A Coupling Analysis of Rainfall Infiltration and Slope Surface Runoff Based on the Numerical Manifold Method
edited-by
edited-by
(Contributed by ZHENG Hong, M. AMM Editorial Board)-
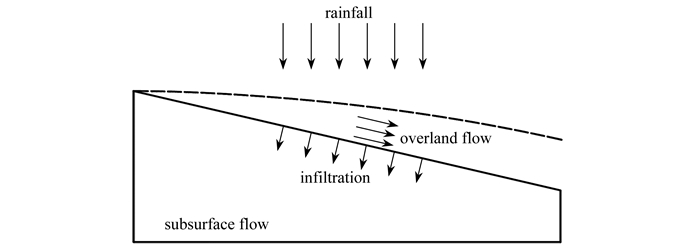
摘要: 降雨时坡地的入渗-产流分析,是降雨型滑坡、泥石流等地质灾害机理研究中的重要课题之一. 为实现边坡降雨-入渗-产流的全过程数值模拟,进一步提高计算效率,考虑将降雨入渗面视作坡面径流与坡体渗流的内部域,基于一维运动波方程和二维压力水头格式的Richards方程建立耦合模型,并推导出其总体控制方程,采用数值流形法(numerical manifold method, NMM)实现其数值求解,通过编制相应的计算程序分析了边坡降雨产流过程. 数值分析结果表明:所建模型的计算结果与试验数据及前人模拟结果吻合良好,验证了该文模型及计算方法的有效性与可靠性;降雨强度越大,产流时间越早,坡面积水深度越大,对坡体内的水分分布影响范围越广. 研究表明,所建模型能真实反映边坡降雨-入渗-产流全过程,可为降雨诱发的各类地质灾害分析提供计算依据.Abstract: The infiltration-runoff processes of slopes during rainfall were of significance in the mechanism study of rainfall-induced landslides, debris flows, and other geological disasters. To realize the numerical simulation of the whole rainfall infiltration-runoff process and further improve the computation efficiency, a coupling model and its total governing equations were derived from the 1D kinematic wave equation and the 2D h-based Richards' equation, with the rainfall infiltration surface deemed as the internal domain of the runoff and the seepage. Then the numerical manifold method (NMM) was used to solve the total governing equations, and the computation program was compiled to simulate the rainfall infiltration-runoff processes of slopes. The numerical analysis results showed that, the coupling model solution is in good agreement with the experimental data and previous results, verifying the validity and reliability of the proposed model. The higher the rainfall intensity is, the earlier the runoff producing time will be; the deeper the ponding depth is, and the wider the influence range on the water distribution within the slope will be. The proposed model can truly reflect the whole rainfall infiltration-runoff process of the slope, and provides a calculation basis for the analysis of various geological disasters induced by rainfall.
-
Key words:
- rainfall infiltration /
- slope runoff /
- saturated-unsaturated seepage /
- numerical manifold method
edited-byedited-by1) (我刊编委郑宏来稿) -
表 1 降雨工况
Table 1. The rainfall intensities
case number 1 2 3 4 5 rainfall intensity I/(m/min) 2.502×10-3 2.085×10-3 1.668×10-3 1.251×10-3 8.340×10-4 -
[1] 姚海林, 郑少河, 李文斌, 等. 降雨入渗对非饱和膨胀土边坡稳定性影响的参数研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2002, 21(7): 1034-1039.YAO Hailin, ZHENG Shaohe, LI Wenbin, et al. Parametric study on the effect of rain infiltration on stability of unsaturated expansive soil slope[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2002, 21(7): 1034-1039. (in Chinese) [2] 董建军, 王思萌, 杨晓萧, 等. 基于非饱和-饱和渗流的降雨入渗边坡稳定性分析[J]. 水利与建筑工程学报, 2018, 16(6): 99-104.DONG Jianjun, WANG Simeng, YANG Xiaoxiao, et al. Analysis of the rainfall infiltration on slope stability based on unsaturated-saturated seepage[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Architectural Engineering, 2018, 16(6): 99-104. (in Chinese) [3] XIONG X, SHI Z, XIONG Y, et al. Unsaturated slope stability around the Three Gorges Reservoir under various combinations of rainfall and water level fluctuation[J]. Engineering Geology, 2019, 261: 105231. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105231 [4] WALLACH R, GRIGORIN G, RIVLIN J. The errors in surface runoff prediction by neglecting the relationship between infiltration rate and overland flow depth[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 1997, 200: 243-259. doi: 10.1016/S0022-1694(97)00017-6 [5] 李根, 韩同春, 吴俊杨, 等. 基于有限体积法的地表径流与土壤水流耦合分析[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2022, 56(5): 947-955.LI Gen, HAN Tongchun, WU Junyang, et al. Coupled analysis on surface runoff and soil water movement by finite volume method[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2022, 56(5): 947-955. (in Chinese) [6] MORITA M, YEN B C. Modeling of conjunctive two-dimensional surface-three-dimensional subsurface flows[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2002, 128(2): 184-200. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2002)128:2(184) [7] PANDAY S, HUYAKORN P S. A fully coupled physically-based spatially-distributed model for evaluating surface/subsurface flow[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2004, 27(4): 361-382. doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2004.02.016 [8] 张培文, 刘德富, 郑宏, 等. 降雨条件下坡面径流和入渗耦合的数值模拟[J]. 岩土力学, 2004, 25(1): 109-113.ZHANG Peiwen, LIU Defu, ZHENG Hong, et al. Coupling numerical simulation of slope runoff and infiltration under rainfall conditions[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2004, 25(1): 109-113. (in Chinese) [9] 埃尔杜拉K S. 一个综合植被地表径流与饱和地下水流之间相互作用的数值模型[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2012, 33(7): 828-844. doi: 10.3879/j.issn.1000-0887.2012.07.004ERDURAN K S. An integrated numerical model for vegetated surface and saturated subsurface flow interaction[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2012, 33(7): 828-844. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3879/j.issn.1000-0887.2012.07.004 [10] 朱磊, 田军仓, 孙骁磊. 基于全耦合的地表径流与土壤水分运动数值模拟[J]. 水科学进展, 2015, 26(3): 322-330.ZHU Lei, TIAN Juncang, SUN Xiaolei. A fully couple numerical simulation for surface runoff and soil water movement[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2015, 26(3): 322-330. (in Chinese) [11] 李尚辉, 刘代文, 阙云, 等. 坡面径流与大孔隙流耦合作用下边坡水分场参数敏感性分析[J]. 济南大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 37(3): 264-272.LI Shanghui, LIU Daiwen, QUE Yun, et al. Parameter sensitivity analysis on slope water fields under slope runoffs and macropore flows coupling[J]. Journal of University of Jinan (Science and Technology), 2023, 37(3): 264-272. (in Chinese) [12] KOLLET S J, MAXWELL R M. Integrated surface-groundwater flow modeling: a free-surface overland flow boundary condition in a parallel groundwater flow model[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2006, 29(7): 945-958. doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2005.08.006 [13] 童富果, 田斌, 刘德富. 改进的斜坡降雨入渗与坡面径流耦合算法研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2008, 29(4): 1035-1040.TONG Fuguo, TIAN Bin, LIU Defu. A coupling analysis of slope runoff and infiltration under rainfall[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2008, 29(4): 1035-1040. (in Chinese) [14] WEILL S, MOUCHE E, PATIN J. A generalized Richards equation for surface/subsurface flow modelling[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2009, 366(1/4): 9-20. [15] TIAN Dongfang, LIU Defu. A new integrated surface and subsurface flows model and its verification[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2011, 35: 3574-3586. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2011.01.035 [16] TIAN Dongfang, ZHENG Hong, LIU Defu. A 2D integrated FEM model for surface water-groundwater flow of slopes under rainfall condition[J]. Landslides, 2017, 14(2): 577-593. doi: 10.1007/s10346-016-0716-4 [17] 王乐, 田东方. 边坡渗流与坡面径流联合求解三维有限元模型[J]. 人民珠江, 2019, 40(5): 24-29.WANG Le, TIAN Dongfang. 3D FEM integrated model for seepage and runoff process[J]. Pearl River, 2019, 40(5): 24-29. (in Chinese) [18] LIU Gang, TONG Fuguo, TIAN Bin. A finite element model for simulating surface run-off and unsaturated seepage flow in the shallow subsurface[J]. Hydrological Processes, 2019, 33(26): 3378-3390. doi: 10.1002/hyp.13564 [19] SHI Genhua. Manifold method of material analysis[C]//Transactions of the 9th Army Conference on Applied Mathematics and Computing. US Army Research Office, 1991. [20] 陈远强, 杨永涛, 郑宏, 等. 饱和-非饱和渗流的数值流形法研究与应用[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2019, 41(2): 338-347.CHEN Yuanqiang, YANG Yongtao, ZHENG Hong, et al. Saturated-unsaturated seepage by numerical manifold method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2019, 41(2): 338-347. (in Chinese) [21] LIN Shan, ZHENG Hong, ZHANG Zhihong, et al. Evaluation of permeability of soil & rock aggregate using meshless numerical manifold method[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2022, 151: 104953. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2022.104953 [22] CHEN Yuanqiang, ZHENG Hong, YIN Boyuan, et al. The MLS-based numerical manifold method for Darcy flow in heterogeneous porous media[J]. Engineering Analysis With Boundary Elements, 2023, 148: 220-242. doi: 10.1016/j.enganabound.2022.12.030 [23] RICHARDS L A. Capillary conduction of liquids through porous mediums[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1931, 1: 318-333. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10006144118 [24] 朱帅润, 李绍红, 钟彩尹, 等. 时间分数阶的非饱和渗流数值分析及其应用[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2022, 43(9): 966-975. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.420334ZHU Shuairun, LI Shaohong, ZHONG Caiyin, et al. Numerical analysis of time fractional-order unsaturated flow and its application[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2022, 43(9): 966-975. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.420334 [25] 刘能胜, 曹恒明. 通用函数边界下潜水非稳定流模型的解及应用[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2020, 41(9): 1048-1056. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.400371LIU Nengsheng, CAO Hengming. Solution and application of the transient phreatic flow motion model under general function boundary[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2020, 41(9): 1048-1056. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.400371 [26] 郑素佩, 李霄, 赵青宇, 等. 求解二维浅水波方程的旋转混合格式[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2022, 43(2): 176-186. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.400124ZHENG Supei, LI Xiao, ZHAO Qingyu, et al. A rotated mixed scheme for solving 2D shallow water equation[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2022, 43(2): 176-186. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.400124 [27] LIGHTHILL M J, WHITHAM G B. On kinematic waves: flood movement in long rivers[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London (Series A): Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1955, 229(1178): 281-316. doi: 10.1098/rspa.1955.0088 [28] PONCE V M, SIMONS D B, LI R M. Applicability of kinematic and diffusion models[J]. Journal of the Hydraulics Division, 1978, 104(3): 353-360. doi: 10.1061/JYCEAJ.0004958 [29] 文康, 金管生, 李蝶娟. 地表径流过程的数学模拟[M]. 北京: 水利电力出版社, 1991.WEN Kang, JIN Guansheng, LI Diejuan. Mathematical Simulation of Surface Runoff Processes[M]. Beijing: China Water & Power Press, 1991. (in Chinese) [30] SMITH R E, WOOLHISER D A. Mathematical simulation of infiltrating watersheds[R]. Colorado: Colorado State University, 1971. [31] VAN GENUCHTEN M T. A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1980, 44(5): 892-898. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1980.03615995004400050002x [32] MUALEM Y. A new model for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated porous media[J]. Water Resources Research, 1976, 12(3): 513-522. doi: 10.1029/WR012i003p00513 [33] GARDNER W R. Some steady-state solutions of the unsaturated moisture flow equation with application to evaporation from a water table[J]. Soil science, 1958, 85(4): 228-232. doi: 10.1097/00010694-195804000-00006 [34] BROOKS R A, COREY A T. Hydraulic properties of porous media[R]. Hydrology Papers, 1964. [35] ABDUL A S, GILLHAM R W. Laboratory studies of the effects of the capillary fringe on streamflow generation[J]. Water Resources Research, 1984, 20(6): 1-18. [36] VANDERKWAAK J E. Numerical simulation of flow and chemical transport in integrated surface-subsurface hydrologic systems[D]. Waterloo: University of Waterloo, 1999. [37] SINGH V, BHALLAMUDI S M. Conjunctive surface-subsurface modeling of overland flow[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 1998, 21(7): 567-579. doi: 10.1016/S0309-1708(97)00020-1 -





 下载:
下载:














 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号