Prediction of Gas-Liquid Pressurization Performances of Multistage Multiphase Pumps Based on Similarity Laws and Neural Networks
-
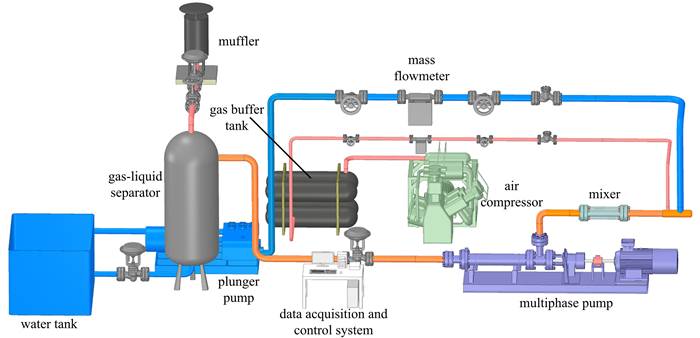
摘要: 准确预测多相混输泵的气液增压性能对油气生产的经济性和安全性至关重要.当前气液增压预测模型与方法存在参数范围窄、增压级数低的局限.该文搭建了工业参数级气液混输增压实验平台,实验获得了25级离心式混输泵的气液增压特性.提出了适用于高增压级数、变转速条件的混输泵气液增压性能预测方法.首先,构建了定转速、低增压级数混输泵气液增压人工神经网络;其次,采用相似规律,将变转速条件气液增压转换至设计转速条件;最后,基于等温压缩假设进行级间流动参数更新和高增压级数混输泵性能预测.不同级数(3~25级)和转速条件(2 500~3 500 r·min-1)混输泵气液增压预测的相对误差低于15%.该方法能够应用于其他类型多相混输泵的增压预测,为指导油气工业现场确定混输泵增压级数和生产评估提供有效方法.Abstract: It is very important to accurately predict the gas-liquid pressurization performance of multiphase pumps for the economy and safety of oil-gas production. Existent prediction models and methods are limited by narrow parameter ranges and low pump stages. A gas-liquid experimental platform at the industrial level was built, and the gas-liquid pressurization performances of a 25-stage centrifugal multiphase pump were obtained. A prediction method for gas-liquid pressurization performances was proposed for multiphase pumps with high stages at variable rotational speeds. Firstly, the artificial neural network of gas-liquid boosting pressure in the pump with low stages at a constant rotational speed, was constructed. Then, the boosting pressures at variable rotational speeds were converted to the designed condition by the 2-phase similarity law. Finally, based on the isothermal compression hypothesis, the inter-stage flow parameters were updated and the boosting pressures in pumps with high stages were acquired. The relative errors of prediction results of gas-liquid pressurization were less than 15% in pumps with different stage numbers (3~25 stages) and rotational speeds (2 500~3 500 r·min-1). The proposed method can be applied to other types of multiphase pumps, to determine the stage numbers of multiphase pumps and make production evaluation in oil-gas industry.
-
Key words:
- multiphase pump /
- gas-liquid pressurization /
- performance prediction /
- similarity law /
- neural network
edited-byedited-by1) (我刊编委郭烈锦来稿) -
表 1 实验参数范围
Table 1. Ranges of experimental parameters
parameter range liquid mass flow rate mw/(kg·min-1) 133.3~433 gas mass flow rate ma/(kg·min-1) 0~5.3 inlet gas volume fraction λ/% 0~40 inlet temperature Tm/℃ 15~30 inlet pressure Pin/MPa 0.5 rotational speed n/(r·min-1) 2 500, 3 000, 3 500 表 2 不同转速和增压级数混输泵气液增压平均预测相对误差
Table 2. The average relative errors for predicting gas-liquid pressurization performances of multiphase pumps with different stages under variable rotational speeds
n/(r·min-1) 3 stages 9 stages 15 stages 21 stages 3 500 2.7% 6.2% 7.6% 8.5% 3 000 4.6% 7.5% 8.9% 12.5% 2 500 4.5% 5.3% 8.2% 13.4% -
[1] TAKACS G. Electrical Submersible Pumps Manual: Design, Operations and Maintenance[M]. MA, USA: Gulf Professional Publishing, 2017. [2] CORTES B, ARAUJO L R, PENIDO D R R. Electrical submersible pump system model to assist oil lifting studies[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2019, 174: 1279-1289. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2018.11.055 [3] 薛敦松. 油气水多相混输泵与计量技术[M]. 北京: 中国石化出版社, 2017.XUE Dunsong. Oil-Gas-Water Multi-Phase Pump and Metering Technology[M]. Beijing: China Petrochemical Press, 2017. (in Chinese) [4] AYDIN H, MEREY S. Design of electrical submersible pump system in geothermal wells: a case study from West Anatolia, Turkey[J]. Energy, 2021, 230: 120891. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2021.120891 [5] 贾承造, 庞雄奇, 姜福杰. 中国油气资源研究现状与发展方向[J]. 石油科学通报, 2016, 1(1): 2-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYKE201601002.htmJIA Chengzao, PANG Xiongqi, JIANG Fujie. Research status and development directions of hydrocarbon resources in China[J]. Petroleum Science Bulletin, 2016, 1(1): 2-23. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYKE201601002.htm [6] 刘超, 刘传岩, 刘健, 等. 水下油气生产系统概述及其发展现状[J]. 石油工程建设, 2021, 47(6): 29-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYGJ202106007.htmLIU Chao, LIU Chuanyan, LIU Jian, et al. Overview and development status of subsea oil and gas production system[J]. Petroleum Engineering Construction, 2021, 47(6): 29-34. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYGJ202106007.htm [7] ZHU J, ZHANG H Q. A review of experiments and modeling of gas-liquid flow in electrical submersible pumps[J]. Energies, 2018, 11(1): 180. doi: 10.3390/en11010180 [8] OFUCHI E, CUBAS J, STEL H, et al. A new model to predict the head degradation of centrifugal pumps handling highly viscous flows[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 187: 106737. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2019.106737 [9] PERISSINOTTO R M, VERDE W M, BIAZUSSI J L, et al. Flow visualization in centrifugal pumps: a review of methods and experimental studies[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2021, 203: 108582. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2021.108582 [10] HE D, ZHAO L, CHANG Z, et al. On the performance of a centrifugal pump under bubble inflow: effect of gas-liquid distribution in the impeller[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2021, 203: 108587. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2021.108587 [11] CUBAS J M, STEL H, OFUCHI E M, et al. Visualization of two-phase gas-liquid flow in a radial centrifugal pump with a vaned diffuser[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 187: 106848. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2019.106848 [12] TURPIN J L, LEA J F, BEARDEN J L. Gas-liquid flow through centrifugal pumps-correlation of data[C]//Proceedings of the 3rd International Pump Symposium. Turbomachinery Laboratories, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Texas A&M University, 1986: 313-320. [13] DURAN J, PRADO M G. ESP stages air-water two-phase performance: modeling and experimental data[C]//2004 SPE ESP Workshop. Houston, TX, USA, 2004. [14] FURUYA O. An analytical model for prediction of two-phase (noncondensable) flow pump performance[J]. Engineering, 1985, 107(1): 139-147. [15] ZHU H, ZHU J, ZHANG H Q. Mechanistic modeling of gas effect on multi-stage electrical submersible pump (ESP) performance with experimental validation[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2022, 252: 117288. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2021.117288 [16] MATSUSHITA N, FURUKAWA A, WATANABE S, et al. Study on design of air-water two-phase flow centrifugal pump based on similarity law[J]. International Journal of Fluid Machinery and Systems, 2009, 2(2): 127-35. doi: 10.5293/IJFMS.2009.2.2.127 [17] 司乔瑞, 崔强磊, 袁寿其, 等. 气液两相条件下进口含气率对离心泵相似定律的影响[J]. 农业机械学报, 2018, 49(2): 107-112. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NYJX201802014.htmSI Qiaorui, CUI Qianglei, YUAN Shouqi, et al. Influence of inlet gas volume fraction on similarity law in centrifugal pumps under gas-liquid two-phase condition[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2018, 49(2): 107-112. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NYJX201802014.htm [18] PATIL A, MORRISON G. Affinity law modified to predict the pump head performance for different viscosities using the Morrison number[J]. ASME Journal of Fluids Engineering, 2019, 141(2): 021203. doi: 10.1115/1.4041066 [19] 周济民, 张海晨, 王沫然. 基于物理经验模型约束的机器学习方法在页岩油产量预测中的应用[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2021, 42(9): 881-890. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.420015ZHOU Jimin, ZHANG Haichen, WANG Moran. Machine learning with physical empirical model constraints for prediction of shale oil production[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2021, 42(9): 881-890. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.420015 [20] 王沐晨, 李立州, 张珺, 等. 基于卷积神经网络气动力降阶模型的翼型优化方法[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2022, 43(1): 77-83. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.420137WANG Muchen, LI Lizhou, ZHANG Jun, et al. An airfoil optimization method based on the convolutional neural network aerodynamic reduced order model[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2022, 43(1): 77-83. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.420137 [21] GÖLCV M. Neural network analysis of head-flow curves in deep well pumps[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2006, 47(7/8): 992-1003. [22] HUANG R, ZHANG Z, ZHANG W, et al. Energy performance prediction of the centrifugal pumps by using a hybrid neural network[J]. Energy, 2020, 213: 119005. [23] CHANG L, XU Q, YANG C, et al. Experimental study of gas-liquid pressurization performance and critical gas volume fractions of a multiphase pump[J]. ASME Journal of Fluids Engineering, 2022, 144(5): 051404. [24] MAJDISOVA Z, SKALA V. Radial basis function approximations: comparison and applications[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2017, 51: 728-43. [25] 关醒凡. 现代泵理论与设计[M]. 北京: 中国宇航出版社, 2011.GUAN Xingfan. Modern Pump Theory and Design[M]. Beijing: China Astronautic Publishing House, 2011. (in Chinese) [26] STEL H, OFUCHI E M, ALVES R F, et al. Experimental analysis of gas-liquid flows in a centrifugal rotor[J]. ASME Journal of Fluids Engineering, 2020, 142(3): 031101. [27] VERDE W M, BIAZUSSI J L, SASSIM N A, et al. Experimental study of gas-liquid two-phase flow patterns within centrifugal pumps impellers[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2017, 85: 37-51. [28] MATSUSHITA N, WATANABE S, OKUMA K, et al. Similarity law of air-water two-phase flow performance of centrifugal pump[C]//Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting. 2007: 915-920. -





 下载:
下载:









 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号