Mechanical Behaviors of Subsurface Bifurcating Cracks
-
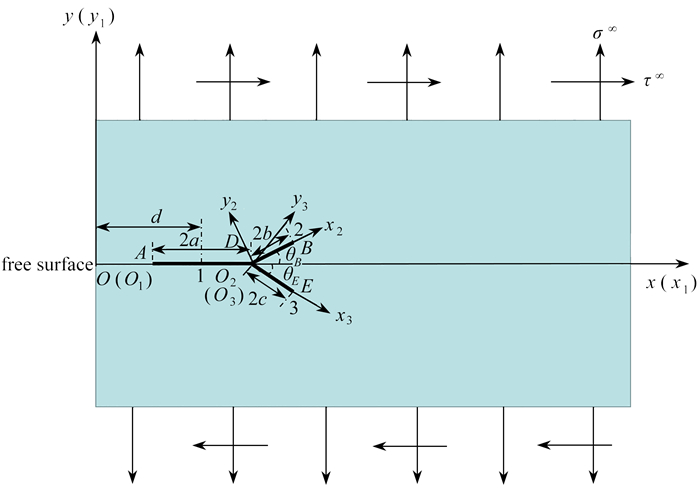
摘要: 在复杂荷载作用下,利用分布位错技术(DDT)对半无限大平面内的分岔裂纹问题进行研究,并进行了正确性验证. 根据等效应力强度因子判据,初步解释了裂纹产生分岔的原因;研究了不同埋深、荷载比值、分支长度比值、分岔角度情况下的分岔裂纹尖端的应力强度因子;同时,研究了多分支分岔裂纹,计算结果与有限元结果吻合. 结果显示:埋深越深,分岔裂纹扩展越困难,当埋深为d/a=1.5时,分支裂尖应力强度因子削弱程度可达15%左右;较长分支会极大地抑制短分支的扩展,当两分支裂纹长度比达到b/c=2以上时,屏蔽效应可达50%以上;另外,分岔角度和荷载比值会改变分岔裂纹主导的扩展模式.
-
关键词:
- 分岔裂纹 /
- 分布位错技术 /
- 等效应力强度因子判据 /
- 应力强度因子 /
- 多分支分岔裂纹
Abstract: Under complex loads, the distributed dislocation technique (DDT) was used to discuss the bifurcating crack problem in a semi-infinite plane, and its correctness was verified. Based on the criterion for the equivalent stress intensity factor, the cause for crack bifurcation was preliminarily explained. The stress intensity factors of bifurcating cracks under different buried depths, loading ratios, bifurcation length ratios, and bifurcation angles were calculated. The multi-branch bifurcating crack was also calculated, with the results agreeing well with the finite element method. The results show that, the deeper the buried depth is, the more difficult the bifurcating crack propagation will be. When the burial depth reaches d/a=1.5, the stress intensity factor at the bifurcating crack tip will decrease by about 15%. Moreover, the longer branch will greatly inhibit the extension of the short branch. When the crack length ratio of the 2 branches reaches more than b/c=2, the shielding effect will reach more than 50%; In addition, the bifurcation angles and loading ratios will change the dominant propagation mode of bifurcating cracks. -
表 1 多分支分岔裂纹有限元计算与本文结果对照
Table 1. Comparison between the results of finite element calculation of the multi branch bifurcation crack and the results in this paper
KⅠA/(MPa·$\sqrt{\mathrm{mm}}$) KⅠE/(MPa·$\sqrt{\mathrm{mm}}$) KⅠB/(MPa·$\sqrt{\mathrm{mm}}$) KⅠF/(MPa·$\sqrt{\mathrm{mm}}$) FEM 2.832 0.618 1.313 1.686 DDT 2.807 0.613 1.289 1.607 KⅡA/(MPa·$\sqrt{\mathrm{mm}}$) KⅡE/(MPa·$\sqrt{\mathrm{mm}}$) KⅡB/(MPa·$\sqrt{\mathrm{mm}}$) KⅡF/(MPa·$\sqrt{\mathrm{mm}}$) FEM -0.032 4 -1.028 1.132 -0.760 DDT -0.023 8 -1.020 1.165 -0.714 -
[1] THEOCARIS P S, IOAKIMIDIS N. The symmetrically branched crack in an infinite elastic medium[J]. Zeitschrift für Angewandte Mathematik und Physik, 1976, 27(6): 801-814. doi: 10.1007/BF01595131 [2] LAM K Y, ONG P P, WUDE N. Interaction between a circular inclusion and a symmetrically branched crack[J]. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics, 1998, 28(3): 197-211. doi: 10.1016/S0167-8442(98)00005-6 [3] YAN X. Stress intensity factors for asymmetric branched cracks in plane extension by using crack-tip displacement discontinuity elements[J]. Mechanics Research Communications, 2005, 32(4): 375-384. doi: 10.1016/j.mechrescom.2004.10.005 [4] YAVUZ A K, PHOENIX S L, TERMAATH S C. An accurate and fast analysis for strongly interacting multiple crack configurations including kinked (V) and branched (Y) cracks[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 2006, 43(22/23): 6727-6750. [5] DAHLAN H, RUSLI M, AS'AD A, et al. Numerical study on the symmetric and asymmetric orientation of the crack branching in 2D plate[J]. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 2020, 830(4): 42026. doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/830/4/042026 [6] 魏华建, 董茜茜, 王酉钰. 拉伸荷载下分支裂隙破坏机理研究[J]. 应用力学学报, 2021, 38(1): 150-157.WEI Huajian, DONG Qianqian, WANG Youyu. Research on failure mechanism of branch crack under tensile loading[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 2021, 38(1): 150-157. (in Chinese) [7] KORNEV V M, KURGUZOV V D. Prefracture zones in quasibrittle materials with branched and kinked cracks[J]. Physical Mesomechanics, 2010, 13(1/2): 54-61. [8] CHEN J, ZHOU X. The enhanced extended finite element method for the propagation of complex branched cracks[J]. Engineering Analysis With Boundary Elements, 2019, 104: 46-62. doi: 10.1016/j.enganabound.2019.03.028 [9] 张端, 董茜茜. 裂隙分支对单轴拉伸下裂纹破坏模式的影响[J]. 矿业研究与开发, 2020, 40(11): 64-70.ZHANG Duan, DONG Qianqian. Effect of fissure branches on crack failure modes under uniaxial tension[J]. Mining Research and Development, 2020, 40(11): 64-70. (in Chinese) [10] LI X, LI X, JIANG X. Influence of a micro-crack on the finite macro-crack[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2017, 177: 95-103. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2017.03.037 [11] LI X, JIANG X, LI X, et al. Solution of an inclined crack in a finite plane and a new criterion to predict fatigue crack propagation[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2016, 119: 217-223. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2016.10.019 [12] 邢帅兵, 王强胜, 生月, 等. 圆形杂质对裂纹扩展的影响[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2019, 40(2): 189-199. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.390136XING Shuaibing, WANG Qiangsheng, SHENG Yue, et al. Effects of circular inhomogeneity on crack propagation[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2019, 40(2): 189-199. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.390136 [13] YAN X. A numerical analysis of stress intensity factors at bifurcated cracks[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2006, 13(4): 629-637. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2004.12.043 [14] 文良华. 钢轨损伤行为的研究[D]. 硕士学位论文. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2015.WEN Lianghua. The research of rail damage behavior[D]. Master Thesis. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2015. (in Chinese) [15] QUINN G D. On crack branching angles in glasses and ceramics[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2020, 40(14): 4711-4721. doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2019.11.024 [16] CHEN Y Z, LIN X Y. Numerical solution for the T-stress in branch crack problem with infinitesimal branch length[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2010, 77(13): 2593-2600. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2010.06.016 [17] GHORBANPOOR R, SABERI-NADJAFI J, LONG N M A N, et al. Stability and convergence analysis of singular integral equations for unequal arms branch crack problems in plane elasticity[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2022, 103: 731-749. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2021.11.009 [18] 李煦, 苏睿, 张欢, 等. 微裂纹群对主裂纹尖端损伤行为的影响[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2022, 43(12): 1347-1358. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.420333LI Xu, SU Rui, ZHANG Huan, et al. Influence of multiple micro cracks on the damage behavior of a macro-crack tip[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2022, 43(12): 1347-1358. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.420333 [19] 郭钊, 郭子涛, 易玲艳. 多裂纹问题计算分析的本征COD边界积分方程方法[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2019, 40(2): 200-209. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.390183GUO Zhao, GUO Zitao, YI Lingyan. Analysis of multicrack problems with eigen COD boundary integral equations[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2019, 40(2): 200-209. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.390183 -





 下载:
下载:









 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号