Numerical Study on the Collision-Separation Process of Glass Bead Droplets
-
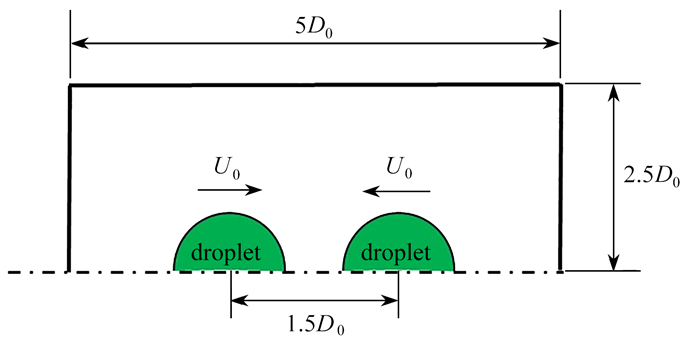
摘要: 采用耦合水平集和流体体积(CLSVOF)法对等直径的玻璃微珠液滴对心碰撞过程进行数值模拟,重点研究了玻璃微珠液滴碰撞分离过程中的物理机制. 在与正十四烷液滴碰撞实验对比验证的基础上,数值研究了分离过程中玻璃微珠液滴的形态变化和能量变化规律. 研究表明,玻璃微珠液滴碰撞分离过程所需能量主要由液滴动能和表面能提供,且动能大部分转化为黏性耗散能. 通过对液滴能量和平均总压变化分析,得出液滴碰撞分离的4种状态,即径向拉伸到极限、径向收缩和轴向拉伸达到平衡、轴向拉伸到极限和液滴液桥夹断分离. 分析了4种状态的速度和压力分布,得出末端夹断机制是液滴碰撞分离的主要原因. 研究结果可为丰富玻璃微珠液滴碰撞理论提供基础.
-
关键词:
- 玻璃微珠 /
- 液滴碰撞 /
- 耦合水平集和流体体积方法 /
- 数值模拟
Abstract: The coupled level set and volume of fluid (CLSVOF) method was used to simulate the collision process of glass bead droplets with the same diameter, with the physical mechanism during the collision-separation behavior of glass bead droplets mainly studied. Based on the comparative verification with n-tetradecane droplet collision experiments, the morphological changes and energy change patterns of glass bead droplets during the separation process were investigated numerically. The research shows that, the energy required for the collision and separation process of glass bead droplets mainly comes from the kinetic energy and surface energy of the droplets, and most of the kinetic energy would convert into viscous dissipation energy. Through the analysis of the changes of droplet energy and average total pressure, 4 important states of droplet collision and separation were obtained, including the radial stretching to limit, the radial contraction and axial stretching to balance, the axial stretching to limit, and the droplet bridge pinching separation. The velocity and pressure distributions of the 4 states were discussed. The results reveal that, the end pinchoff mechanism is a main cause for droplet collisional separation. The work provides a basis for enriching the theory about glass bead droplet collisions.-
Key words:
- glass bead /
- droplet collision /
- CLSVOF method /
- numerical simulation
-
表 1 正十四烷液滴的物理参数
Table 1. Physical parameters of n-tetradecane
parameter name liquid density ρl/(kg/m3) liquid viscosity μl/(N·s/m2) gas density ρg/(kg/m3) gas viscosity μg/(N·s/m2) surface tension coefficient σ/(N/m) value 758 2.128×10-3 1.138 1.787×10-5 0.026 表 2 玻璃微珠液滴的物理参数
Table 2. Physical parameters of glass beads
parameter name liquid density ρl/(kg/m3) liquid viscosity μl/(N·s/m2) gas density ρg/(kg/m3) gas viscosity μg/(N·s/m2) surface tension coefficient σ/(N/m) value 2 310 1.5×10-2 1.225 1.794×10-5 0.6 -
[1] LIU L, YU S, NIU Y, et al. Preparation and properties of hollow glass microspheres reinforced Mg alloy degradable composites[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 835: 155198. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155198 [2] 彭寿, 陈淑勇, 陈凯, 等. 玻璃粉料熔融球化过程的模拟研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2016, 35(6): 1800-1806.PENG Shou, CHEN Shuyong, CHEN Kai, et al. Simulation research of glass powder particle melt spheroidizing process[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2016, 35(6): 1800-1806. (in Chinese) [3] 夏盛勇, 胡春波. 三氧化二铝液滴对心碰撞直接数值模拟[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2014, 35(4): 377-388. doi: 10.3879/j.issn.1000-0887.2014.04.004XIA Shengyong, HU Chunbo. Direct numerical simulation of head-on binary collision of aluminum oxide droplets[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2014, 35(4): 377-388. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3879/j.issn.1000-0887.2014.04.004 [4] FOSTIROPOULOS S, STROTOS G, NIKOLOPOULOS N, et al. Numerical investigation of heavy fuel oil droplet breakup enhancement with water emulsions[J]. Fuel, 2020, 278: 118381. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.118381 [5] 尹强, 齐晓霓, 梁伟. 二元海水液滴对心碰撞过程数值模拟[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2020, 41(3): 268-279. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.400196YIN Qiang, QI Xiaoxia, LIANG Wei. Numerical simulation of head-on binary collision between seawater droplets[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2020, 41(3): 268-279. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.400196 [6] AMANI A, BALCAZAR N, GUTIÉRREZ E, et al. Numerical study of binary droplets collision in the main collision regimes[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 370: 477-498. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.188 [7] ASHNA M, RAHIMIAN M H. LMB simulation of head-on collision of evaporating and burning droplets in coalescence regime[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2017, 109: 520-536. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.01.108 [8] LIU X, WANG C, ZHAO Y, et al. Shear-driven two colliding motions of binary double emulsion droplets[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2018, 121: 377-389. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.01.021 [9] ZHANG Y R, ZHAO Z, LUO K H, et al. Size effects on dynamics of nanodroplets in binary head-on collisions[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2021, 341: 117383. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2021.117383 [10] LI D, ZHANG D, ZHENG Z. Numerical analysis of hollow droplet impacts on a dry flat surface[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2019, 129: 753-763. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.09.063 [11] QIAN L, CONG H, ZHU C. A numerical investigation on the collision behavior of polymer droplets[J]. Polymers, 2020, 12(2): 263. doi: 10.3390/polym12020263 [12] YUAN S, DABIRIAN R, SHOHAM O, et al. Numerical simulation of liquid droplet coalescence and breakup[J]. Journal of Energy Resources Technology, 2020, 142(10): 102101. doi: 10.1115/1.4046603 [13] QIAN J, LAW C K. Regimes of coalescence and separation in droplet collision[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1997, 331: 59-80. doi: 10.1017/S0022112096003722 [14] 王金城, 关晖, 卫志军, 等. 壁面结构对三维可压缩气泡群影响的数值模拟研究[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2022, 43(1): 49-62. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.420041WANG Jincheng, GUAN Hui, WEI Zhijun, et al. Numerical analysis on effects of wall structures on bubble groups[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2022, 43(1): 49-62. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.420041 [15] 雷阳, 封建湖. 基于参数化水平集法的材料非线性子结构拓扑优化[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2021, 42(11): 1150-1160. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.420090LEI Yang, FENG Jianhu. Topology optimization of nonlinear material structures based on parameterized level set and substructure methods[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2021, 42(11): 1150-1160. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.420090 [16] SUSSMAN M, PUCKETT E G. A coupled level set and volume-of-fluid method for computing 3D and axisymmetric incompressible two-phase flows[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2000, 162(2): 301-337. doi: 10.1006/jcph.2000.6537 [17] TANG C, ZHANG P, LAW C K. Bouncing, coalescence, and separation in head-on collision of unequal-size droplets[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2012, 24(2): 022101. doi: 10.1063/1.3679165 [18] YOSHINO M, SAWADA J, SUZUKI K. Numerical simulation of head-on collision dynamics of binary droplets with various diameter ratios by the two-phase lattice kinetic scheme[J]. Computers & Fluids, 2018, 168: 304-317. [19] MOQADDAM A M, CHIKATAMARLA S S, KARLIN I V. Simulation of binary droplet collisions with the entropic lattice Boltzmann method[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2016, 28(2): 022106. doi: 10.1063/1.4942017 [20] 赵峻逸, 薛士东, 韩敬坤, 等. 双液滴碰撞行为及调控机制的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(5): 2354-2372.ZHAO Junyi, XUE Shidong, HAN Jingkun, et al. Research progress of binary droplet collision behavior and regulation mechanism[J]. CIESC Journal, 2021, 72(5): 2354-2372. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载:









 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号