Buckling Analysis of Re-Entrant Honeycomb Structures Under General Macroscopic Stress States
-
摘要:
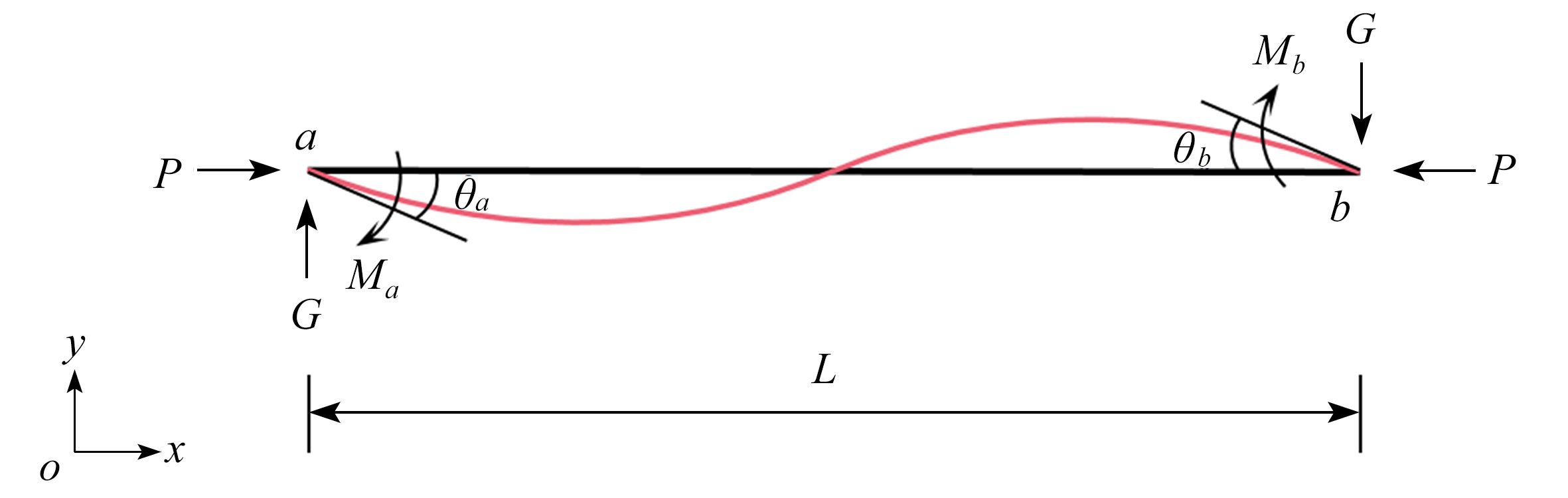
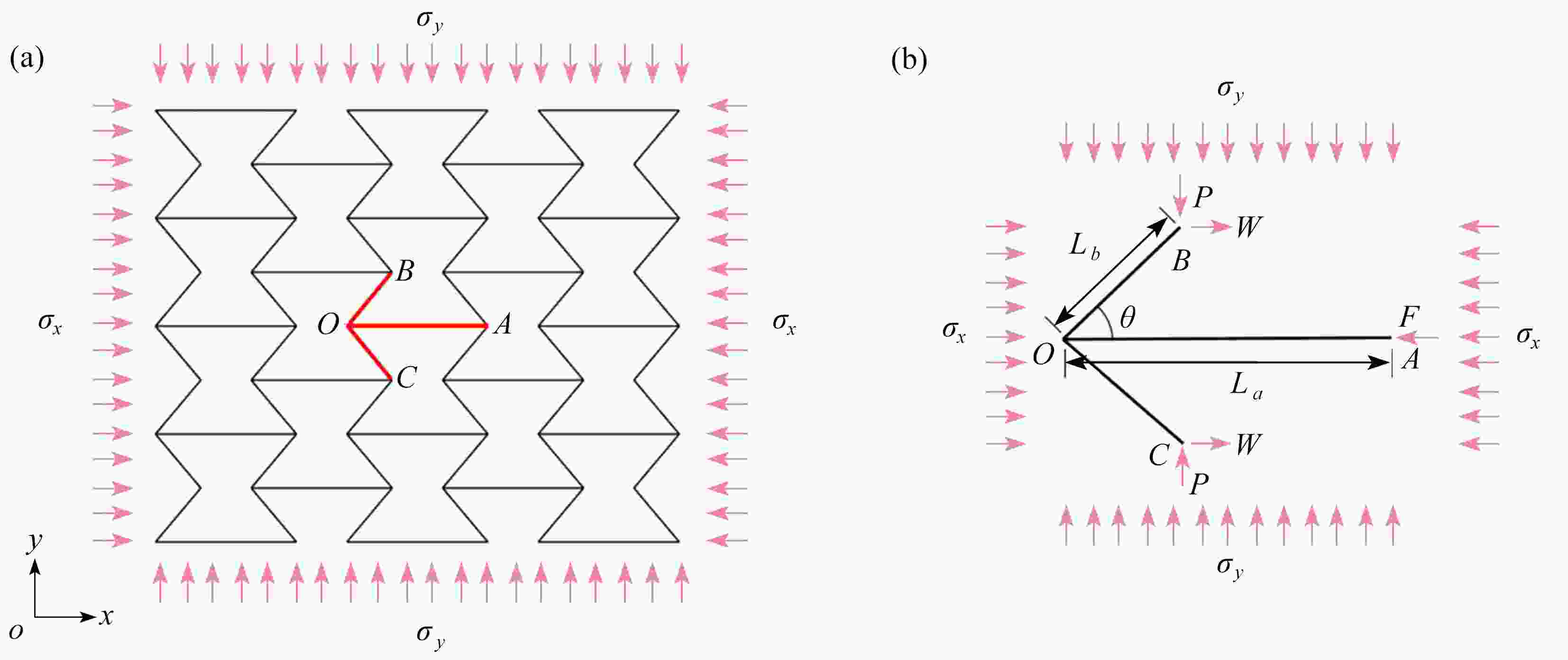
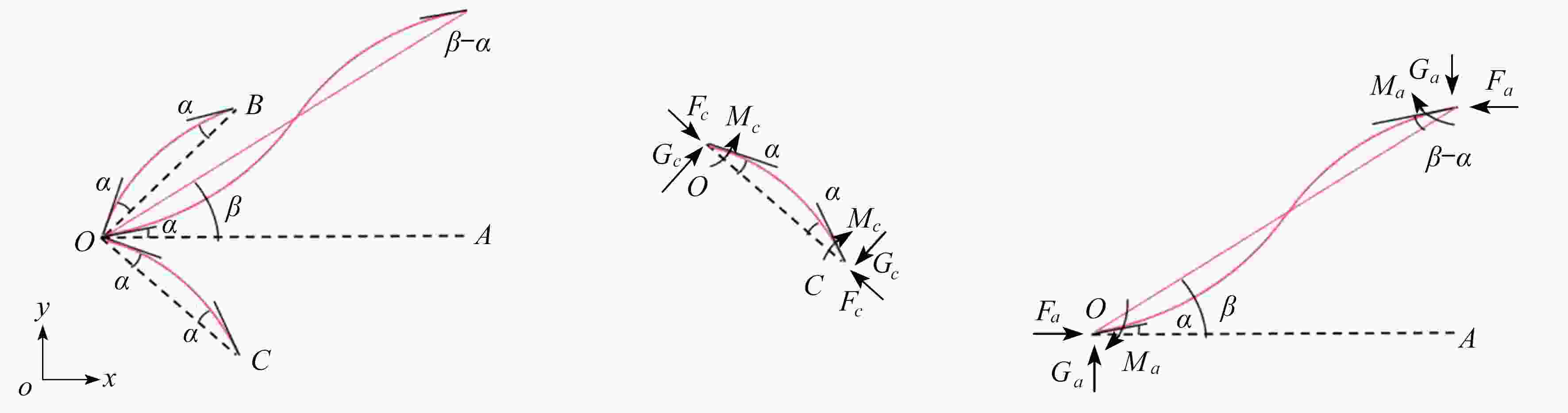
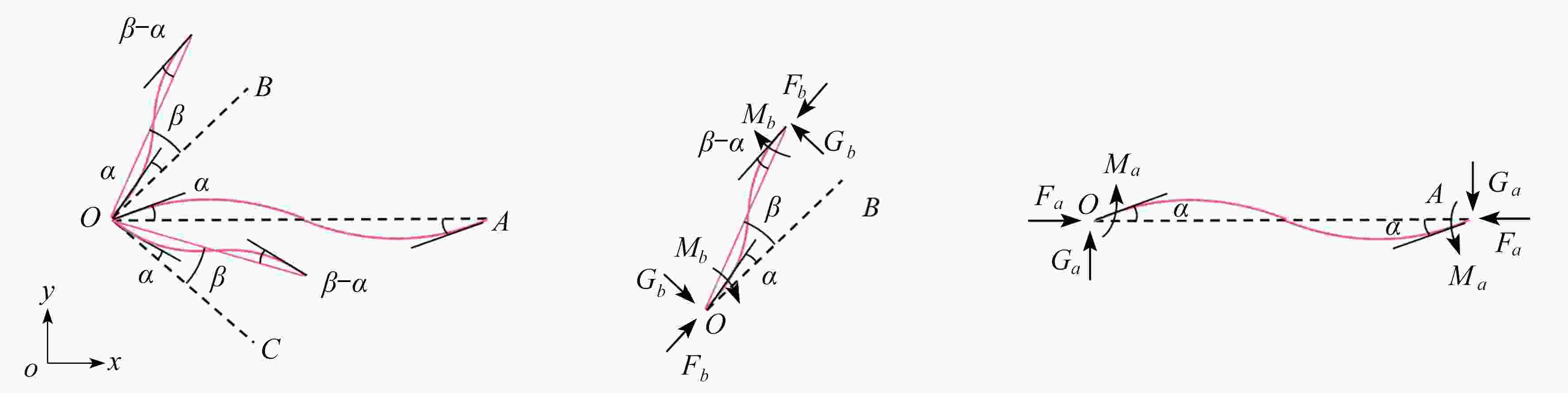
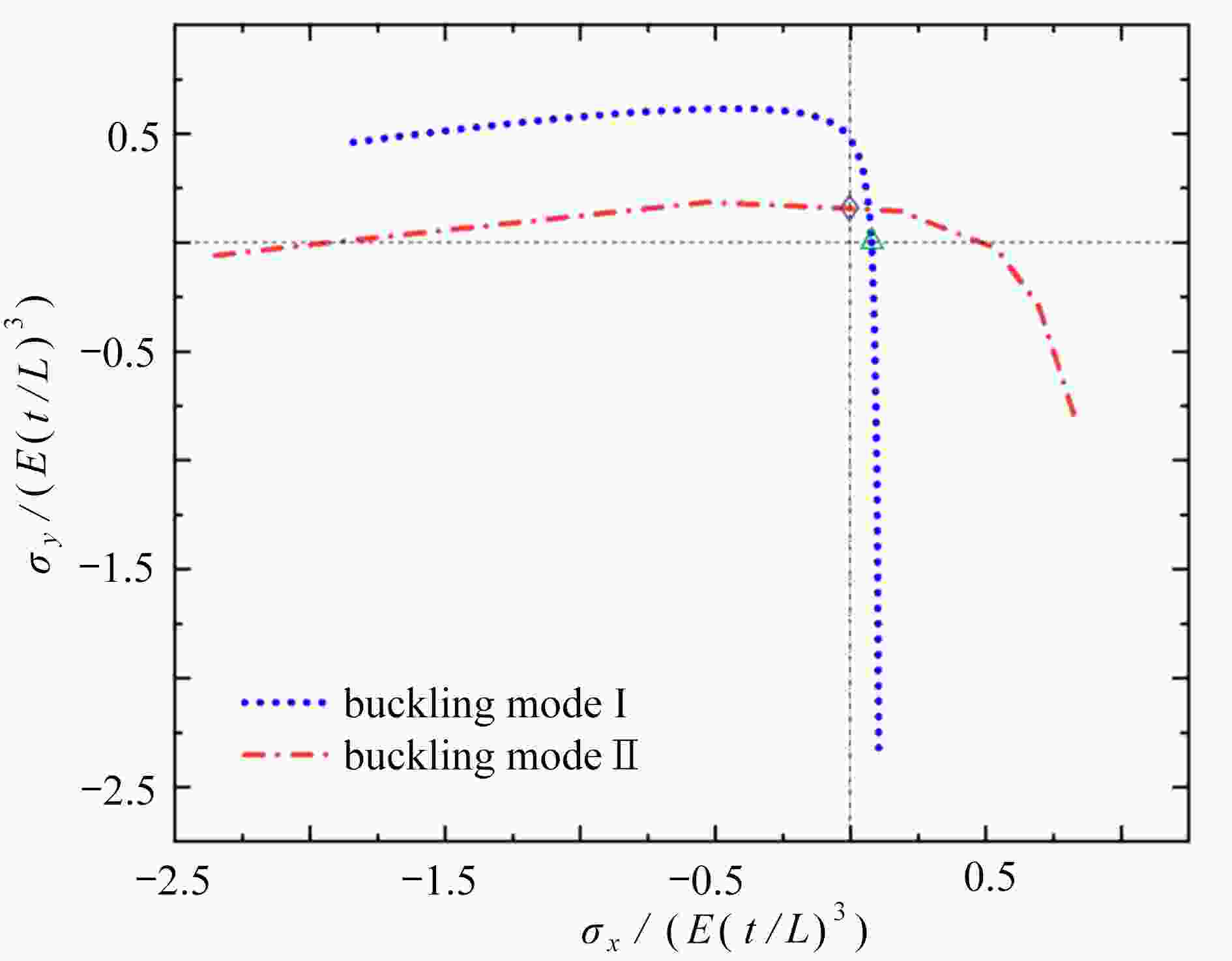
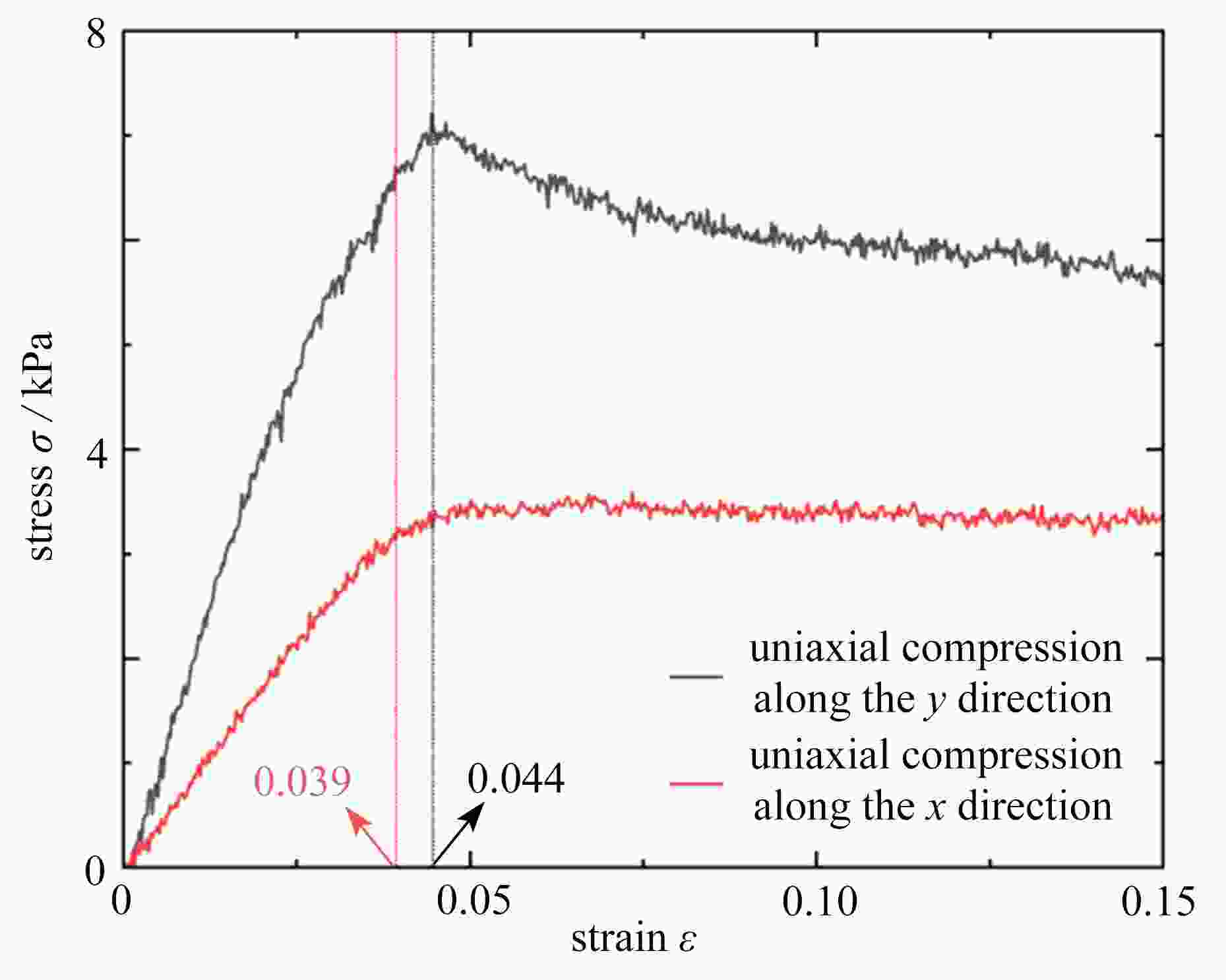
基于凹角蜂窝的负Poisson比拉胀效应,对其屈曲力学性能进行了有限元仿真分析,得出区别于传统正六边形蜂窝结构的两种屈曲模态。为了研究这两种屈曲模态的屈曲强度以及产生机理,采用梁柱理论对其进行了理论分析。根据梁-柱方程和平衡关系建立包含杆端弯矩和杆端转角的方程组,利用屈曲临界条件建立稳定方程,得到屈曲强度的解析表达式。采用增材制造技术打印凹角蜂窝试件,对其屈曲性能进行实验验证。结果表明,双轴加载条件的不同会引起屈曲模态的显著变化;区别于传统蜂窝结构,凹角蜂窝的负Poisson比拉胀效应使其在双轴受拉状态下发生屈曲失稳;双轴应力状态下的屈曲失效界面分析获得了典型的屈曲分岔现象。这项研究对凹角蜂窝因失稳而破坏以及利用凹角蜂窝失稳实现特殊力学性能的研究具有一定的指导意义。
Abstract:Based on the negative Poisson’s ratio effect of the re-entrant honeycomb, the finite element simulation of its buckling mechanical properties was carried out, and 2 buckling modes other than those of the traditional hexagonal honeycomb structures were obtained. The beam-column theory was applied to analyze the buckling strength and mechanism of the 2 buckling modes, where the equilibrium equations including the beam end bending moments and rotation angles were established. The stability equation was built through application of the buckling critical condition, and then the analytical expression of the buckling strength was obtained. The re-entrant honeycomb specimen was printed with the additive manufacturing technology, and its buckling performance was verified by experiments. The results show that, the buckling modes vary significantly under different biaxial loading conditions; the re-entrant honeycomb would buckle under biaxial tension due to the auxetic effect, being quite different from the traditional honeycomb structure; the typical buckling bifurcation phenomenon emerges in the analysis of the buckling failure surfaces under biaxial stress states. This research provides a significant guide for the study on the failure of re-entrant honeycomb structures due to instability, and the active application of this instability to achieve special mechanical properties.
-
Key words:
- re-entrant honeycomb /
- buckling mode /
- negative Poisson’s ratio
-
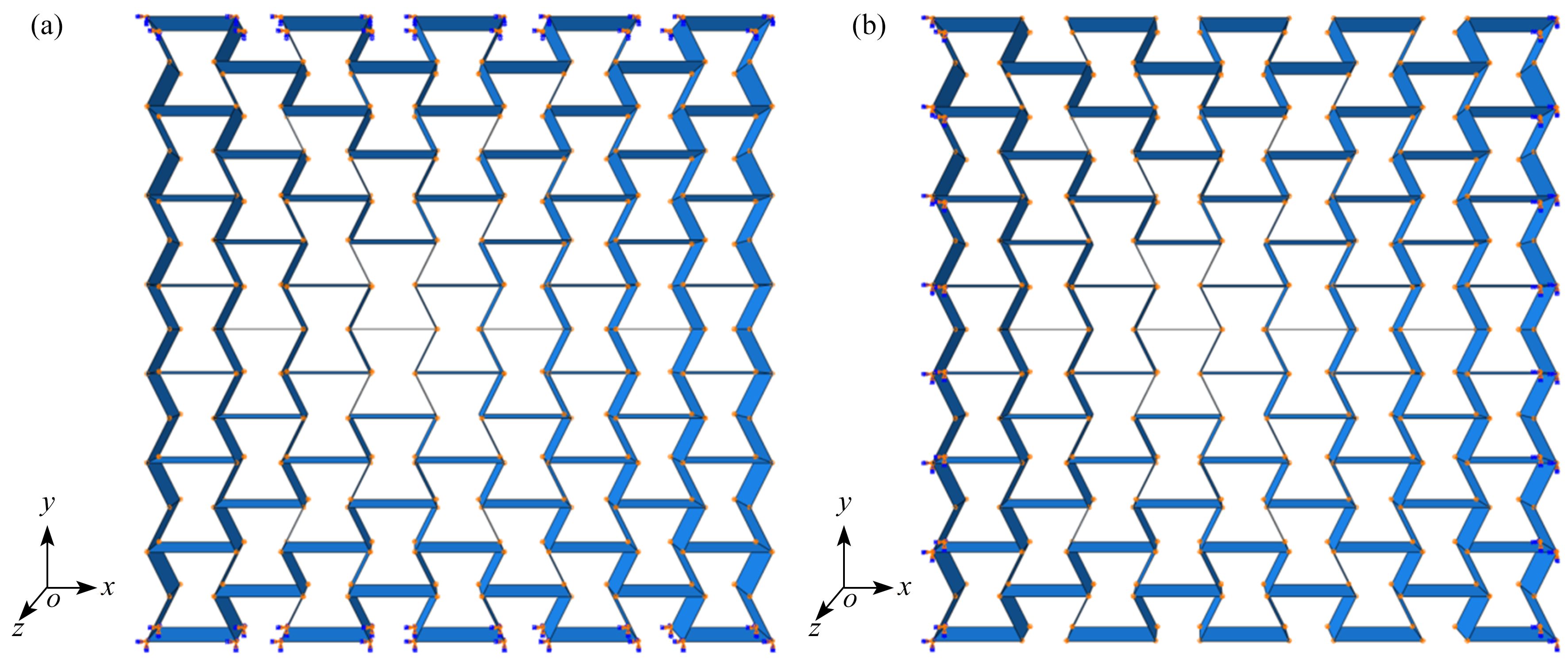
图 1 凹角蜂窝的有限元模型和边界条件:(a) 沿着
$ x $ 方向准静态压缩的边界条件;(b) 沿着$ y $ 方向准静态压缩的边界条件注 为了解释图中的颜色,读者可以参考本文的电子网页版本,后同。
Figure 1. The finite element model and boundary conditions for the re-entrant honeycomb: (a) boundary conditions for the quasi-static compression along the x direction; (b) boundary conditions for the quasi-static compression along the y direction
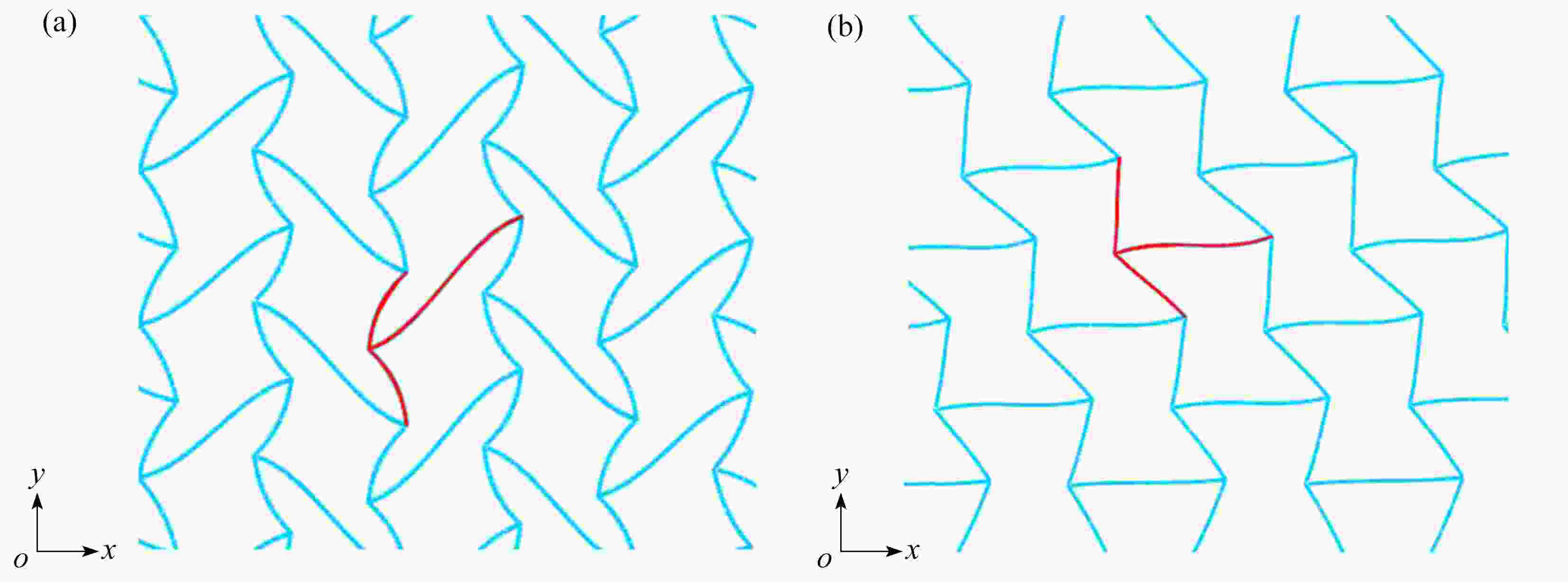
图 4 凹角蜂窝的第一阶模态:(a) 沿着
$ x $ 方向准静态压缩得到屈曲模态Ⅰ;(b) 沿着$ y $ 方向准静态压缩得到屈曲模态ⅡFigure 4. The 1st buckling modes of the re-entrant honeycomb: (a) buckling mode Ⅰ obtained under quasi-static compression along the
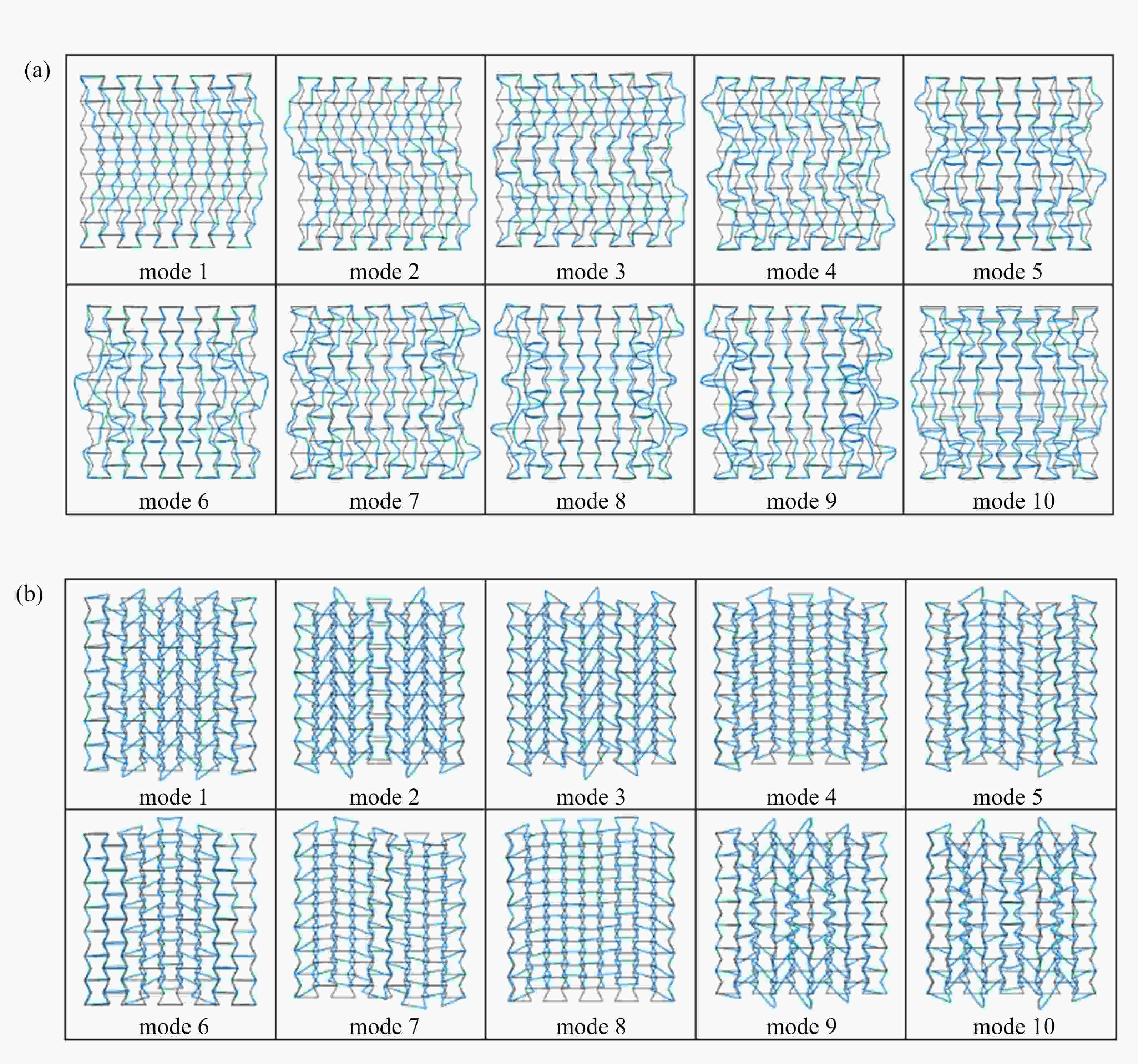
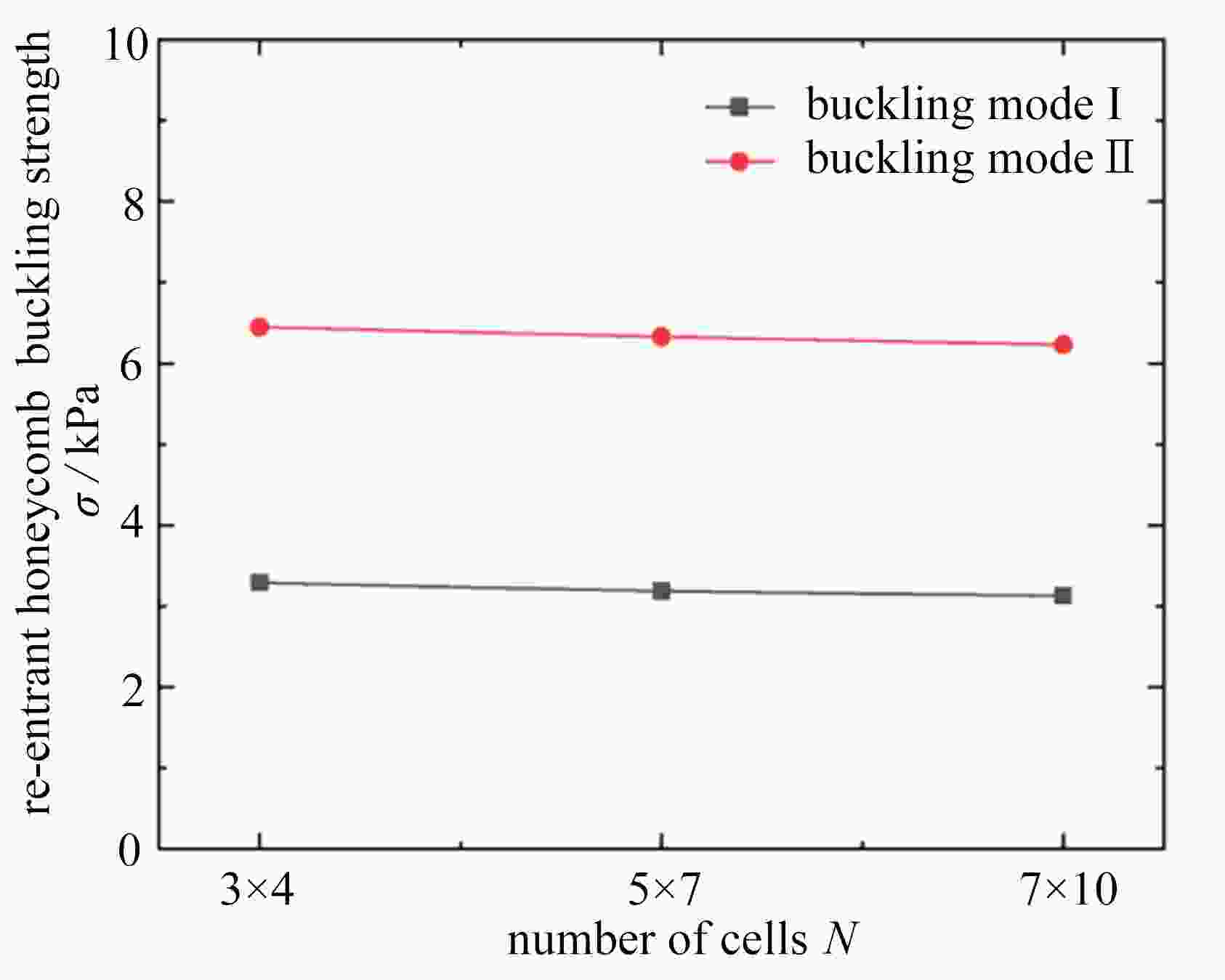
$ x $ direction; (b) buckling mode Ⅱ obtained under quasi-static compression along the$ y $ direction图 5 不同单胞数量的凹角蜂窝的屈曲模态:(a) 3×4构型沿着y方向单轴压缩;(b) 3×4构型沿着x方向单轴压缩;(c) 7×10构型沿着y方向单轴压缩;(d) 7×10构型沿着x方向单轴压缩
Figure 5. Buckling modes of the re-entrant honeycomb with different numbers of unit cells: (a) the 3×4 configuration under uniaxial compression in the y direction; (b) the 3×4 configuration under uniaxial compression in the x direction; (c) the 7×10 configuration under uniaxial compression in the y direction; (d) the 7×10 configuration under uniaxial compression in the x direction
表 1 实验、数值和理论研究得到的凹角蜂窝屈曲强度对比
Table 1. Comparison of buckling strengths of re-entrant honeycombs obtained from experimental, numerical and theoretical studies
experiment simulation theory error between
simulation and experimenterror between
theory and experimentuniaxial compression along
the x direction (mode I)3.114 8 kPa 3.162 8 kPa 2.839 5 kPa 1.51% 8.83% uniaxial compression along
the y direction (mode Ⅱ)6.279 5 kPa 6.326 2 kPa 5.903 2 kPa 0.74% 5.99% -
[1] QUAN C, HAN B, HOU Z, et al. 3D printed continuous fiber reinforced composite auxetic honeycomb structures[J]. Composites (Part B) : Engineering, 2020, 187: 107858. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.107858 [2] SON M A, CHAE K W, KIM J S, et al. Structural origin of negative thermal expansion of cordierite honeycomb ceramics and crystal phase evolution with sintering temperature[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2019, 39(7): 2484-2492. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2019.02.017 [3] TAO R, JI L, LI Y, et al. 4D printed origami metamaterials with tunable compression twist behavior and stress-strain curves[J]. Composites (Part B) : Engineering, 2020, 201: 108344. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.108344 [4] GAO Q, LIAO W H, WANG L. On the low-velocity impact responses of auxetic double arrowed honeycomb[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2020, 98: 105698. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2020.105698 [5] QI C, JIANG F, YU C, et al. In-plane crushing response of tetra-chiral honeycombs[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2019, 130: 247-265. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2019.04.019 [6] CHEN Z, LIU L, GAO S, et al. Dynamic response of sandwich beam with star-shaped reentrant honeycomb core subjected to local impulsive loading[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2021, 161: 107420. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2020.107420 [7] 贠昊, 邓子辰, 朱志韦. 弹性波在星形节点周期结构蜂窝材料中的传播特性研究[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2015, 36(8): 814-820 doi: 10.3879/j.issn.1000-0887.2015.08.003YUN Hao, DENG Zichen, ZHU Zhiwei. Bandgap properties of periodic 4-point star-shaped honeycomb materials with negative Poisson’s ratios[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2015, 36(8): 814-820.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3879/j.issn.1000-0887.2015.08.003 [8] PAPKA S D, KYRIAKIDES S. In-plane compressive response and crushing of honeycomb[J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 1994, 42(10): 1499-1532. doi: 10.1016/0022-5096(94)90085-X [9] AJDARI A, NAYEB-HASHEMI H, VAZIRI A. Dynamic crushing and energy absorption of regular, irregular and functionally graded cellular structures[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2011, 48(3/4): 506-516. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2010.10.018 [10] LIU Y, ZHANG X C. The influence of cell micro-topology on the in-plane dynamic crushing of honeycombs[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2009, 36(1): 98-109. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2008.03.001 [11] YUAN C, MU X, DUNN C K, et al. Thermomechanically triggered two-stage pattern switching of 2D lattices for adaptive structures[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(18): 1705727. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201705727 [12] PAPAKOSTAS A, POTTS A, BAGNALL D M, et al. Optical manifestations of planar chirality[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2003, 90(10): 107404. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.90.107404 [13] SPADONI A, RUZZENE M, GONELLA S, et al. Phononic properties of hexagonal chiral lattices[J]. Wave Motion, 2009, 46(7): 435-450. doi: 10.1016/j.wavemoti.2009.04.002 [14] HOU X H, DENG Z C, ZHANG K, et al. Dynamic crushing strength analysis of auxetic honeycombs[J]. Acta Mechanica Solida Sinica, 2016, 29: 490-501. doi: 10.1016/S0894-9166(16)30267-1 [15] BERTOLDI K, REIS P M, WILLSHAW S, et al. Negative Poisson’s ratio behavior induced by an elastic instability[J]. Advanced Materials, 2010, 22(3): 361-366. doi: 10.1002/adma.200901956 [16] YANG D, MOSADEGH B, AINLA A, et al. Buckling of elastomeric beams enables actuation of soft machines[J]. Advanced Materials, 2015, 27(41): 6323-6327. doi: 10.1002/adma.201503188 [17] JIMÉNEZ F L, TRIANTAFYLLIDIS N. Buckling of rectangular and hexagonal honeycomb under combined axial compression and transverse shear[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2013, 50(24): 3934-3946. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2013.08.001 [18] COMBESCURE C, ELLIOTT R, TRIANTAFYLLIDIS N. Deformation patterns and their stability in finitely strained circular cell honeycombs[J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2020, 142: 103976. doi: 10.1016/j.jmps.2020.103976 [19] 梁观坡, 傅禹鑫, 娄本亮, 等. 负压激励下含椭圆孔高弹体的屈曲分析[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2021, 42(12): 1221-1228LIANG Guanpo, FU Yuxin, LOU Benliang, et al. Buckling behaviors of elastomers with periodic elliptical holes under negative pressure activation[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2021, 42(12): 1221-1228.(in Chinese) [20] PENG X, ZHONG Y, SHI J, et al. Global buckling analysis of composite honeycomb sandwich plate with negative Poisson’s ratio using variational asymptotic equivalent model[J]. Composite Structures, 2021, 264(5): 113721. [21] GAVAZZONI M, FOLETTI S, PASINI D. Cyclic response of 3D printed metamaterials with soft cellular architecture: the interplay between as-built defects, material and geometric non-linearity[J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2022, 158: 104688. doi: 10.1016/j.jmps.2021.104688 [22] 赵艳萍, 李琳, 金明. 柔性约束下压杆的一些稳定和不稳定的临界状态[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2017, 38(8): 877-887ZHAO Yanping, LI Lin, JIN Ming. Some stable and unstable critical states of a compression rod with a flexible support[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2017, 38(8): 877-887.(in Chinese) [23] TIMOSHENKO S P, GERE J M. Theory of Elastic Stability[M]. 2nd ed. Dover Publications, 2009. -







 下载:
下载:















 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号