shangchun, ZOU Zheng, XU Funiu. Potential impact of global warming on malaria transmission[J]. Chinese Journal of Parasitic Diseases Control, 2004, 17(1): 63-64.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5234.2004.01.020 [3] DAN X, YONG L, WANG S Q, et al. Spatiotemporal distribution of malaria and the association between its epidemic and climate factors in Hainan, China[J]. Malaria Journal, 2010, 9(1): 185. [4] LACROIX R, MUKABANA W R, GOUAGNA L C, et al. Malaria infection increases attractiveness of humans to mosquitoes[J]. PLoS Biology, 2005, 3(9): e298. [5] KESAVAN S K, REDDY N P. On the feeding strategy and the mechanics of blood sucking in insects[J]. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 1983, 105(4): 661-677. [6] CHAMCHOD F, BRITTON N F. Analysis of a vector-bias model on malaria transmission[J]. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology, 2011, 73: 639-657. [7] WANG X N, ZHAO X Q. A periodic vector-bias malaria model with incubation period[J]. SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, 2017, 77: 181-201. [8] SMITH D L, DUSHOFF J, MCKENZIE F E. The risk of a mosquito-borne infection in a heterogeneous environment[J]. PLoS Biology, 2004, 2: 1957-1964. [9] LOU Y J, ZHAO X Q. A reaction-diffusion malaria model with incubation period in the vector population[J]. Journal of Mathematical Biology, 2011, 62: 543-568. [10] BAI Z G, PENG R, ZHAO X Q. A reaction-diffusion malaria model with seasonality and incubition period[J]. Journal of Mathematical Biology, 2018, 77: 201-228. [11] SHI Y Y, ZHAO H Y. Analysis of two-strain malaria transmission model with spatial heterogeneity and vector-bias[J]. Journal of Mathematical Biology, 2021, 82: 24. [12] WANG C Y, WANG J. Analysis of a malaria epidemic model with age structure and spatial diffusion[J]. Zeitschrift fur Angewandte Mathematik and Physik, 2021, 72: 74. [13] ZHANG Y, LIU S Y, BAI Z G. A periodic malaria model with two delays[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2019, 541: 123327. [14] GAO D Z, LOU Y J, RUAN S G. A periodic ross-Macdonald model in a patchy environment[J]. Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems (Series B), 2014, 19(10): 3133-3145. [15] COSTANTINI C, LI S G, TOREE A D, et al. Density, survival and dispersal of anopheles gambiae complex mosquitoes in a west African Sudan savanna village[J]. Medical and Veterinary Entomology, 1996, 10(3): 203-219. [16] MARTIN R H, SMITH H L. Abstract functional differential equations and reaction-diffusion systems[J]. Transactions of the American Mathematical Society, 1990, 321: 1-44. [17] ZHAO X Q. Dynamical Systems in Population Biology[M]. 2nd ed. New York: Springer, 2017. [18] 郭大钧. 非线性泛函分析[M]. 济南: 山东科学技术出版社, 2001: 1-550.GUO Dajun. Nonlinear Functional Analysis[M]. Jinan: Shandong Science and Technology Press, 2001: 1-550. (in Chinese) [19] WANG J L, WANG J. Analysis of a reaction-diffusion cholera model with distinct dispersal rates in the human population[J]. Journal of Dynamics and Differential Equations, 2021, 33: 549-575. [20] HALE J K. Asymptotic Behavior of Dissipative Systems[M]. Providence: American Mathematical Society, 1988. [21] HESS P. Periodic Parabolic Boundary Value Problems and Positivity[M]. London: Longman Scientific and Technical, 1991: 1-139. [22] THIEME H R. Spectral bound and reproduction number for infinite-dimensional population structure and time heterogeneity[J]. SIAM Journal of Applied and Mathematics, 2009, 70(1): 188-211. [23] YANG T H, ZHANG L. Remarks on basic reproduction ratios for periodic abstract functional differential equations[J]. Discrete and Continuous Dynamical Systems (Series B), 2019, 24: 6771-6782. [24] LIANG X, ZHANG L, ZHAO X Q. The principal eigenvalue for degenerate periodic reaction-diffusion systems[J]. SIAM Journal of Mathematical Analysis, 2017, 49(5): 3603-3636. [25] YU X, ZHAO X Q. A periodic reaction-advection-diffusion model for a stream population[J]. Journal of Differential Equations, 2015, 258(9): 3037-3062. [26] PROTTER M H, WEINBERGER H F. Maximum Principles in Differential Equations[M]. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1984. [27] LI F X, ZHAO X Q. Global dynamics of a nonlocal periodic reaction-diffusion model of bluetongue disease[J]. Journal of Differential Equations, 2021, 272: 127-163. [28] MAGAL P, ZHAO X Q. Global attractors and steady states for uniformly persistent dynamical systems[J]. SIAM Journal of Mathematical Analysis, 2005, 37: 251-275. [29] WU R W, ZHAO X Q. A reaction-diffusion model of vector-borne disease with periodic delays[J]. Journal of Nonlinear Science, 2019, 29: 29-64. [30] LIANG X, ZHANG L, ZHAO X Q. Basic reproduction ratios for periodic abstract functional differential equations (with application to a spatial model for Lyme disease)[J]. Journal of Dynamical and Differential Equations, 2019, 31: 1247-1278. [31] WANG K, ZHAO H Y, WANG H, et al. Traveling wave of a reaction-diffusion vector-borne disease model with nonlocal effects and distributed delay[J]. Journal of Dynamics and Differential Equations, 2021. DOI: 10.1007/s10884-01-10062-w. [32] 张笑嫣. 一类具有非线性发生率与时滞的离散扩散SIR模型临界行波解的存在性[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2021, 42(12): 1317-1326ZHANG Xiaoyan. Existence of critical traveling wave solutions for a class of discrete diffusion SIR models with nonlinear incidence and time delay[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2021, 42(12): 1317-1326.(in Chinese) [33] 陈妍. 时间周期的离散SIS模型的传播动力学[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2022, 43(10): 1155-1163CHEN Yan. Propagation dynamics of a discrete SIS model with time periodicity[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2022, 43(10): 1155-1163.(in Chinese) -








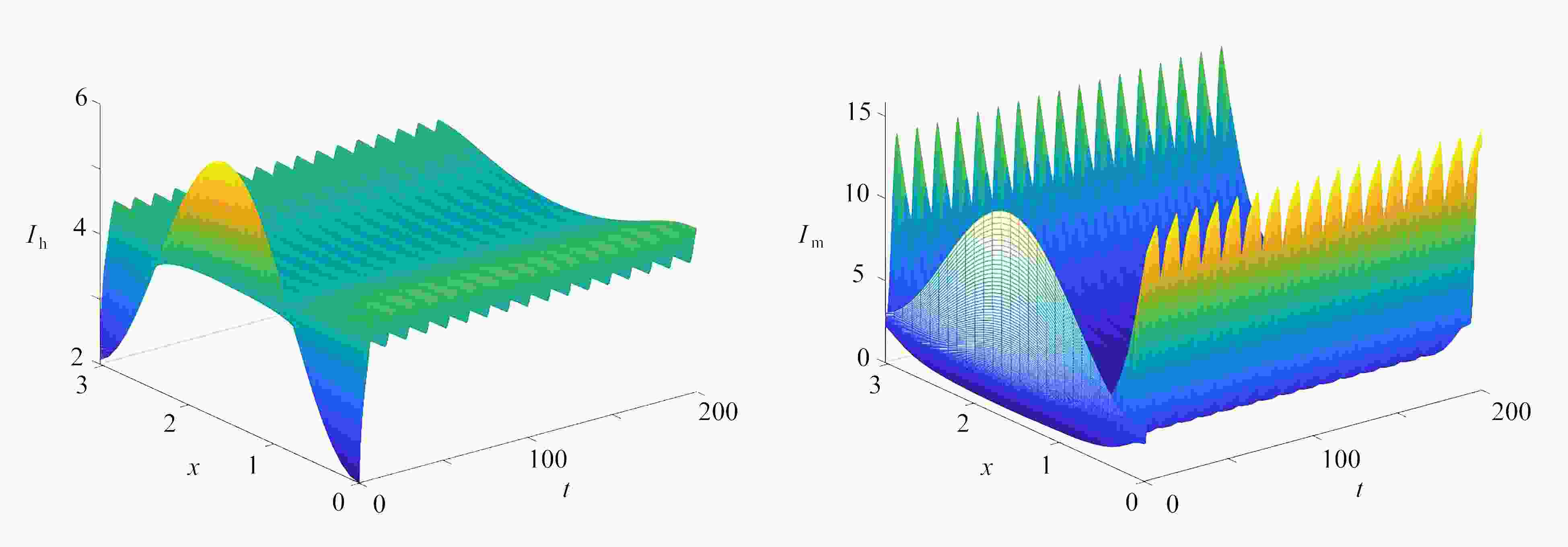






 下载:
下载:
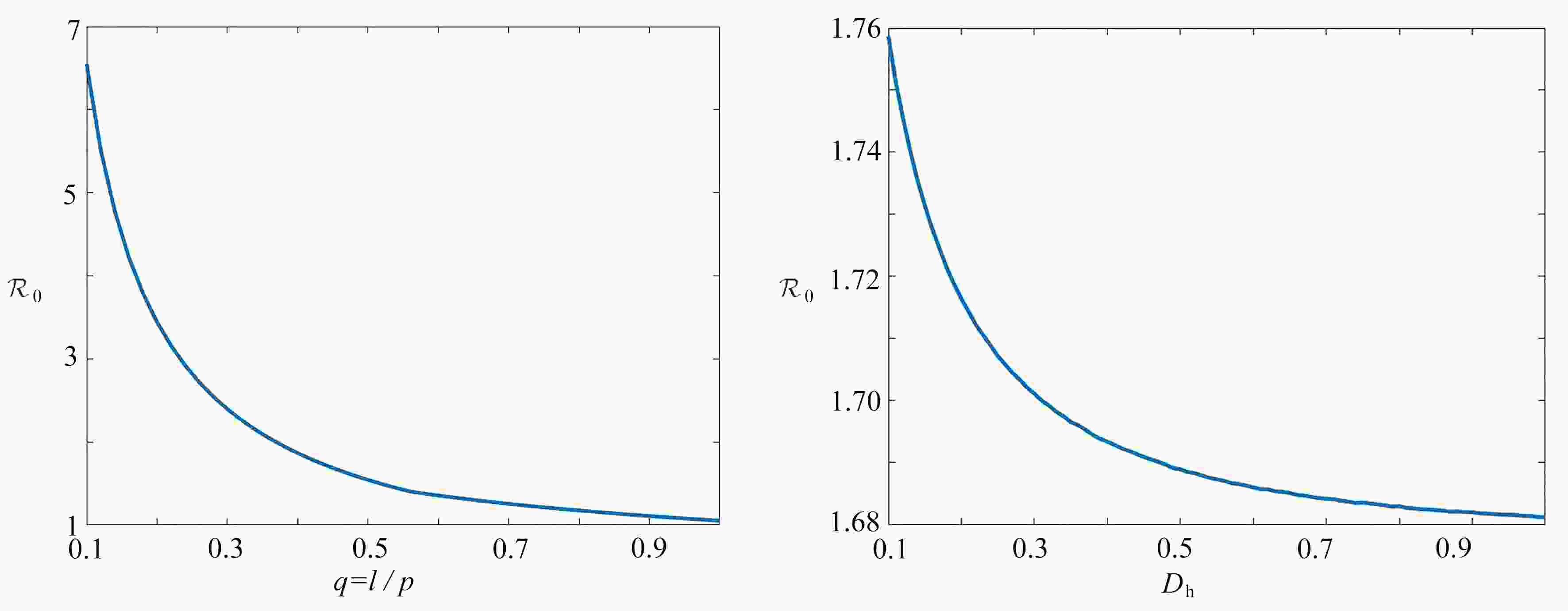


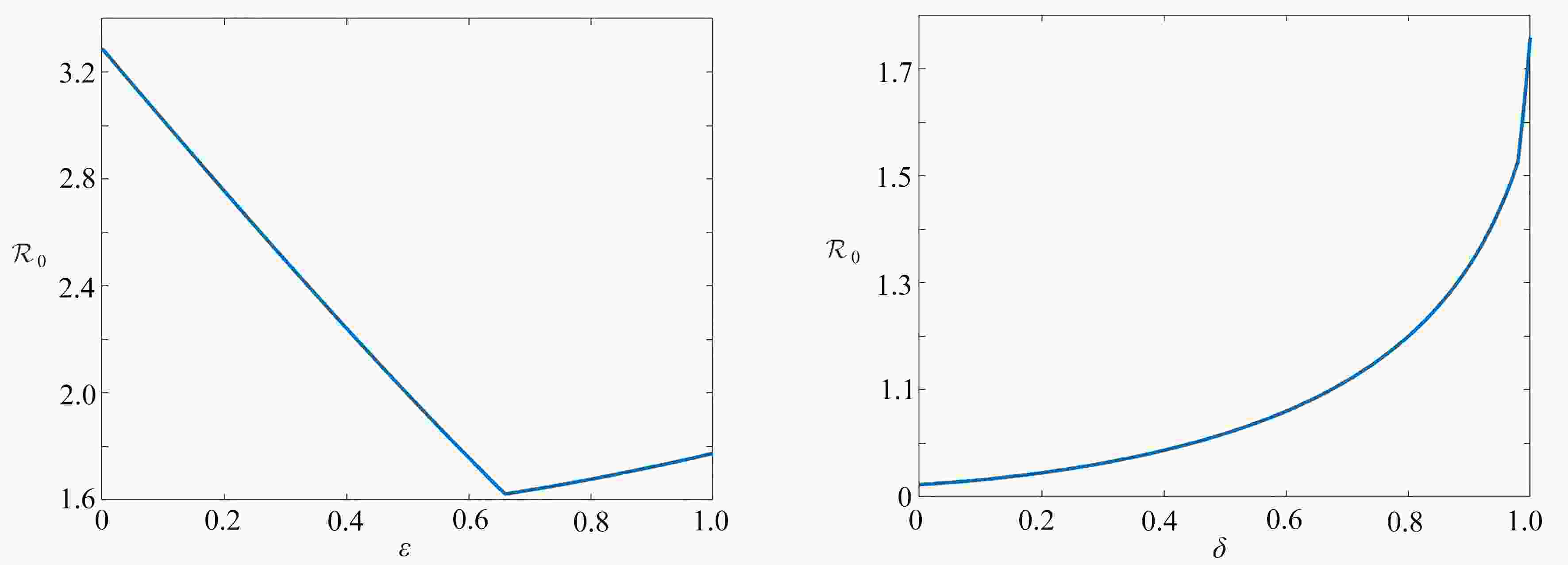


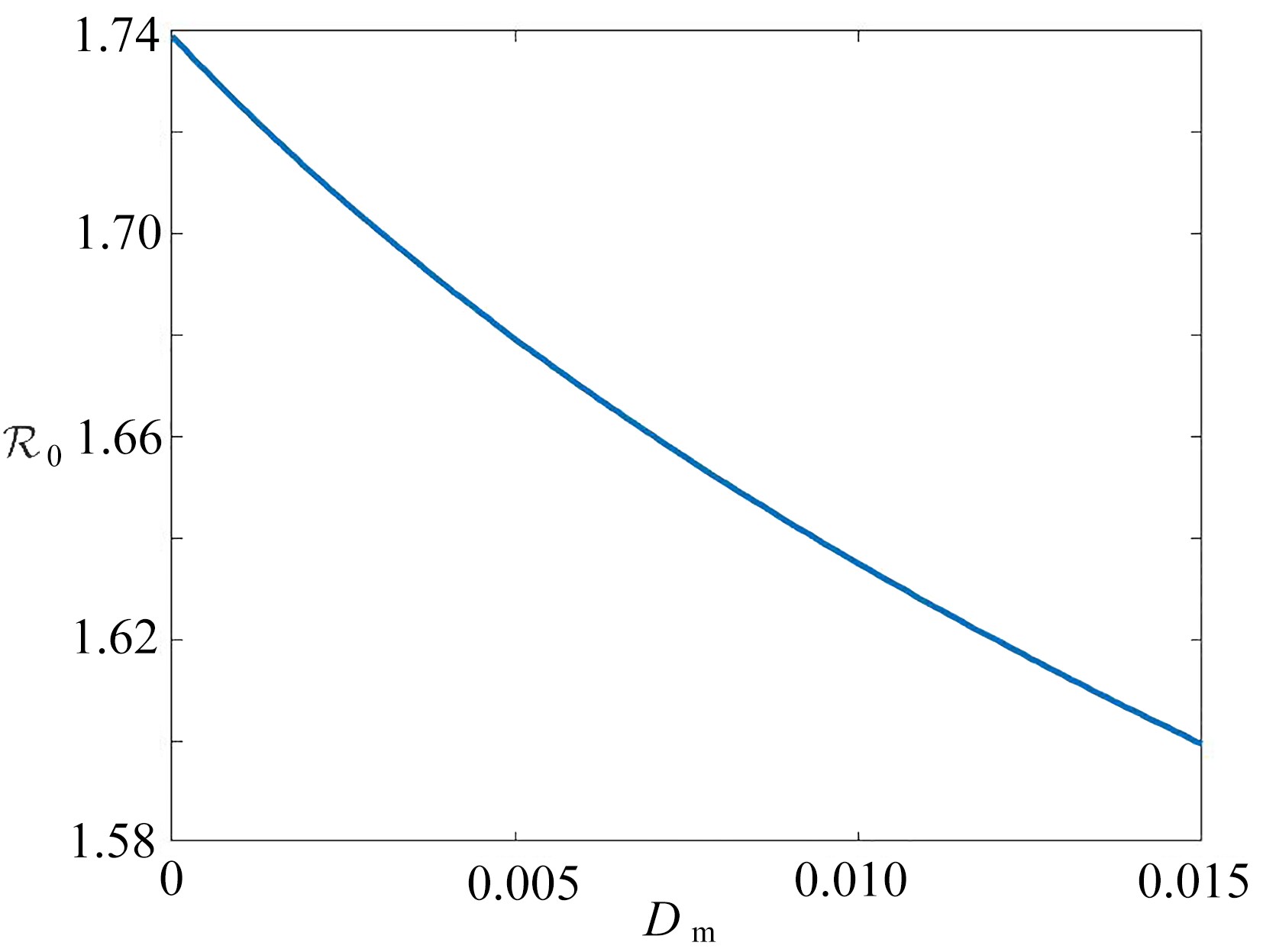





 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号