Study on Impact Resistance of Shape Memory Alloy Honeycomb Structures
-
摘要: 形状记忆合金(shape memory alloy,SMA)在外载荷作用下可发生伪塑性变形,利用这一特性设计了可重复使用的冲击吸能结构. 基于经典的形状记忆合金本构模型,建立了薄壁结构有限元模型,分析了不同类型蜂窝结构在不同冲击速度下的变形模式和能量吸收等动力特性,得到了具有最优能量吸收性能的形状记忆合金结构. 此外,对比形状记忆合金和传统金属铝蜂窝结构的吸能性能发现,在不同速度冲击下,不同结构形式的形状记忆合金蜂窝同铝蜂窝在能量吸收方面具有较大差异,最优结构发生改变. 该文成果可为形状记忆合金抗冲击蜂窝结构的选型和设计提供参考.Abstract: The shape memory alloy (SMA) can deform pseudo-plastically under external load, based on which a reusable impact energy absorption structure was designed. According to the classical SMA constitutive model, the finite element model for thin-wall structures was established, and the dynamic characteristics such as deformation modes and energy absorption of different forms of honeycomb structures under different impacting velocities, were analyzed, and the optimal energy absorption performance of the SMA structures was obtained. In addition, through comparison of the energy absorption performance of the SMA honeycomb with that of the aluminum honeycomb, the energy absorption of the SMA honeycomb with different structure configurations was different from that of the aluminum honeycomb under different-velocity impacts, with the optimal structure changes. The work provides a reference for the selection and design of the SMA honeycomb structures.
-
Key words:
- shape memory alloy /
- honeycomb structure /
- ABAQUS /
- deformation mode /
- energy absorption
-
0. 引言
蜂窝结构是一种广泛应用于能量吸收和结构防护的多孔结构,具有密度小、比模量大、比强度大、压缩变形能力大且变形可控等优点. 蜂窝结构在受到撞击时,其本身能够发生规则的塑性变形,吸收运动物体的动能,从而实现保护人员或设备的功能. 相比于传统结构,蜂窝结构仅需通过改变内部胞体单元的结构即可改变其性能. 随着研究的不断深入,众多学者提出了诸多新型结构,如Lakes[1]提出的手性蜂窝结构,Theocaris等[2]提出的星形胞元结构,Qi等[3]提出的双圆单胞蜂窝等结构,进一步提高了蜂窝结构的吸能特性,使蜂窝结构在车辆碰撞保护、航空探测器着陆缓冲等相关领域中具有广阔的应用前景[4-7]. 然而,这些结构均基于铝等可恢复应变很小的传统金属材料,由这些传统材料构成的蜂窝结构在承受荷载发生变形后不能表现出令人满意的形状恢复性,只能够一次性使用,造成资源的巨大浪费.
在金属材料中存在着一类可恢复应变较大的材料——形状记忆合金(SMA). 形状记忆合金具有独特的力学与物理特性,是最早被用于智能结构的一类功能金属材料. 与普通金属材料相比,它能够在受外界温度刺激时改变自身内部晶体状态,从而呈现出优秀的形状恢复能力. 形状记忆合金作为一种集感知与驱动于一身的功能材料,以其独特的形状记忆效应、超弹性效应、高阻尼特性以及良好的生物兼容性等优异特性被广泛应用于航空航天、生物医疗、桥梁工程以及自检测/修复结构等方面. 随着制造技术的发展,在Shaw等[8]的研究中,使用新型焊接技术成功制造出了形状记忆合金蜂窝,这种将形状记忆合金应用于蜂窝结构的技术,使蜂窝结构的能量吸收特性与形状记忆合金的超弹性和应变恢复特性相结合,使结构在发生变形之后仍能够恢复至有效结构,从而达到循环利用,减少浪费的目的. 目前,已有诸多学者对于形状记忆合金蜂窝的特性进行了研究:Xiong等[9]研究了形状记忆合金六边形蜂窝结构的变形模式;Hassan等[10]研究了形状记忆合金手性蜂窝结构的变形模式及可恢复性;Watkins等[11]研究了形状记忆合金六边形蜂窝结构参数的变化对于能量吸收性能的影响.
但是,目前的研究大多是仅针对单一的蜂窝结构进行分析,而对形状记忆合金应用于不同蜂窝结构中能量吸收特性的对比分析较少. 在此,本文选取5种典型蜂窝结构,使用ABAQUS显式动力学有限元仿真技术,分析了不同结构在面内冲击荷载作用下的动态力学性能,同时对比分析了形状记忆合金和金属铝应用于不同蜂窝结构时变形模式、能量吸收等动态力学性能的异同,可为形状记忆合金抗冲击蜂窝的选型和设计提供参考.
1. 模型的建立
1.1 形状记忆合金本构模型理论
本文采用Boyd-Lagoudas三维形状记忆合金本构关系模型[12],该模型以实验研究为基础,将理论模型纳入热力学框架中,利用弹性预测与相变修正的方法构建了本构模型. 该模型通过对各个形状记忆合金体积单元构造Gibbs自由能函数,并构造相变函数,从而得出形状记忆合金的相变特征方程,进而确立三维形状记忆合金本构关系模型.
对于多晶形状记忆合金材料,其特征Gibbs自由能G为
$$ \begin{aligned} & G\left(\boldsymbol{\sigma}, T, \xi, \boldsymbol{\varepsilon}^{t}\right)=-\frac{1}{2} \frac{1}{\rho} \boldsymbol{\sigma}: \boldsymbol{S}: \boldsymbol{\sigma}-\frac{1}{\rho} \boldsymbol{\sigma}:\left[\boldsymbol{\alpha}\left(T-T_{0}\right)+\boldsymbol{\varepsilon}^{t}\right]+ \\ & \quad c\left[\left(T-T_{0}\right)-T \ln \frac{T}{T_{0}}\right]-s_{0} T+u_{0}+f(\xi), \end{aligned}$$ (1) 式中σ,ξ,T,T0和εt分别表示形状记忆合金的应力张量、马氏体体积分数、温度、初始参考温度和相变应变张量,其中马氏体体积分数ξ∈[0, 1].S,ρ,α,c,s0和u0分别表示形状记忆合金材料的柔度张量、密度、热膨胀张量、等效比热、参考温度下的比熵和参考温度下的内能. 这些参数与马氏体体积分数ξ存在如下关系:
$$ \left\{\begin{array}{l} \boldsymbol{S}(\xi)=\boldsymbol{S}^{\mathrm{A}}+\xi\left(\boldsymbol{S}^{\mathrm{M}}-\boldsymbol{S}^{\mathrm{A}}\right), {\rho}(\xi)=\rho^{\mathrm{A}}+\xi\left(\rho^{\mathrm{M}}-\rho^{\mathrm{A}}\right), \boldsymbol{\alpha}(\xi)=\boldsymbol{\alpha}^{\mathrm{A}}+\xi\left(\boldsymbol{\alpha}^{\mathrm{M}}-\boldsymbol{\alpha}^{\mathrm{A}}\right), \\ C(\xi)=C^{\mathrm{A}}+\xi\left(C^{\mathrm{M}}-C^{\mathrm{A}}\right), \boldsymbol{S}_{0}(\xi)=\boldsymbol{S}_{0}^{\mathrm{A}}+\xi\left(\boldsymbol{S}_{0}^{\mathrm{M}}-\boldsymbol{S}_{0}^{\mathrm{A}}\right), u_{0}(\xi)=u_{0}^{\mathrm{A}}+\xi\left(u_{0}^{\mathrm{M}}-u_{0}^{\mathrm{A}}\right), \end{array}\right.$$ (2) 式中带有上标A和M的量表示纯相状态下的相应参数. 在式(1)中,f是相变硬化函数,其表示形状记忆合金在马氏体相与奥氏体相之间相互转变过程的应变能. 通过选择该函数不同的函数形式,可以获得不同的形状记忆合金本构模型.
总应变ε为
$$ \boldsymbol{\varepsilon}=\boldsymbol{S}: \boldsymbol{\sigma}+\boldsymbol{\alpha}\left(T-T_{0}\right)+\boldsymbol{\varepsilon}^{t} .$$ (3) 在形状记忆合金相变过程中的相变应变εt和马氏体体积分数ξ的演化方程为
$$\dot{\boldsymbol{\varepsilon}}^{\prime}==\boldsymbol{\varLambda} \dot{\xi}, $$ (4) 式中Λ称之为相变转换张量,表征相变应变演化的方向,其具体形式为
$$ \boldsymbol{\varLambda}= \begin{cases}\frac{3}{2} H \frac{\boldsymbol{\sigma}^{\prime}}{\overline{\boldsymbol{\sigma}}}, & \dot{\xi}>0, \\ H \frac{\boldsymbol{\varepsilon}^{t-r}}{\overline{\boldsymbol{\varepsilon}}^{t-r}}, & \dot{\xi}<0, \end{cases}$$ (5) 式中H为形状记忆合金相变过程中产生的最大可恢复应变,σ′, σ′和εt-r分别为偏应力张量、等效应力和马氏体逆相变开始时的应变状态.
偏应力张量为
$$ \boldsymbol{\sigma}^{\prime}=\boldsymbol{\sigma}-\frac{1}{3}(\operatorname{tr} \boldsymbol{\sigma}) \boldsymbol{I}, \overline{\boldsymbol{\sigma}}^{\prime}=\sqrt{\frac{3}{2}\left\|\boldsymbol{\sigma}^{\prime}\right\|^{2}}, \overline{\boldsymbol{\varepsilon}}^{t-r}=\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}\left\|\boldsymbol{\varepsilon}^{t-r}\right\|^{2}}.$$ (6) 定义相变驱动力π为
$$ \begin{aligned} \pi= & \boldsymbol{\sigma}: \boldsymbol{\varLambda}+\frac{1}{2} \boldsymbol{\sigma}: \Delta \boldsymbol{S}: \boldsymbol{\sigma}+\Delta \boldsymbol{\alpha}: \boldsymbol{\sigma}\left(T-T_{0}\right)- \\ & \rho \Delta c\left[\left(T-T_{0}\right)-T \ln \frac{T}{T_{0}}\right]+\rho \Delta s_{0} T-\frac{\partial f}{\partial \xi}-\rho \Delta u_{0}. \end{aligned}$$ (7) 相变函数Ф以热力学表示,其表达式为
$$ \varPhi= \begin{cases}\pi-Y, & \dot{\xi}>0, \\ -\pi-Y, & \dot{\xi}<0 .\end{cases}$$ (8) 对于Boyd-Lagoudas三维形状记忆合金本构关系模型,函数f为
$$ f(\xi)= \begin{cases}\frac{1}{2} \rho b^{\mathrm{M}} \xi^{2}+\left(\mu_{1}^{\mathrm{P}}+\mu_{2}^{\mathrm{P}}\right) \xi, & \dot{\xi}>0, \\ \frac{1}{2} \rho b^{\mathrm{A}} \xi^{2}+\left(\mu_{1}^{\mathrm{P}}-\mu_{2}^{\mathrm{P}}\right) \xi, & \dot{\xi}<0.\end{cases} $$ (9) 式中ρbM, ρbA, μ1和μ2均为与材料参数有关的常量.
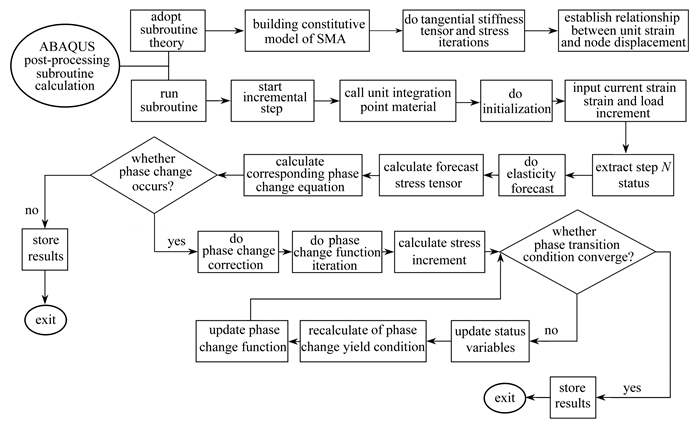
1.2 形状记忆合金子程序计算流程
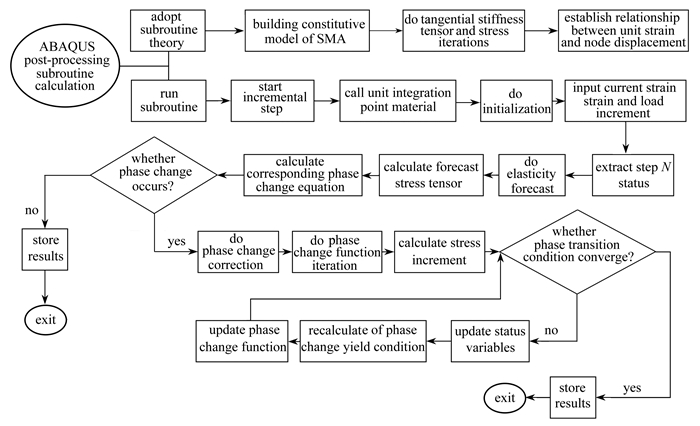
如图 1所示,ABAQUS用户子程序(user material subroutine,UMAT)通过位移增量法对形状记忆合金本构关系进行求解. 在求解时,首先对用户子程序进行初始化,即根据Boyd-Lagoudas模型进行形状记忆合金本构关系建模,输入ABAQUS增量步所需关键信息,例如单元积分点应变增量、载荷增量、时间步长等. 随后进行弹性预测,即通过切向刚度张量及相变函数,得到下一增量步的形状记忆合金的应力、状态变量等信息,并通过计算相应相变函数,对形状记忆合金弹性状态进行判定:若仍处于弹性阶段,则认为材料未发生相变,保存相应的状态变量信息;若形状记忆合金在弹性预测结果中不满足约束条件,则认为材料发生相变,需要对弹性预测结果进行修正,即相变修正阶段. 通过应力迭代计算,对其状态变量进行更新,使其满足约束条件,并保存更新后的状态变量以及应力结果.
1.3 有限元模型
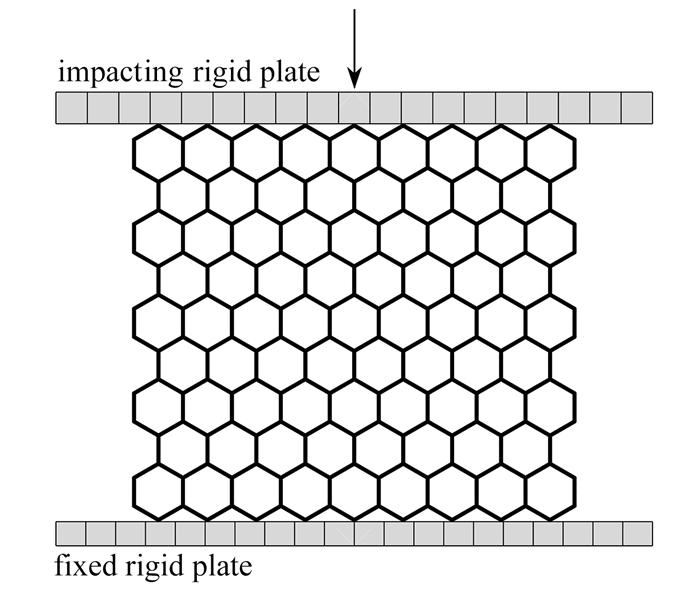
选取六边形蜂窝(hexagonal honeycomb)[13]、四边手性蜂窝(quadrilateral chiral honeycomb)[14]、六边手性蜂窝(hexagonal chiral honeycomb)[15]、星形蜂窝(star honeycomb)[16]和星形加强蜂窝(star-triangular honeycomb)[17]共5种蜂窝结构进行面内压缩特性和能量吸收特性分析,这些结构主要由长度l、壁厚d、半径r,倾角a等相关参数进行定义,表 1给出了各个蜂窝结构的几何构型与具体参数.
表 1 各个蜂窝结构的几何构型与具体参数Table 1. The geometric configuration and specific parameters of each honeycomb structure
采用ABAQUS显式动力学对蜂窝结构面内冲击特性进行数值分析. 模型基体材料为形状记忆合金,其相关参数如表 2所示. 各蜂窝模型在两个方向上均选取9个胞体单元,厚度定义为10 mm,为了增强有限元分析的收敛性与稳定性,模型选用4节点四边形有限薄膜应变线性缩减积分壳单元(S4R),沿厚度方向定义5个积分点. 如图 2所示,模型放置在上、下2个刚性板中间,模型与刚性板之间采用通用接触算法,接触属性为硬接触(hard contact),摩擦因数取为0.2[18]. 计算过程中将下刚性板固定,上刚性板以一初速度向下冲击蜂窝模型,选取10 m/s与100 m/s的冲击速度, 冲击长度为整个模型高度的75%. 计算中限制整个蜂窝模型所有节点的面外位移,以保证平面应变状态.
表 2 形状记忆合金材料参数Table 2. Material parameters of SMAmaterial parameter value Austenite elastic stiffness EA/GPa 70 Martensite elastic stiffness EM/GPa 30 Poisson’s ratio (equal for both phases) υ 0.33 thermal expansion coefficient for Austenite αA/K-1 2.2×10-5 thermal expansion coefficient for Martensite αM/K-1 2.2×10-5 Martensitic start temperature M0s/K 291 Martensitic finish temperature M0f/K 271 Austenitic start temperature A0s/K 295 Austenitic finish temperature A0f/K 315 maximum transformation strain H 0.05 stress influence coefficient for Austenite ρΔsA/(MPa·K-1) -0.35 stress influence coefficient for Martensite ρΔsM/(MPa·K-1) -0.35 此外,由于本文仅对形状记忆合金模型受冲击阶段进行有限元模拟分析,该过程主要与形状记忆合金的超弹性与伪塑性有关,故本文首先使用形状记忆合金子程序对该形状记忆合金材料进行有限元分析得到其应力-应变曲线,再使用超弹性本构模型进行拟合并进行相关模拟,从而保证在各个冲击速度下有限元模型的收敛性与稳定性. 同时,为了与传统材料构成的蜂窝结构的冲击力学性能进行比较,选取金属铝进行有限元分析,在研究中,将其假定为理想弹塑性材料[19],材料参数如下:弹性模量Ea=69 GPa,屈服应力σys=76 MPa,密度ρs=2 700 kg/m3,Poisson比υs=0.3,其余设置和形状记忆合金蜂窝相同.
1.4 模型验证
为确保有限元分析的收敛性与稳定性,本文对模型进行多种单元尺寸的网格划分,进行对比分析. 如表 3所示,分别列出了单元数为5 000,10 000,20 000,40 000时,模型在相同条件冲击下的变形模式图. 在模型的单元数量为5 000时,变形模式与其余三种数量网格存在着显著不同. 当模型单元数量达到10 000及以上时,变形模式基本保持一致,对网格的敏感性不强. 再选取模型名义应变达到70%时的能量吸收值进行分析,以40 000单元模型的能量吸收数值作为标准值进行误差分析,如表 4所示,单元数为5 000的模型误差大于15%,10 000与20 000个单元的误差小于4%. 综合考虑计算成本与计算结果准确性,我们认为当模型单元数达到10 000时,数值仿真结果已收敛,得到网格无关解. 故本文在进行模型的网格划分时均设置10 000个以上的单元数.
表 3 不同单元数模型变形图Table 3. Deformation diagrams of the model with different numbers of elements 表 4 能量吸收误差Table 4. Energy absorption errors
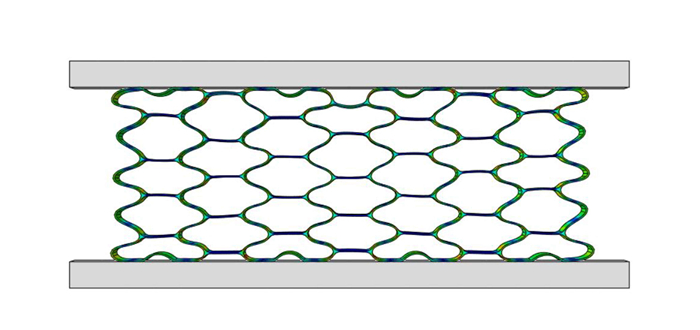
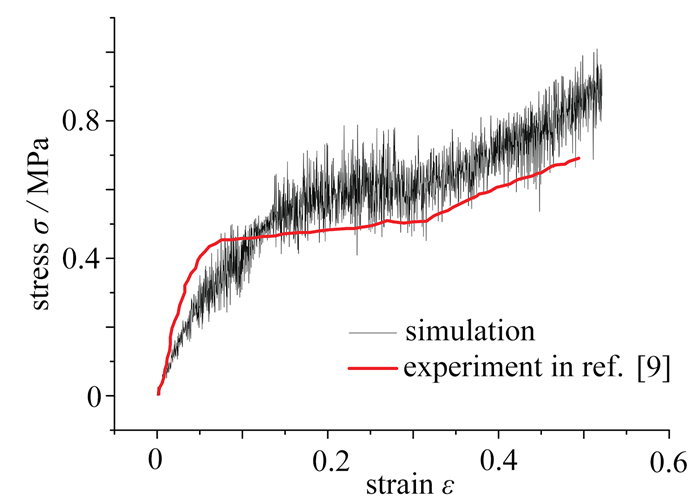
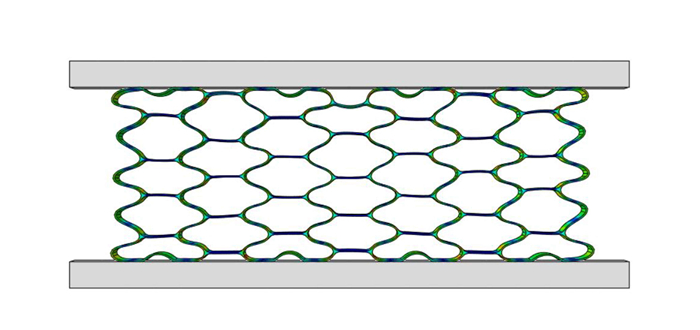
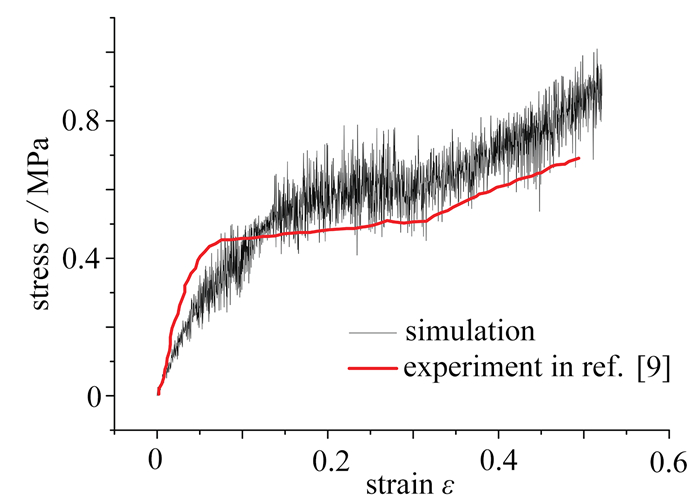
表 4 能量吸收误差Table 4. Energy absorption errorsN engergy absorption value at 70% strain E/J error ε/% 5×103 2 717.74 15.15 1×104 2 411.24 2.17 2×104 2 272.02 3.37 4×104 2 360.10 0 同时,为验证有限元模拟的正确性,建立与Xiong等[9]研究相同的模型进行对比,施加相同的边界条件,对比结构在冲击下的变形模式与应力-应变关系. 图 3给出了该蜂窝结构的变形模式,与文献中的变形模式基本吻合;图 4给出了仿真模拟和文献中实验得到的应力-应变曲线,仿真模拟得到的应力数值和应力-应变变化趋势都与实验结果较为一致,验证了有限元模拟的可靠性.
2. 结果分析
2.1 变形模式分析
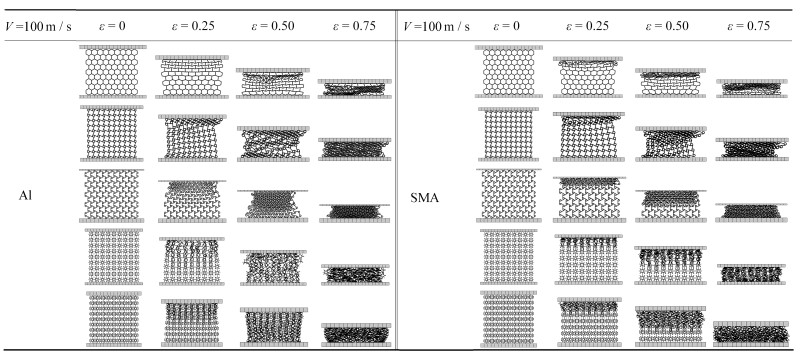
表 5、6分别给出了在10 m/s与100 m/s的冲击下,形状记忆合金蜂窝和铝(Al)蜂窝结构的变形模式,其中ε为蜂窝结构的名义压缩应变,即蜂窝结构顶面的压缩位移与模型初始高度之比.
表 5 10 m/s下的蜂窝结构变形图Table 5. Deformation diagrams of the honeycomb structure at 10 m/s 表 6 100 m/s下的蜂窝结构变形图Table 6. Deformation diagrams of the honeycomb structure at 100 m/s
表 6 100 m/s下的蜂窝结构变形图Table 6. Deformation diagrams of the honeycomb structure at 100 m/s
当刚性板的冲击速度为10 m/s时,形状记忆合金和金属铝蜂窝的面内动态压缩行为有很大区别. 对于六边形蜂窝,铝蜂窝首先在中上部形成局部变形带,呈较为平缓V形,随着压缩的进行,变形带进一步扩展,模型进入密实阶段,这与文献[14]中的变形模式相似. 而形状记忆合金蜂窝的应变均匀地分布在各个胞体中,随着压缩的进行,各个胞体发生均匀压缩变形直至进入密实阶段. 对于四边手性蜂窝,铝蜂窝在刚性板附近的斜支柱首先发生弯曲变形,自左向右逐渐传播开来,在上下两端产生了两个较显著的局部变形带,伴随着支柱的弯曲与圆型孔壁的坍塌,模型进入密实阶段. 在该结构中,形状记忆合金蜂窝表现出与铝相似的变形过程. 对于六边手性蜂窝,铝蜂窝在模型的中部首先产生变形,紧接着由于连接带的弯曲,带动圆形节点转动,胞体弯曲卷绕变形由中部逐渐扩散至整个模型,使整个模型表现出典型的负Poisson比行为,随着圆形孔壁的变形,模型逐渐进入密实阶段;而形状记忆合金蜂窝的变形更加均匀,胞体的弯曲缠绕均匀地分布在整个模型中,随着压缩的进行,最终进入密实阶段. 对于星形蜂窝,铝蜂窝在刚性板处先产生变形,之后随着星形结构的旋转与弯曲,在模型上下端均出现倾斜应变带,之后随着压缩的进行进入密实阶段;而形状记忆合金蜂窝首先发生每个星型结构的收缩,表现出明显的负Poisson比行为,之后在上下两端呈现出V形变形带,并逐渐扩展到整个模型,最后进入密实阶段. 对于星形三角加强蜂窝,铝蜂窝在开始的星形结构变形后,由于支柱的弯曲旋转,在模型中下部出现倾斜应变带,之后逐渐压缩进入密实阶段;而形状记忆合金蜂窝的变形与星形形状记忆合金蜂窝相似,在星形结构收缩后,在上下端出现V形变形带,之后进入密实阶段.
当刚性板的冲击速度为100 m/s时,各个结构均表现出靠近冲击端胞体的崩塌与折叠,此时应力在结构中的传递较为滞后,固定端受力较迟,各个结构在模型上部均形成了局部应变带,呈I形,并自上而下,一层一层地传播,直至到达模型的底部进入密实阶段,但形状记忆合金蜂窝的局部应变带更加集中地分布在模型上端,而铝蜂窝的局部应变带较为分散.
综上所述,在两种速度下,形状记忆合金蜂窝和铝蜂窝的变形模式都存在着很大不同. 在10 m/s的速度下,铝蜂窝往往表现出较为明显的局部应变带,而形状记忆合金蜂窝的应变分布更加均匀. 在100 m/s的速度下,呈现出相反的现象,铝蜂窝的应变分布更加均匀,而形状记忆合金蜂窝的局部应变带更为明显.
2.2 能量吸收分析
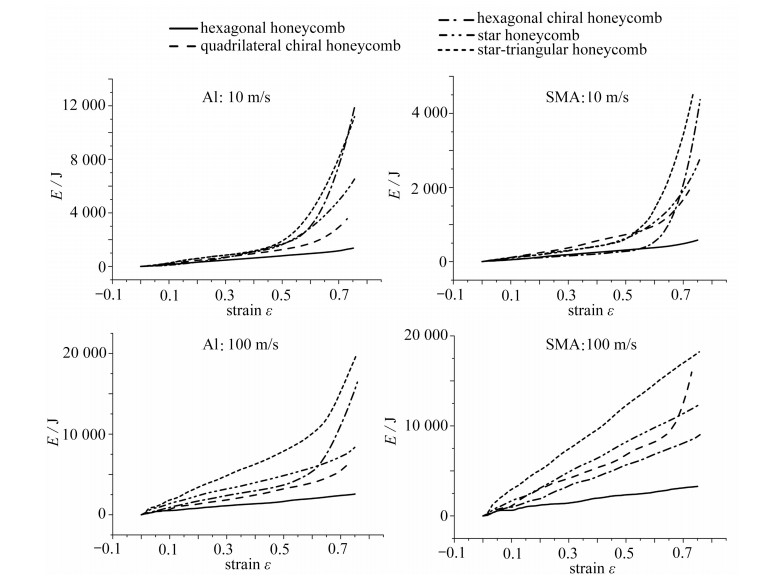
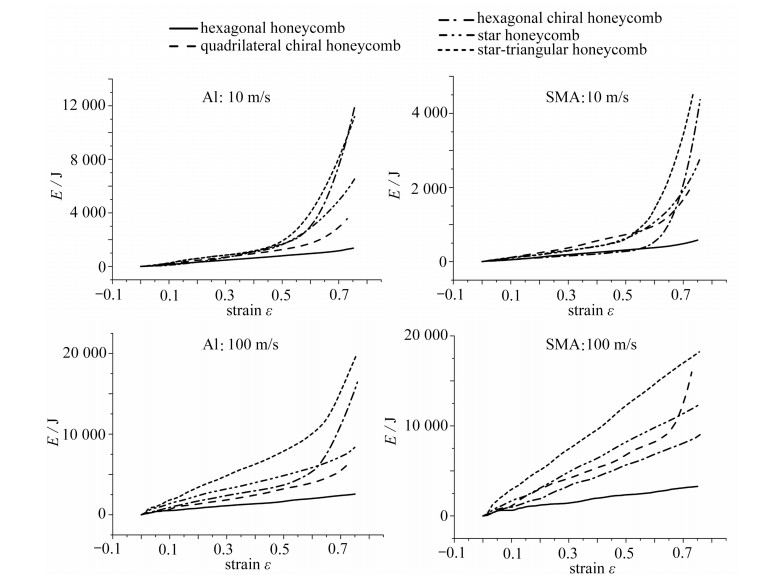
图 5给出了两种材料在冲击速度为10 m/s与100 m/s时的能量吸收-名义应变曲线,结构的能量吸收随着名义应变的增大而增大. 对于蜂窝材料,吸能特性指标能够反映出结构的能量吸收能力,而比吸能SEA是评价结构吸能能力的重要指标,比吸能SEA指的是结构单位质量所吸收的能量,其表达式为
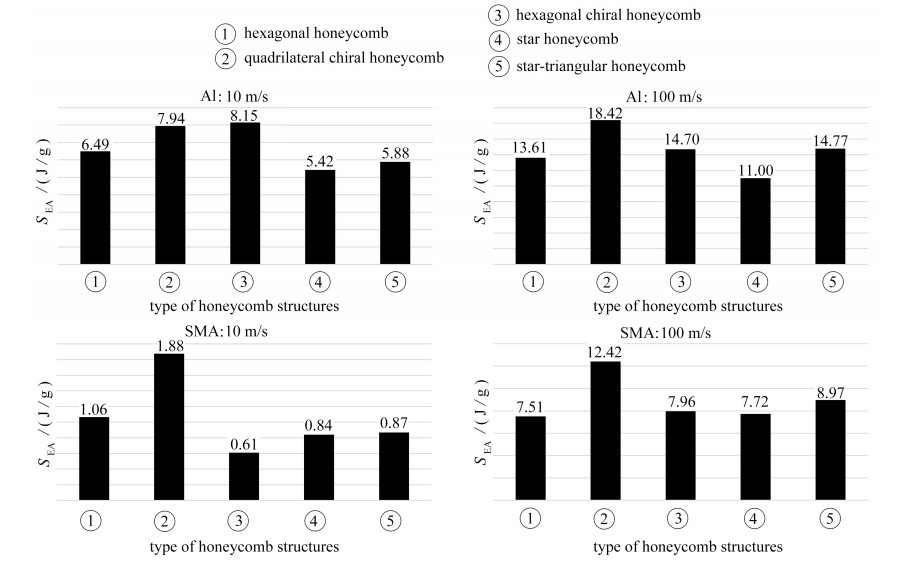
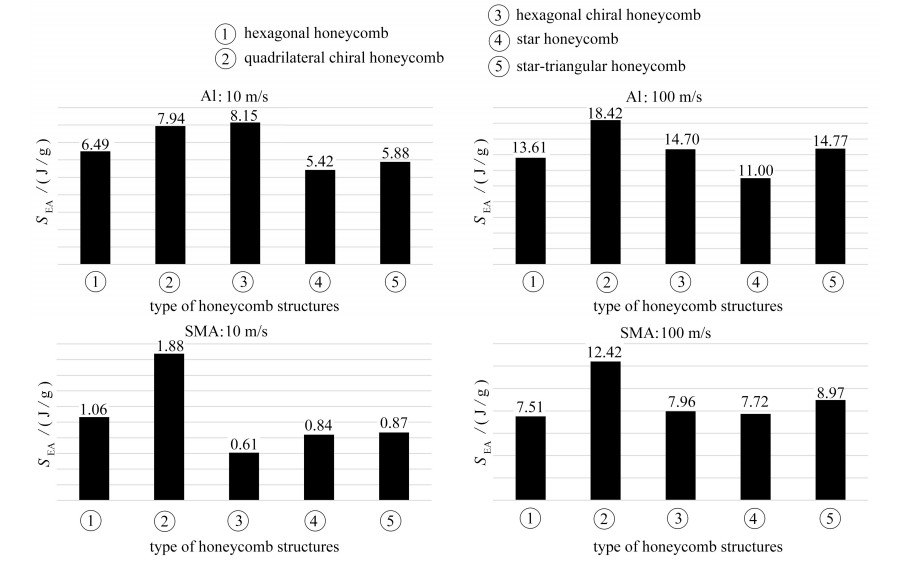
$$S_{\mathrm{EA}}=\frac{E}{M}, $$ (10) 其中E指的是结构吸收的总能量,M指的是结构的质量. 为了更好地进行分析,我们选取蜂窝结构应变达到60%时的比吸能数值进行对比,如图 6所示. 在相同的冲击速度下,形状记忆合金和铝在不同蜂窝结构中的能量吸收规律存在较大差别.
在10 m/s的冲击速度下,铝蜂窝的比吸能从大到小依次为六边手性蜂窝、四边手性蜂窝、六边形蜂窝、星形加强蜂窝、星形蜂窝. 其中,六边手性蜂窝为比吸能最大结构,而形状记忆合金蜂窝的比吸能规律与铝蜂窝相比存在着显著不同,其比吸能由大到小依次为四边手性蜂窝、六边形蜂窝、星形加强蜂窝、星形蜂窝、六边手性蜂窝,比吸能最大结构为四边手性蜂窝,两者存在较大差异.
在承受10 m/s的冲击速度时,星形蜂窝与星形加强蜂窝由于其结构的致密性而具有最为优良的能量吸收数值,但这种结构的致密性使其整体质量大大增加,在比吸能的比较中较为落后;手性蜂窝具有负Poisson比效应,并且其结构中的圆形设计有着优良的承压性能,平台应力阶段应力大,质量较轻,具有较好的能量吸收性能;传统六边形蜂窝具有在这5种蜂窝中最小的质量. 对于铝,六边手性蜂窝的变形更为均匀、具有圆形抗压优良结构而成为吸能最优结构;对于形状记忆合金,其具有二次硬化、超弹性效应和自增强行为. 四边手性蜂窝在承受冲击时一个圆形节点带动四条韧带发生扭曲,具有圆形结构,且自重较轻而成为比吸能最大结构. 同时,形状记忆合金六边形蜂窝展现出极为均匀的应变分布,模型各部分都能参与到抗冲击中进而展现出较为优秀的比吸能;六边手性蜂窝在冲击初期几乎仅发生韧带卷曲,在后期过快地进入致密阶段,比吸能较小.
在100 m/s的冲击速度下,形状记忆合金蜂窝不同结构的比吸能规律与铝蜂窝仍存在差异,但差异性减小. 铝蜂窝的比吸能由大到小依次为四边手性蜂窝、星形加强蜂窝、六边手性蜂窝、六边形蜂窝、星形蜂窝. 而形状记忆合金蜂窝的比吸能由大到小依次为四边手性蜂窝、星形加强蜂窝、六边手性蜂窝、星形蜂窝、六边形蜂窝.
在承受100 m/s的冲击速度时,各个蜂窝均表现出明显的局部应变带. 手性蜂窝以其圆形结构的优良性能以及较轻的模型自重而呈现出优秀的比吸能. 星形加强蜂窝由于在压缩时可以形成三角形这一稳定结构而展现出最好的能量吸收值,但因其结构自重过大而使其比吸能逊于四边手性蜂窝. 同时,高速冲击使星形蜂窝结构的致密性在能量吸收数值上的表现更为优秀,从而减小了其较大质量在比吸能比较时的劣势.
2.3 冲击速度影响
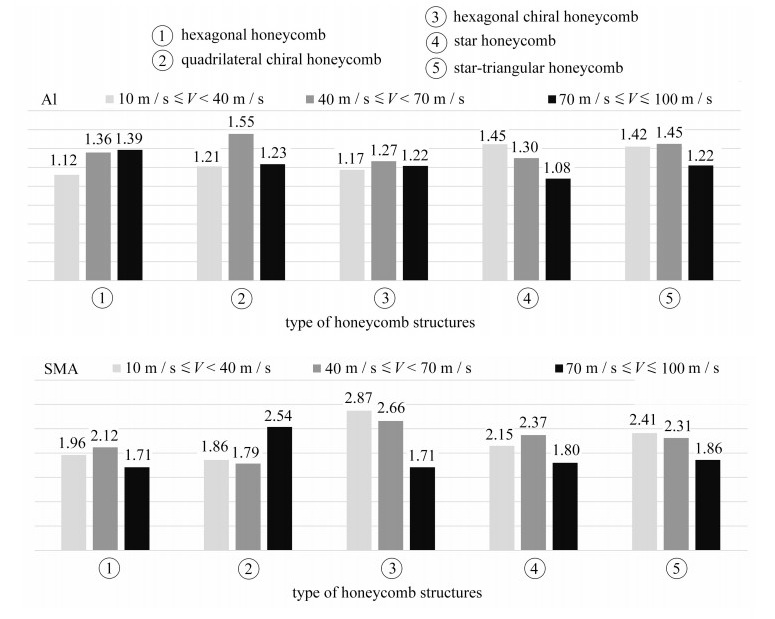
从图 5可以看出,随着冲击速度的增大,各个结构的能量吸收能力也得到了显著提高,这主要是由于在高速冲击下,冲击端的胞体已经被压溃,峰值应力与平台应力得到了显著的提高.
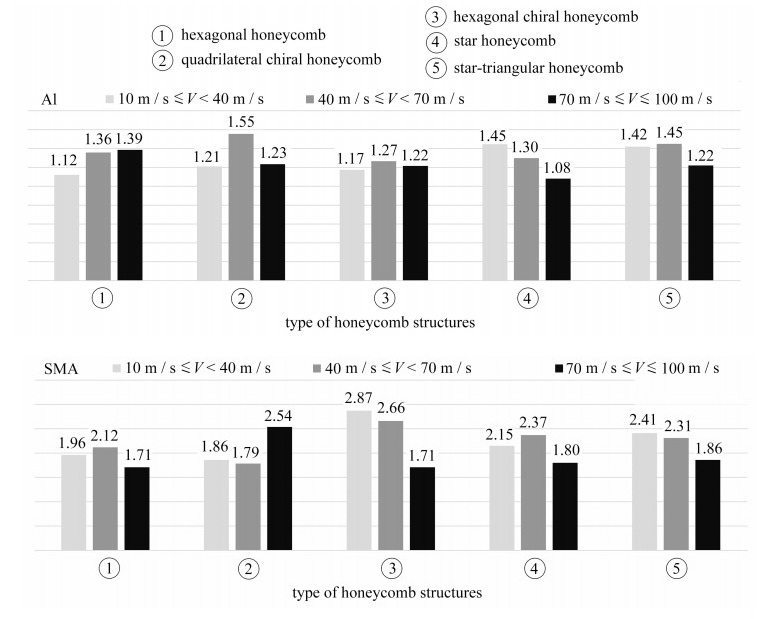
图 7为由两种材料构成的蜂窝结构在速度由10 m/s变化至40 m/s,40 m/s变化至70 m/s,70 m/s变化至100 m/s的能量吸收提升的倍数. 从图中可以观察到,速度的提高对形状记忆合金蜂窝的影响明显大于铝蜂窝. 随着速度的提升,铝蜂窝能量吸收提升普遍在1.2~1.5倍左右,而形状记忆合金蜂窝能量吸收的提升可达1.7~2.8倍.
3. 结论
本文围绕形状记忆合金蜂窝的抗冲击性能开展研究,设计并研究了5种形状记忆合金蜂窝结构,利用数值模拟的方法,对提出的结构开展了系统分析. 主要结论如下:
1) 提出了5种由形状记忆合金构成的可恢复抗冲击蜂窝结构,基于有限元ABAQUS/Explicit,给出了在面内冲击过程中各个结构的变形模式和能量吸收曲线.
2) 通过与传统金属铝蜂窝的对比,发现形状记忆合金蜂窝在承受低速冲击时能够表现出更为均匀的应变分布,在承受高速冲击时能够表现出更为集中的应变分布. 同时,随着速度的提高,形状记忆合金蜂窝的吸能特性得到了更为显著的提升.
3) 在10 m/s和100 m/s的冲击速度下,通过对比5种形状记忆合金蜂窝结构的比吸能,发现四边手性蜂窝具有在单位质量下最好的吸能效果.
综上所述,将形状记忆合金应用于手性、星形等具有负Poisson比效应的新型蜂窝结构,使结构具有优良抗冲击性能的同时又具备独特的形状可恢复性,为形状记忆合金蜂窝结构的设计提供了新的思路. 同时,本研究指出了形状记忆合金与传统材料在变形模式、吸能特性等方面的差异,这对形状记忆合金抗冲击结构的研究有着重要的意义.
-
表 1 各个蜂窝结构的几何构型与具体参数
Table 1. The geometric configuration and specific parameters of each honeycomb structure
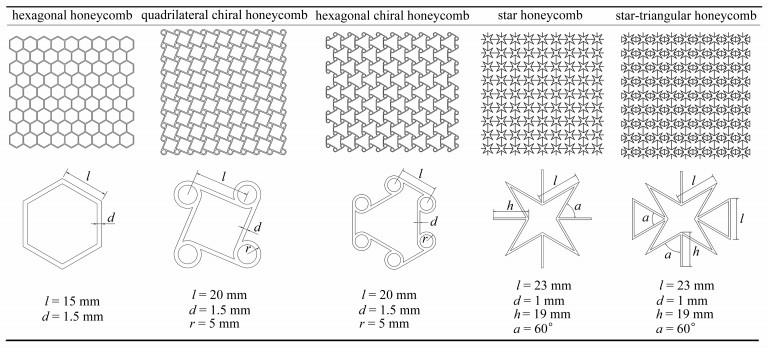
表 2 形状记忆合金材料参数
Table 2. Material parameters of SMA
material parameter value Austenite elastic stiffness EA/GPa 70 Martensite elastic stiffness EM/GPa 30 Poisson’s ratio (equal for both phases) υ 0.33 thermal expansion coefficient for Austenite αA/K-1 2.2×10-5 thermal expansion coefficient for Martensite αM/K-1 2.2×10-5 Martensitic start temperature M0s/K 291 Martensitic finish temperature M0f/K 271 Austenitic start temperature A0s/K 295 Austenitic finish temperature A0f/K 315 maximum transformation strain H 0.05 stress influence coefficient for Austenite ρΔsA/(MPa·K-1) -0.35 stress influence coefficient for Martensite ρΔsM/(MPa·K-1) -0.35 表 3 不同单元数模型变形图
Table 3. Deformation diagrams of the model with different numbers of elements
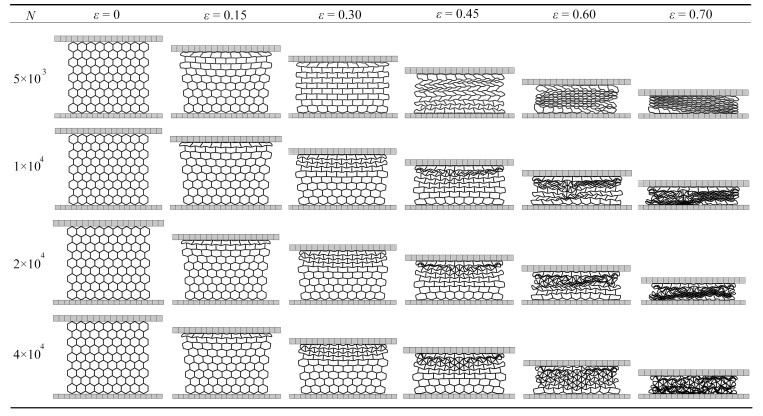
表 4 能量吸收误差
Table 4. Energy absorption errors
N engergy absorption value at 70% strain E/J error ε/% 5×103 2 717.74 15.15 1×104 2 411.24 2.17 2×104 2 272.02 3.37 4×104 2 360.10 0 表 5 10 m/s下的蜂窝结构变形图
Table 5. Deformation diagrams of the honeycomb structure at 10 m/s
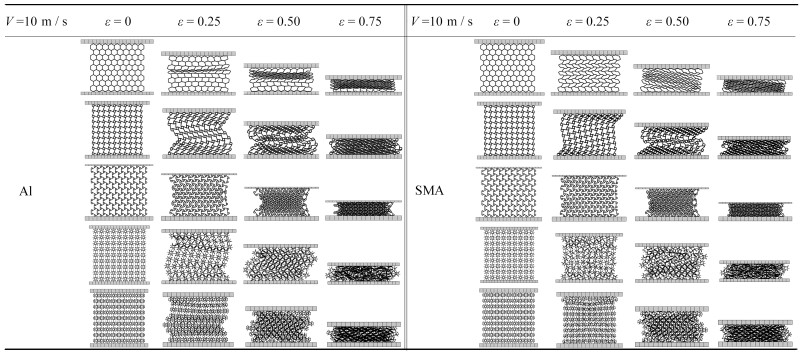
表 6 100 m/s下的蜂窝结构变形图
Table 6. Deformation diagrams of the honeycomb structure at 100 m/s
-
[1] LAKES R. Foam Structures with a negative Poisson's ratio[J]. Science, 1987, 235(4792): 1038-1040. doi: 10.1126/science.235.4792.1038 [2] THEOCARIS P S, STAVROULAKIS G E, PANAGIOTOPOULOS P D. Negative Poisson's ratios in composites with star-shaped inclusions: a numerical homogenization approach[J]. Archive of Applied Mechanics, 1997, 67(4): 274-286. doi: 10.1007/s004190050117 [3] QI C, JIANG F, ALEX R, et al. Quasi-static crushing behavior of novel re-entrant circular auxetic honeycombs[J]. Composites (Part B): Engineering, 2020, 197: 108117. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.108117 [4] THOMAS T, TIWARI G. Crushing behavior of honeycomb structure: a review[J]. International Journal of Crashworthiness, 2019, 24(5): 555-579. doi: 10.1080/13588265.2018.1480471 [5] 王永福, 漆文凯, 沈承. 弹性约束边界条件下矩形蜂窝夹芯板的自由振动分析[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2019, 40(6): 583-594. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.390348WANG Yongfu, QI Wenkai, SHEN Cheng. Free vibration analysis of rectangular honeycomb-cored plates under elastically constrained boundary conditions[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2019, 40(6): 583-594. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.390348 [6] LIANG H X, SONG B, PENG P, et al. Preparation of three-dimensional honeycomb carbon materials and their adsorption of Cr(Ⅵ)[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 367: 9-16. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.02.121 [7] 刘鑫, 吴倩倩, 于国财, 等. 碳纤维/树脂基复合材料曲壁蜂窝夹芯结构的三点弯曲性能[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2022, 43(5): 490-498. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.430061LIU Xin, WU Qianqian, YU Guocai, et al. Three-point bending properties of carbon fiber reinforced polymer composite honeycomb sandwich structures with curved wall[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2022, 43(5): 490-498. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.430061 [8] SHAW J A, GRUMMON D S, FOLTZ J. Superelastic NiTi honeycombs: fabrication and experiments[J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 2007, 16(1): S170-S178. doi: 10.1088/0964-1726/16/1/S17 [9] XIONG Z W, LI M, HAO S J, et al. 3D-printing damage-tolerant architected metallic materials with shape recoverability via special deformation design of constituent material[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(33): 39915-39924. [10] HASSAN M R, SCARPA F, RUZZENE M, et al. Smart shape memory alloy chiral honeycomb[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2008, 481/482: 654-657. [11] WATKINS R T, SHAW J A, TRIANTAFYLLIDIS N, et al. Design study of shape memory alloy honeycombs for energy absorption[C]//ASME Conference on SMART Materials, Adaptive Structures and Intelligent Systems. Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 2011: 593-602. [12] QIDWAI M A, LAGOUDAS D C. Numerical implementation of a shape memory alloy thermomechanical constitutive model using return mapping algorithms[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2000, 47(6): 1123-1168. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0207(20000228)47:6<1123::AID-NME817>3.0.CO;2-N [13] RUAN D, LU G, WANG B, et al. In-plane dynamic crushing of honeycombs: a finite element study[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2003, 28(2): 161-182. doi: 10.1016/S0734-743X(02)00056-8 [14] 卢子兴, 李康. 四边手性蜂窝动态压溃行为的数值模拟[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2014, 34(2): 181-187.LU Zixing, LI Kang. Numerical simulation of four-sided chiral honeycomb dynamic crushing behavior[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves, 2014, 34(2): 181-187. (in Chinese) [15] ALDERSON A, ALDERSON K L, ATTARD D, et al. Elastic constants of 3-, 4- and 6-connected chiral and anti-chiral honeycombs subject to uniaxial in-plane loading[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2009, 70(7): 1042-1048. [16] 贠昊, 邓子辰, 朱志韦. 弹性波在星形节点周期结构蜂窝材料中的传播特性研究[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2015, 36(8): 814-820. doi: 10.3879/j.issn.1000-0887.2015.08.003YUN Hao, DENG Zichen, ZHU Zhiwei. Bandgap properties of periodic 4-point star-shaped honeycomb materials with negative Poisson's ratios[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2015, 36(8): 814-820. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3879/j.issn.1000-0887.2015.08.003 [17] WEI L L, ZHAO X, YU Q, et al. A novel star auxetic honeycomb with enhanced in-plane crushing strength[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2020, 149: 106623. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2020.106623 [18] 董琳, 彭瑞岩, 张琪, 等. 六边形形状记忆合金蜂窝材料面内变形特性的研究[J]. 山西建筑, 2019, 45(14): 84-85.DONG Lin, PENG Ruiyan, ZHANG Qi, et al. Research on the in-plane deformation characteristics of hexagonal shape memory alloy honeycombs[J]. Shanxi Architecture, 2019, 45(14): 84-85. (in Chinese) [19] 周世奇, 侯秀慧, 邓子辰. 一般宏观应力状态下凹角蜂窝结构的屈曲性能分析[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2023, 44(1): 12-24. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.430202ZHOU Shiqi, HOU Xiuhui, DENG Zichen. Buckling analysis of re-entrant honeycomb structures under general macroscopic stress states[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2023, 44(1): 12-24. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.430202 期刊类型引用(4)
1. 唐智亮,高永强,许卫锴. 凹截面薄壁管轴向冲击时的变形模式及能量吸收性能研究. 应用数学和力学. 2025(02): 165-174 .  本站查看
本站查看2. 陈然,张迪,蔡登安. 碳/芳纶混杂复合材料蜂窝夹芯板低速冲击及冲击后压缩实验研究. 南京航空航天大学学报(自然科学版). 2025(01): 109-119 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 郑冰倩,强鹭升,宋萧彤,倪长也,张瑞. 陶瓷混杂点阵夹芯超结构的承载与抗多点侵彻性能. 应用数学和力学. 2024(08): 1037-1046 .  本站查看
本站查看4. 张智扬,赵振宇,任建伟,高辉遥. 蜂窝夹芯结构用连接接头抗冲击性能研究. 应用数学和力学. 2024(08): 1024-1036 .  本站查看
本站查看其他类型引用(0)
-






 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载:

 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号