An Asymptotic-Homogenization Explicit Time-Domain Method for Random Multiscale Vibration Analysis of Porous Material Structures
-
摘要:
由于具有高比强、高比刚度等优点,多孔结构在土木工程、机械工程和航天航空工程等领域得到了广泛应用。在随机动力荷载作用下多孔结构的随机响应分析是值得关注的研究方向之一。采用多尺度渐近均匀化法,推导了周期性多孔结构动力问题的多尺度控制微分方程,并建立了多孔结构宏观和细观动力响应的时域显式表达式。在此基础上,结合结构随机振动时域显式法,实现了非平稳随机激励下多孔结构动力响应统计矩的计算。所提出的渐近均匀化-时域显式法,一方面可以发挥多尺度动力分析渐近均匀化法的计算优势,高效建立多孔结构宏观和细观动力响应的时域显式表达式;另一方面也可以利用随机振动时域显式法的计算特点,快速精确地求解非平稳随机激励下多孔结构的随机振动问题。通过数值算例,验证了所提方法在多孔结构非平稳随机振动问题求解中的计算精度和计算效率。
Abstract:Porous material structures have been widely used in civil engineering, mechanical engineering, aerospace engineering and other fields due to their high specific strength and specific stiffness. The stochastic response analysis of porous material structures under random excitations deserves more attention. The multiscale governing differential equations for porous material structures were derived based on the multiscale asymptotic-homogenization method (AHM), and the macroscale and microscale explicit time-domain expressions of structural responses were further established. On this basis, the statistical moments of dynamic responses of porous material structures under non-stationary random excitations were achieved with the explicit time-domain method (ETDM). The proposed method combines the advantages of the AHM for high-efficiency explicit formulation of macroscale and microscale dynamic responses of porous material structures and the benefits of the ETDM for fast analysis of non-stationary random vibration problems. A numerical example shows the computation accuracy and efficiency of the presented approach for non-stationary random vibration analysis of porous material structures.
-
表 1 各时刻显式表达式的系数矩阵
Table 1. Coefficient matrices for explicit formulation at different instants
instant coefficient matrix ${{\boldsymbol{F}}_0}$ ${{\boldsymbol{F}}_1}$ ${{\boldsymbol{F}}_2}$ ${{\boldsymbol{F}}_3}$ … $ {{\boldsymbol{F}}_{n - 2}} $ ${{\boldsymbol{F}}_{n - 1}}$ ${{\boldsymbol{F}}_n}$ ${t_1}$ ${{\boldsymbol{A}}_{1,0}}$ $ {{\boldsymbol{A}}_{1,1}} $ ${t_2}$ $ {{\boldsymbol{A}}_{2,0}} $ ${{\boldsymbol{A}}_{2,1}}$ ${{\boldsymbol{A}}_{1,1}}$ ${t_3}$ $ {{\boldsymbol{A}}_{3,0}} $ ${{\boldsymbol{A}}_{3,1}}$ $ {{\boldsymbol{A}}_{2,1}} $ ${{\boldsymbol{A}}_{1,1}}$ $ \vdots $ $ \vdots $ $ \vdots $ $ \vdots $ $ \vdots $ $ \ddots $ ${t_{n - 2}}$ $ {{\boldsymbol{A}}_{n - 2,0}} $ $ {{\boldsymbol{A}}_{n - 2,1}} $ $ {{\boldsymbol{A}}_{n - 3,1}} $ $ {{\boldsymbol{A}}_{n - 4,1}} $ … ${{\boldsymbol{A}}_{1,1}}$ ${t_{n - 1}}$ ${{\boldsymbol{A}}_{n - 1,0}}$ ${{\boldsymbol{A}}_{n - 1,1}}$ $ {{\boldsymbol{A}}_{n - 2,1}} $ $ {{\boldsymbol{A}}_{n - 3,1}} $ … ${{\boldsymbol{A}}_{2,1}}$ ${{\boldsymbol{A}}_{1,1}}$ ${t_n}$ ${{\boldsymbol{A}}_{n,0}}$ $ {{\boldsymbol{A}}_{n,1}} $ ${{\boldsymbol{A}}_{n - 1,1}}$ $ {{\boldsymbol{A}}_{n - 2,1}} $ … ${{\boldsymbol{A}}_{3,1}}$ ${{\boldsymbol{A}}_{2,1}}$ ${{\boldsymbol{A}}_{1,1}}$ 表 2 两种方法的计算时间(单位:s)
Table 2. Time costs of the 2 methods(unit: s)
method construction of explicit time-domain
expressions of dynamic responsescalculation of statistical moments
of dynamic responsestotal computation
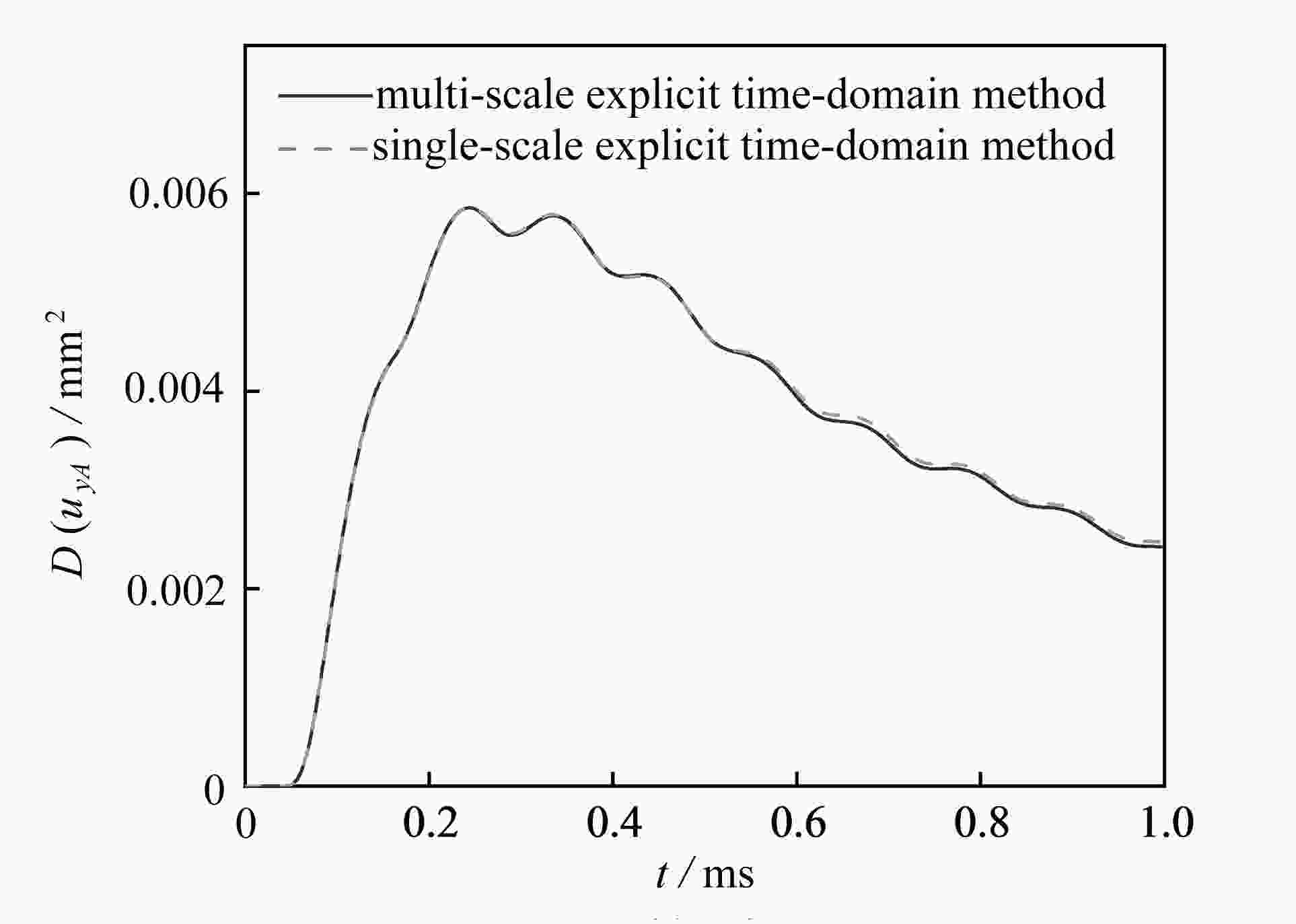
timemulti-scale explicit time-domain method 42.00 2.46 44.46 single-scale explicit time-domain method 4482.00 2.46 4484.46 -
[1] 刘培生. 多孔材料引论[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2012.LIU Peisheng. Introduction to Porous Materials[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2012. (in Chinese) [2] 卢天健, 何德坪, 陈常青, 等. 超轻多孔金属材料的多功能特性及应用[J]. 力学进展, 2006, 36(4): 517-535 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0992.2006.04.004LU Tianjian, HE Deping, CHEN Changqing, et al. The multi-functionality of ultra-light porous metals and their applications[J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2006, 36(4): 517-535.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0992.2006.04.004 [3] SMITH B H, SZYNISZEWSKI S, HAJJAR J F, et al. Steel foam for structures: a review of applications, manufacturing and material properties[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2012, 71: 1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2011.10.028 [4] 任石磊, 韩飞鹏, 谢斌, 等. 基于三维CFD-DEM的多孔介质流场数值模拟[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2017, 38(10): 1093-1102REN Shilei, HAN Feipeng, XIE Bin, et al. Numerical simulation of flow fields in porous media based on the 3D CDF-DEM[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2017, 38(10): 1093-1102.(in Chinese) [5] SUN Y, LI Q M. Dynamic compressive behaviour of cellular materials: a review of phenomenon, mechanism and modelling[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2018, 112: 74-115. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2017.10.006 [6] PIÑEIRO L T, PARRY T, HAUGHEY F, et al. Architected cellular particles to mitigate asphalt stone loss[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 328: 127056. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.127056 [7] 郑晓霞, 郑锡涛, 缑林虎. 多尺度方法在复合材料力学分析中的研究进展[J]. 力学进展, 2010, 40(1): 41-56 doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-2010-1-J2008-104ZHENG Xiaoxia, ZHENG Xitao, GOU Linhu. The research progress on multiscale method for the mechanical analysis of composites[J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2010, 40(1): 41-56.(in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-2010-1-J2008-104 [8] 陈玉丽, 马勇, 潘飞, 等. 多尺度复合材料力学研究进展[J]. 固体力学学报, 2018, 39(1): 1-68 doi: 10.19636/j.cnki.cjsm42-1250/o3.2017.030CHEN Yuli, MA Yong, PAN Fei, et al. Research progress in multi-scale mechanics of composite materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Solid Mechanics, 2018, 39(1): 1-68.(in Chinese) doi: 10.19636/j.cnki.cjsm42-1250/o3.2017.030 [9] HASSANI B, HINTON E. A review of homogenization and topology optimization Ⅰ: homogenization theory for media with periodic structure[J]. Computers & Structures, 1998, 69(6): 707-717. [10] HASSANI B, HINTON E. A review of homogenization and topology optimization Ⅱ: analytical and numerical solution of homogenization equations[J]. Computers & Structures, 1998, 69(6): 719-738. [11] 李鸿鹏, 凌松, 戚振彪, 等. 热力耦合问题数学均匀化方法的计算精度[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2020, 41(1): 54-69LI Hongpeng, LING Song, QI Zhenbiao, et al. Accuracy of the mathematical homogenization method for thermomechanical problems[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2020, 41(1): 54-69.(in Chinese) [12] 周凤玺, 李丹, 曹小林. 含液饱和不可压多孔弹性板的随机振动[J]. 振动与冲击, 2017, 36(10): 168-174 doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2017.10.027ZHOU Fengxi, LI Dan, CAO Xiaolin. Random vibration of fluid-saturated porous elastic plates[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2017, 36(10): 168-174.(in Chinese) doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2017.10.027 [13] 苏成, 徐瑞. 非平稳随机激励下结构体系动力可靠度时域解法[J]. 力学学报, 2010, 42(3): 512-520 doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-2010-3-2009-042SU Cheng, XU Rui. Time-domain method for dynamic reliability of structural systems subjected to non-stationary random excitations[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2010, 42(3): 512-520.(in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-2010-3-2009-042 [14] SU C, XU R. Random vibration analysis of structures by a time-domain explicit formulation method[J]. Structural Engineering and Mechanics, 2014, 52(2): 239-260. doi: 10.12989/sem.2014.52.2.239 [15] 苏成, 黄志坚, 刘小璐. 高层建筑地震作用计算的时域显式随机模拟法[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2015, 36(1): 13-22 doi: 10.14006/j.jzjgxb.2015.01.002SU Cheng, HUANG Zhijian, LIU Xiaolu. Time-domain explicit random simulation method for seismic analysis of tall buildings[J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2015, 36(1): 13-22.(in Chinese) doi: 10.14006/j.jzjgxb.2015.01.002 [16] SU C, HUANG H, MA H T. Fast equivalent linearization method for nonlinear structures under nonstationary random excitations[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 2016, 142(8): 04016049. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)EM.1943-7889.0001094 [17] 陈玉震, 张盛, 陈飙松, 等. 非均质结构非平稳随机响应的快速算法[J]. 振动与冲击, 2015, 34(19): 24-30 doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2015.19.004CHEN Yuzhen, ZHANG Sheng, CHEN Biaosong, et al. A fast algorithm for non-stationary random responses of heterogeneous material structures[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2015, 34(19): 24-30.(in Chinese) doi: 10.13465/j.cnki.jvs.2015.19.004 [18] 李家春, 周显初. 数学物理中的渐近方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1998.LI Jiachun, ZHOU Xianchu. Asymptotic Methods in Mathematical Physics[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1998. (in Chinese) [19] HASSANI B. A direct method to derive the boundary conditions of the homogenization equation for symmetric cells[J]. Communications in Numerical Methods in Engineering, 1996, 12(3): 185-196. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1099-0887(199603)12:3<185::AID-CNM970>3.0.CO;2-2 [20] PAVLIOTIS G A, STUARTA M. Multiscale Methods[M]. New York: Springer, 2008. [21] 宣立新, 马明. 周期函数初论[M]. 合肥: 安徽教育出版社, 1990.XUAN Lixin, MA Ming. Introduction to Periodic Functions[M]. Hefei: Anhui Education Press, 1990. (in Chinese) [22] HU Z Q, SU C, CHEN T C, et al. An explicit time-domain approach for sensitivity analysis of non-stationary random vibration problems[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2016, 382: 122-139. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2016.06.034 [23] 范金娟, 张卫方, 陈新文. 定向有机玻璃的拉伸断裂行为研究[J]. 航空材料学报, 2006, 26(5): 106-108 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5053.2006.05.024FAN Jinjuan, ZHANG Weifang, CHEN Xinwen. Investigation of tensile fracture behavior of directional PMMA[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2006, 26(5): 106-108.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5053.2006.05.024 -





 下载:
下载:
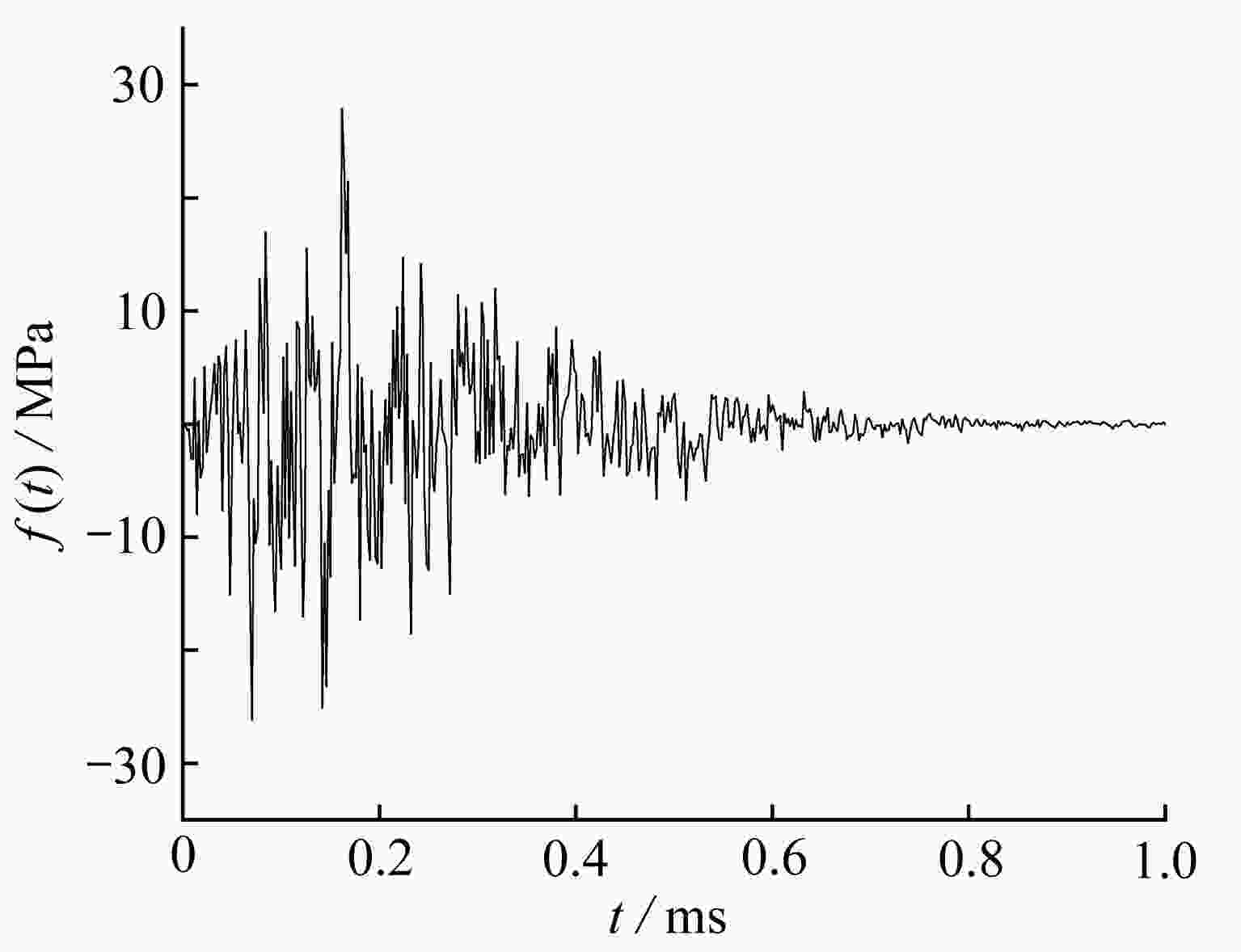


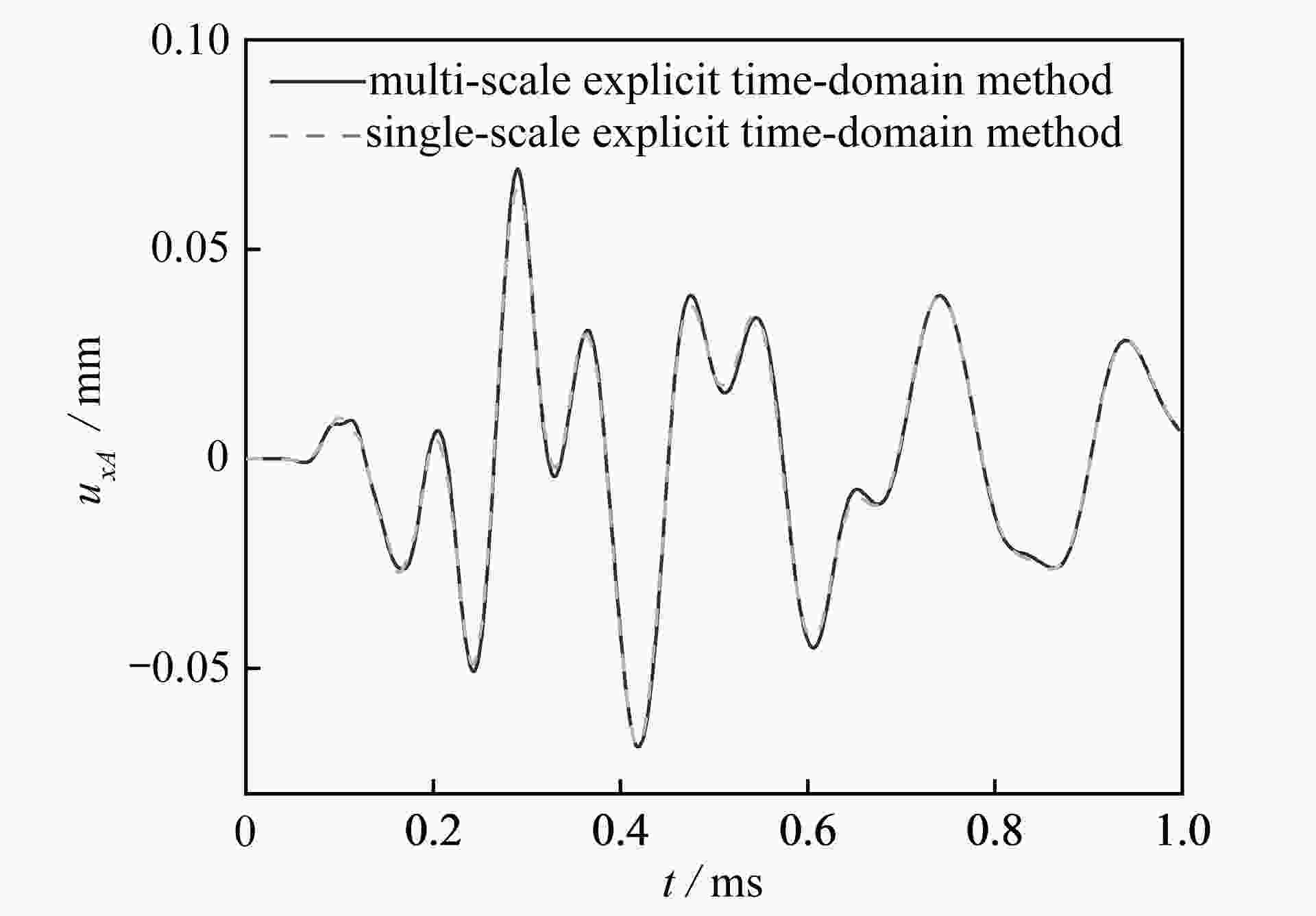
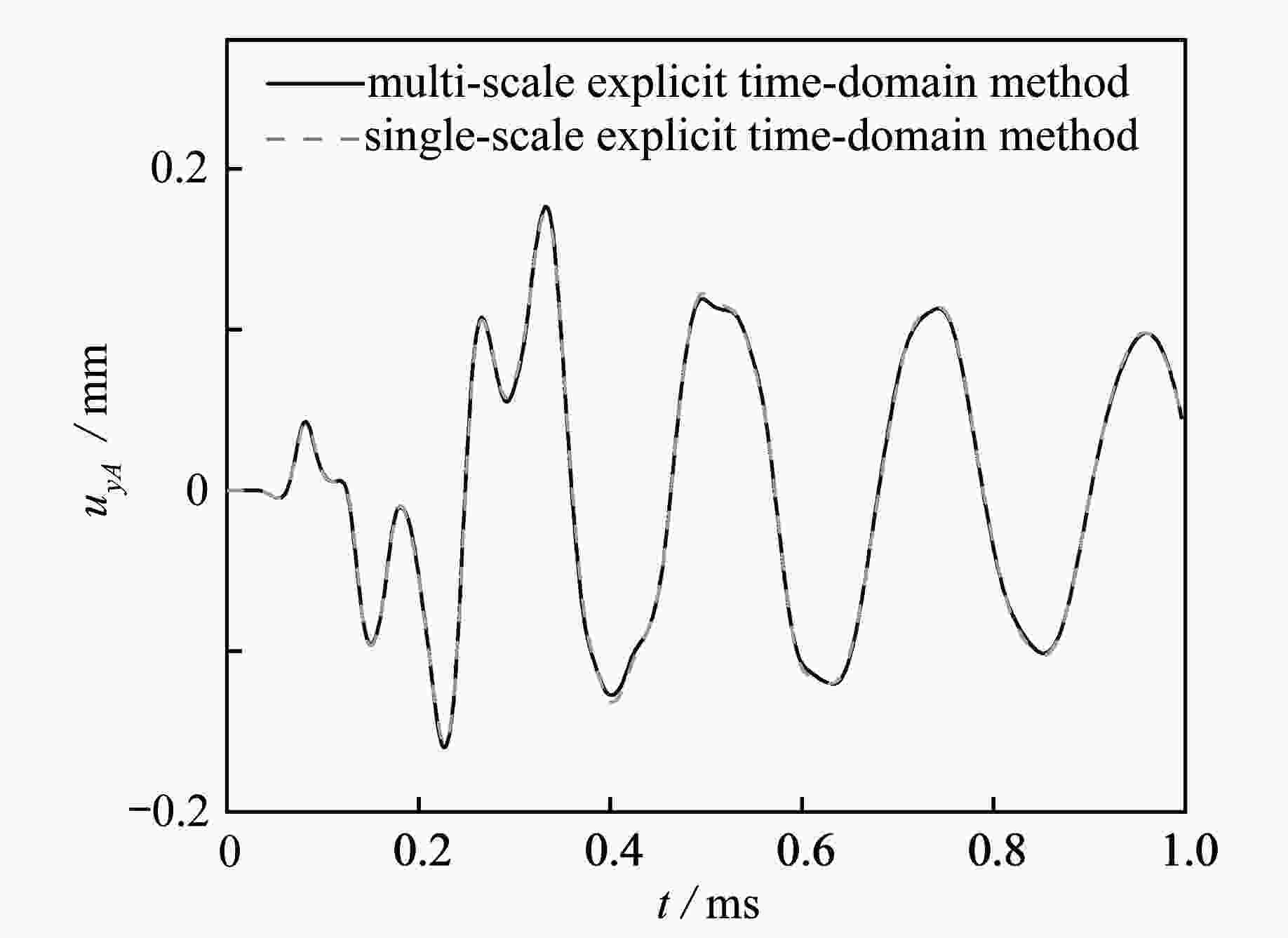
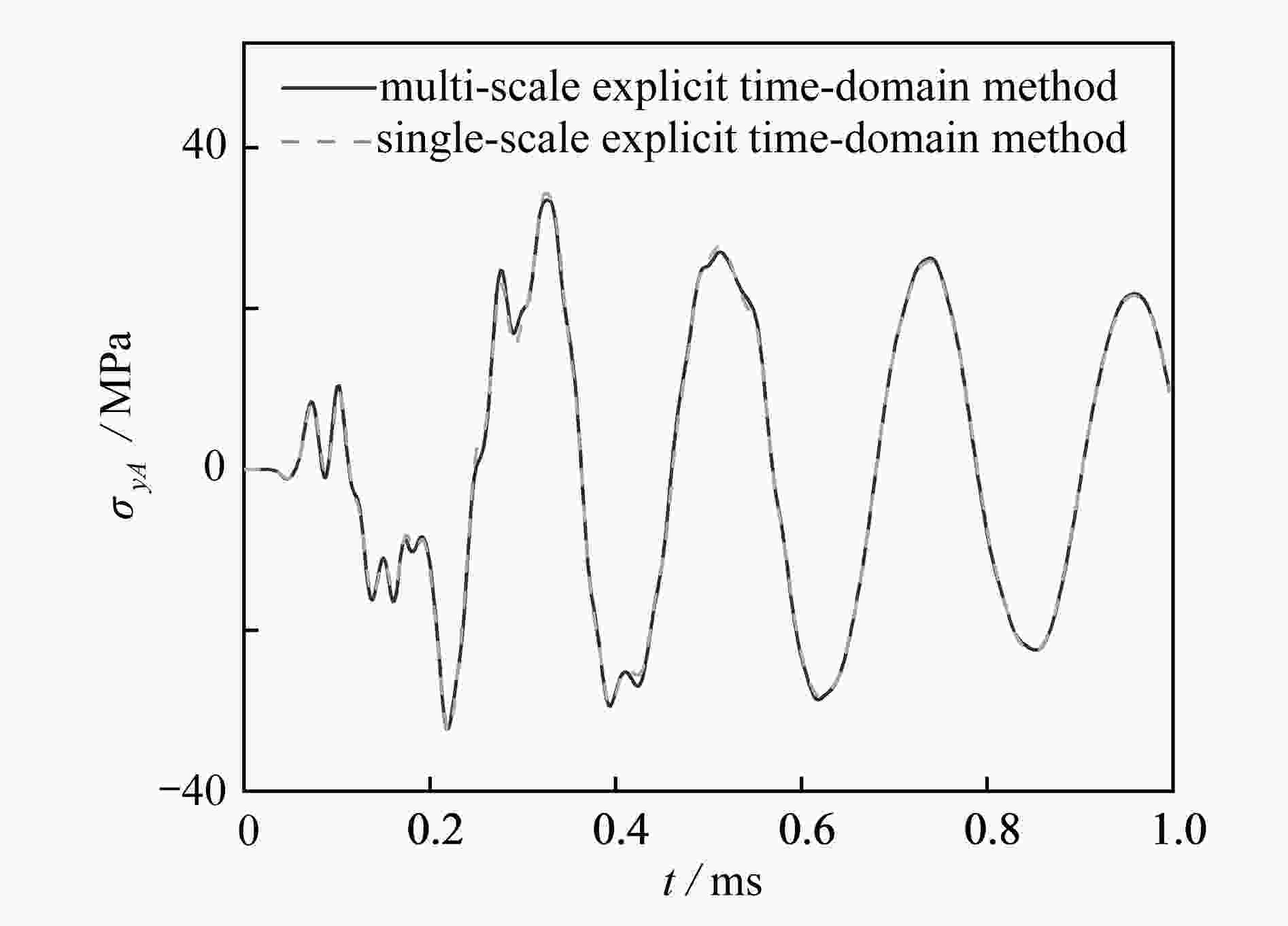




 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号