An Infectious Disease Model With Media Coverage and Limited Medical Resources
-
摘要:
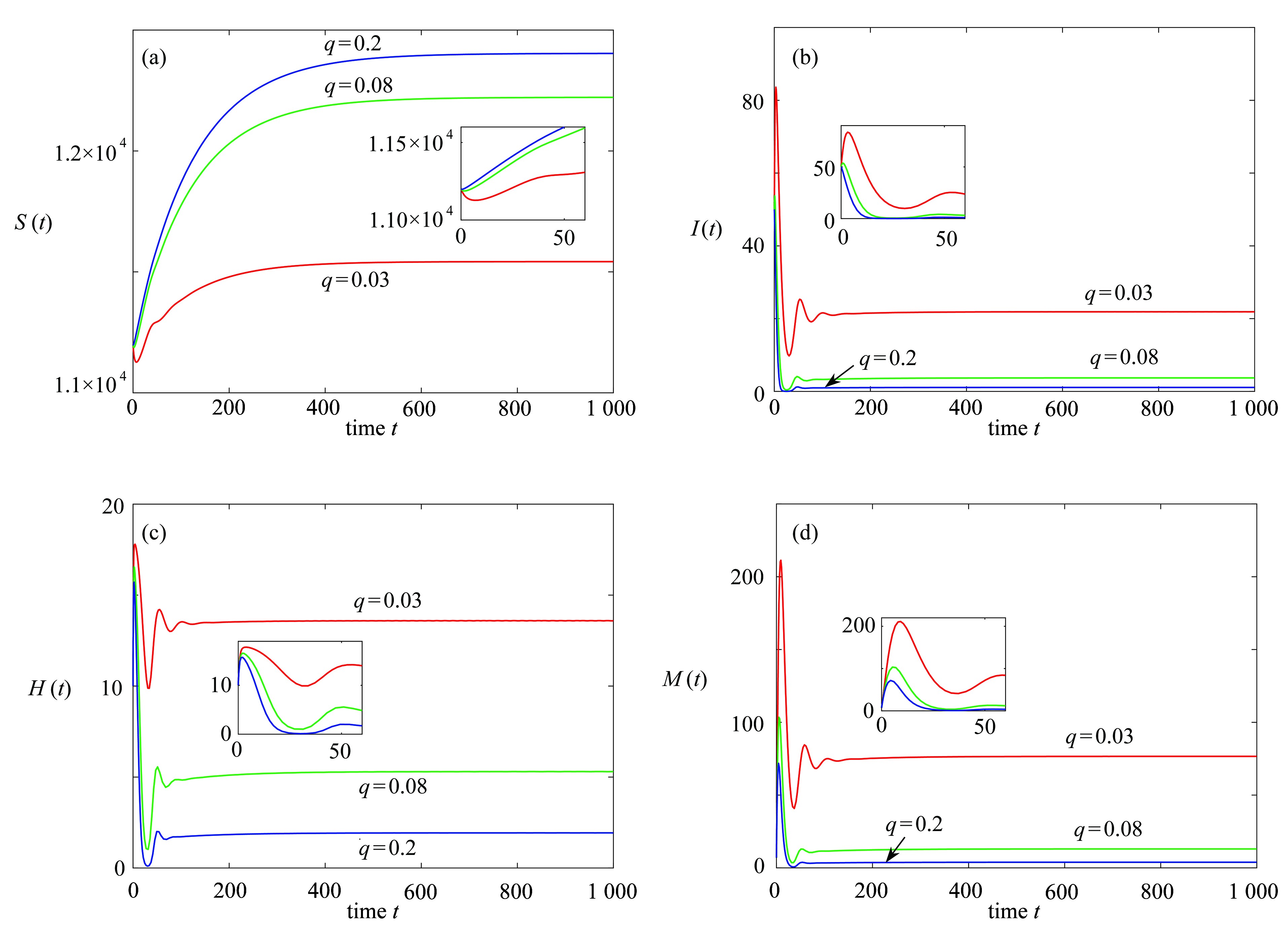
该文建立和分析了一类具有媒体报道效应和有限医疗资源的传染病动力学模型,定义了疾病的基本再生数,分析了平衡点的存在性和稳定性,给出了系统发生前向分支、后向分支和Hopf分支的条件。通过数值模拟发现:提高媒体报道的信息覆盖率或医院对病人的最大容纳量,可以显著降低疾病流行的峰值或稳态时的感染人数;随着参数变化,系统不仅可能会产生后向分支或前向分支,还可能会出现鞍结点分支、Hopf 分支以及地方病平衡点稳定性随参数变化而变化等动力学行为。
-
关键词:
- 媒体报道 /
- 有限医疗资源 /
- 后向分支 /
- Lyapunov 稳定
Abstract:A dynamical model for infectious disease with media coverage effects and limited medical resources was established and analyzed. The basic reproduction number of the disease was defined, the existence and stability of the equilibria were analyzed, and the conditions for the forward bifurcation, the backward bifurcation and the Hopf bifurcation to occur in the system were given. Numerical simulation results show that, increasing the media coverage rate or the maximum hospital capacity can significantly reduce the number of infections at the peak or in the steady state of the epidemic. With the variations of parameters, the system will exhibit dynamic behaviors including not only the backward bifurcation or the forward bifurcation, but also the saddle node bifurcation, the Hopf bifurcation, or the change of the endemic equilibrium point stability with parameters.
-
Key words:
- limited medical resources /
- media coverage /
- backward bifurcation /
- Lyapunov stability
-
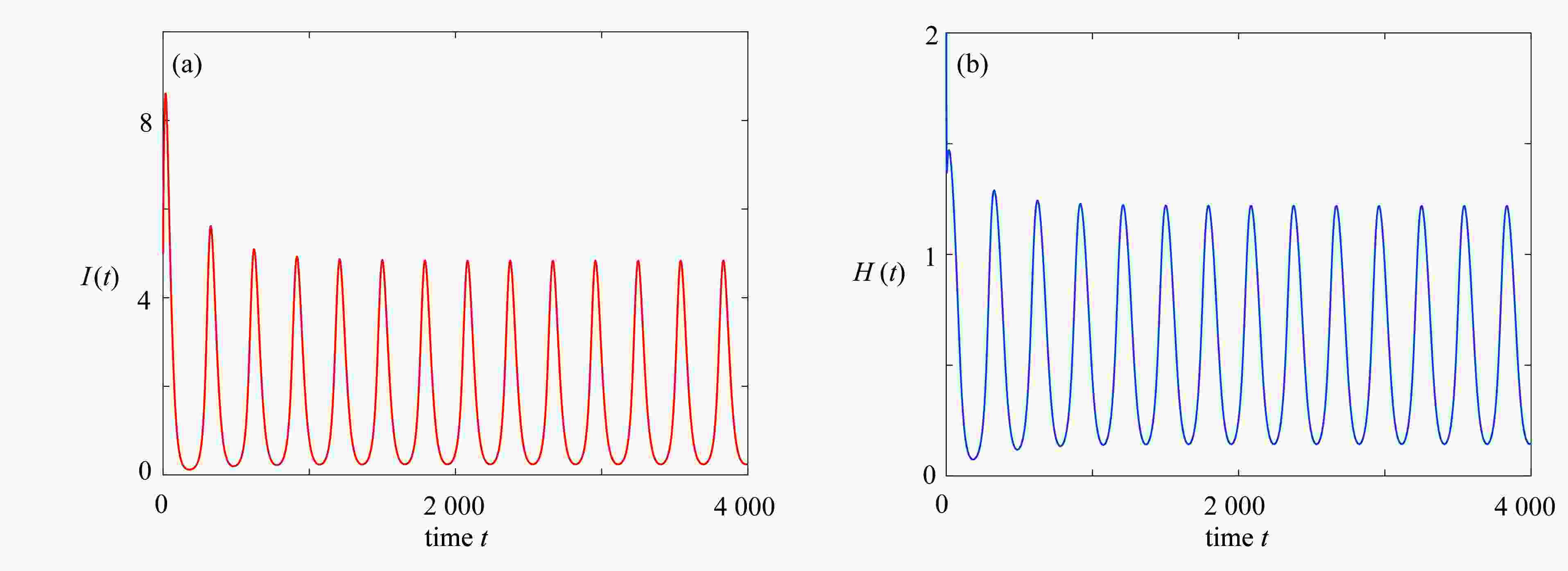
图 5 当
$R_{0}=1.3$ 时,模型(2)解的长期行为,其中$\varLambda=1,\; \mu=0.008,\; K=2,\; r=0.2,\; \gamma_1=0.06,\;\gamma_2=0.3$ ,$d_1=0.01,\;d_2=0.001,\; a=0.7,\; \tau=0.2,\; q=0.03$ ,初值为$(100,5,2,10)$ Figure 5. For
$R_{0}=1.3$ , the long-term behavior of the solution for model (2), where$\varLambda=1,\; \mu=0.008,\; K=2,\; r=0.2,\; \gamma_1=0.06,\;\gamma_2=0.3$ ,$d_1=0.01,\;d_2=0.001,\; a=0.7,\; \tau=0.2,\; q=0.03$ , and the initial value is$(100,5,2,10)$ -
[1] 陈兴志, 田宝单, 王代文, 等. 基于SEIR模型的COVID-19疫情防控效果评估和预测[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2021, 42(2): 199-211CHEN Xingzhi, TIAN Baodan, WANG Daiwen, et al. Evaluation and prediction of prevention and control effects of the COVID-19 epidemic based on the SEIR model[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2021, 42(2): 199-211.(in Chinese) [2] LIU R, WU J, ZHU H. Media psychological impact on multiple outbreaks of emerging infectious diseases[J]. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, 2007, 8(3): 153-164. doi: 10.1080/17486700701425870 [3] CUI J, SUN Y, ZHU H. The impact of media on the control of infectious diseases[J]. Journal of Dynamics and Differential Equations, 2008, 20(1): 31-53. doi: 10.1007/s10884-007-9075-0 [4] XIAO Y, ZHAO T, TANG S. Dynamics of an infectious diseases with media/psychology induced non-smooth incidence[J]. Mathematical Biosciences and Engineering, 2013, 10(2): 445-461. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2013.10.445 [5] LIU Y, CUI J. The impact of media coverage on the dynamics of infections disease[J]. International Journal of Biomathematics, 2008, 1(1): 65-74. doi: 10.1142/S1793524508000023 [6] TCHUENCHE J M, DUBE N, BHUNU C P, et al. The impact of media coverage on the transmission dynamics of human influenza[J]. BMC Public Health, 2011, 11(1): 31-53. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-11-31 [7] 刘玉英, 肖燕妮. 一类受媒体影响的传染病模型的研究[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2013, 34(4): 399-407 doi: 10.3879/j.issn.1000-0887.2013.04.008LIU Yuying, XIAO Yanni. An epidemic with saturated media/psychological impact[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2013, 34(4): 399-407.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3879/j.issn.1000-0887.2013.04.008 [8] CUI J, TAO X, ZHU H. An SIS infection model incorporating media coverage[J]. Rocky Mountain Journal of Mathematics, 2008, 38(5): 1323-1334. [9] D’ONOFRIO A, MANFREDI P. Information-related changes in contact patterns may trigger oscillations in the endemic prevalence of infectious diseases[J]. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 2009, 256(3): 473-478. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2008.10.005 [10] BUONOMO B, D’ONOFRIO A, LACITIGNOLA D. Globally stable endemicity for infectious diseases with information-related changes in contact patterns[J]. Applied Mathematics Letters, 2012, 25(7): 1056-1060. doi: 10.1016/j.aml.2012.03.016 [11] HUO H, YANG P, XIANG H. Stability and bifurcation for an SEIS epidemic model with the impact of media[J]. Physica A, 2018, 490: 702-720. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2017.08.139 [12] 廖书, 杨炜明. 考虑媒体播报效应的双时滞传染病模型[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2017, 38(12): 1412-1424LIAO Shu, YANG Weiming. An epidemic model with dual delays in view of media coverage[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2017, 38(12): 1412-1424.(in Chinese) [13] ALQAHTANI R T, AJBAR A. Study of dynamics of a COVID-19 model for Saudi Arabia with vaccination rate, saturated treatment function and saturated incidence rate[J]. Mathematics, 2021, 9(23): 3134. doi: 10.3390/math9233134 [14] AVILA-VALES E, PEREZ A G C. Dynamics of a time-delayed SIR epidemic model with logistic growth and saturated treatment[J]. Chaos Soliton & Fractals, 2019, 127: 55-69. [15] LI J, TENG Z, WANG G, et al. Stability and bifurcation analysis of an SIR epidemic model with logistic growth and saturated treatment[J]. Chaos Soliton & Fractals, 2017, 99: 63-71. [16] WANG W. Backward bifurcation of an epidemic model with treatment[J]. Mathematical Biosciences, 2006, 201(1/2): 58-71. [17] ZHANG X, LIU X. Backward bifurcation and global dynamics of an SIS epidemic model with general incidence rate and treatment[J]. Nonlinear Analysis: Real World Applications, 2009, 10(2): 565-575. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2007.10.011 [18] HEFFERNAN J M, SMITH R J, WAHL L M. Perspectives on the basic reproductive ratio[J]. Journal of the Royal Society Interface, 2005, 2(4): 281-293. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2005.0042 [19] CASTILLO-CHOVEZ C, SONG B J. Dynamical models of tuberculosis and their applications[J]. Mathematical Bioscience and Engineering, 2004, 1(2): 361-404. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2004.1.361 -




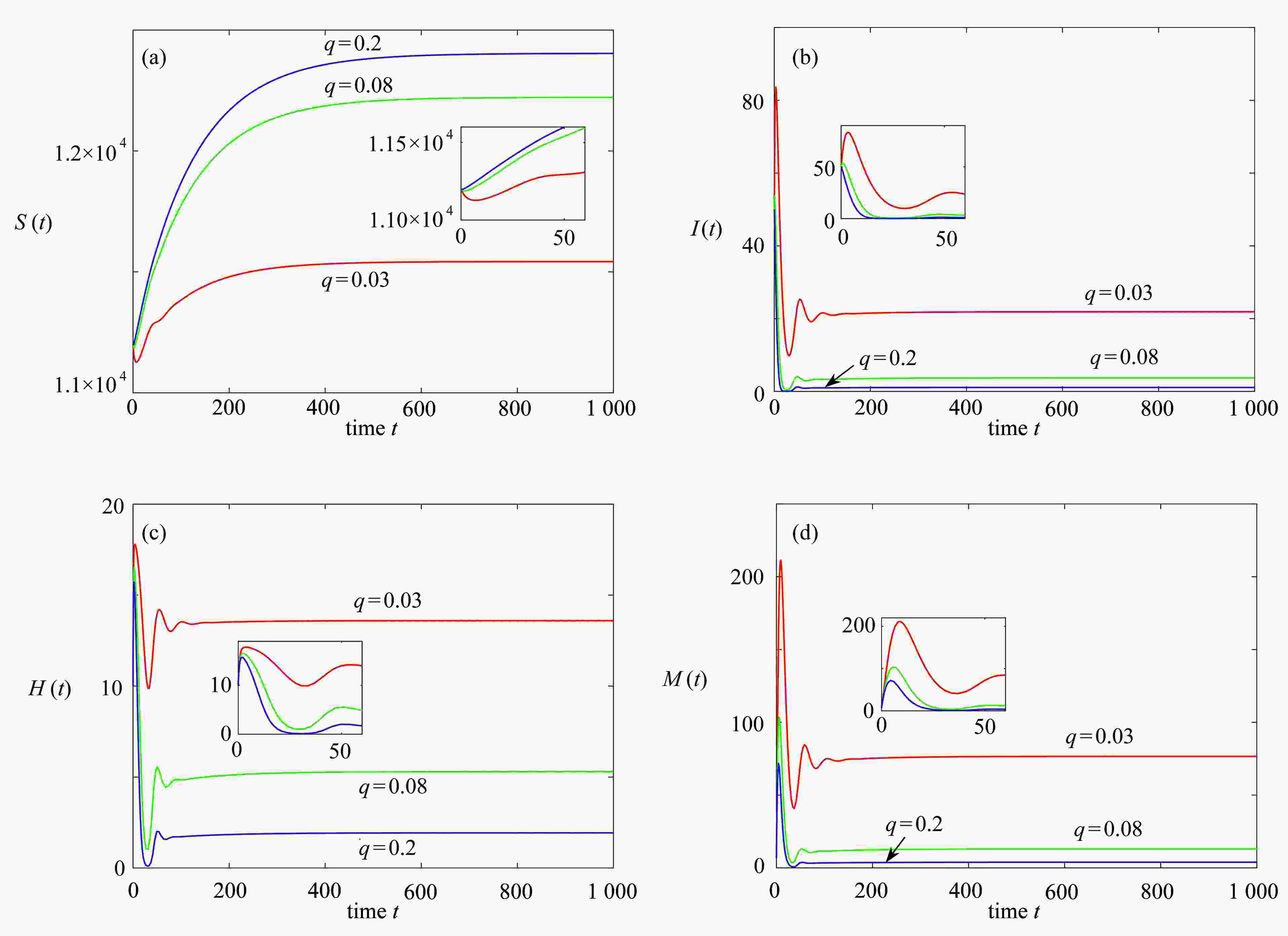


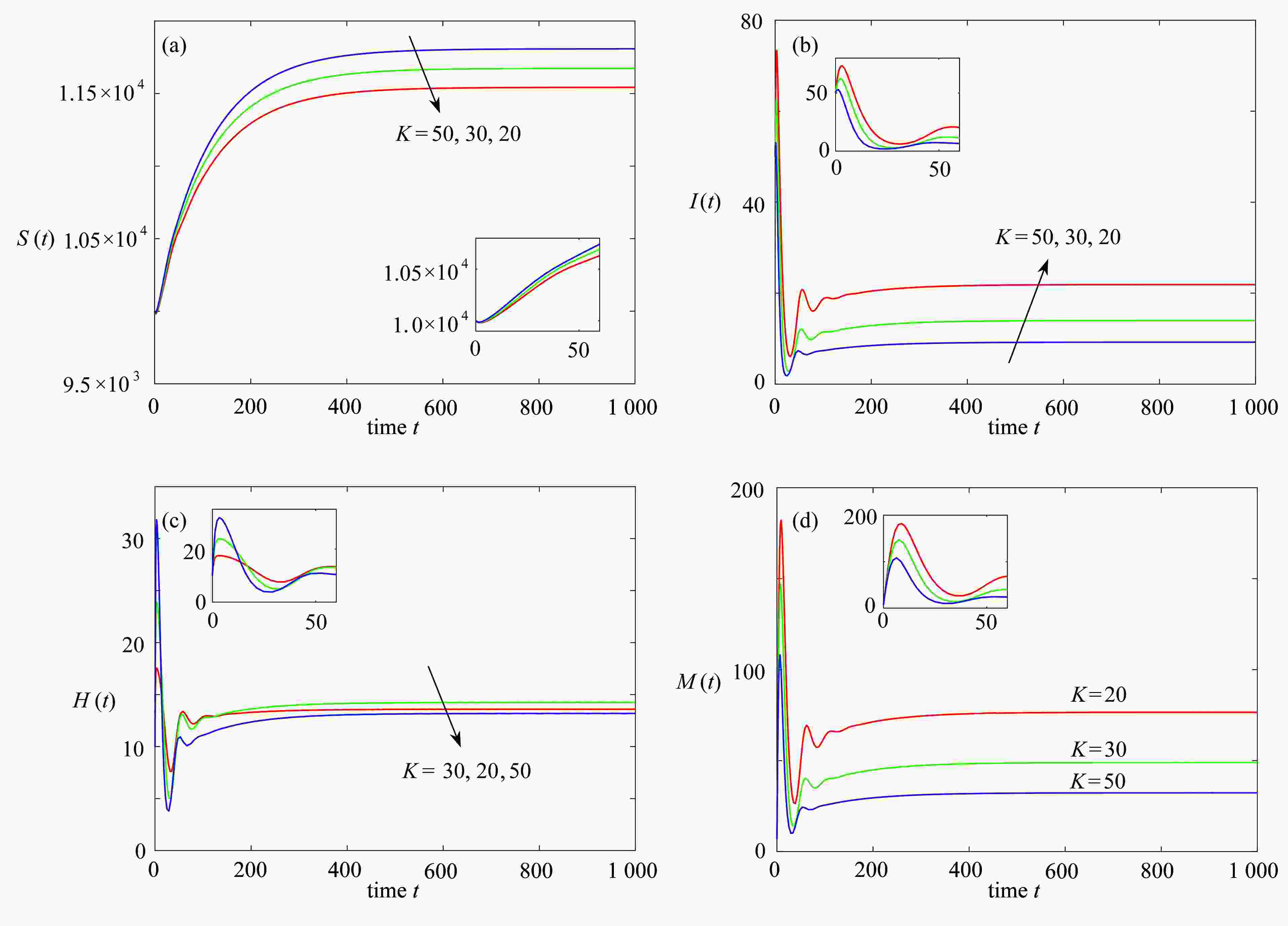
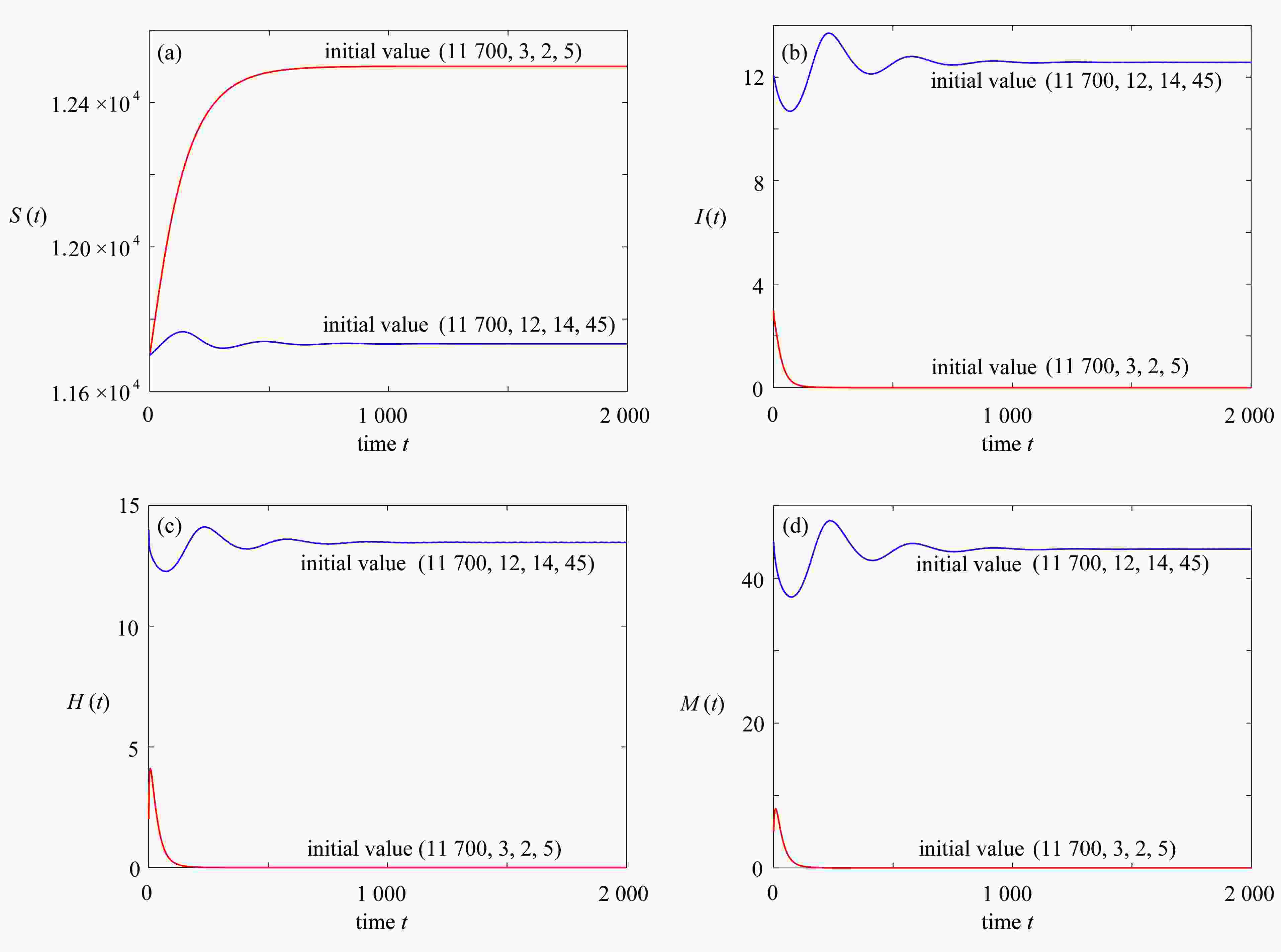
 下载:
下载:




















 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号