Surface Effects on Thermal Stresses Around the Nanohole in Thermoelectric Material
-
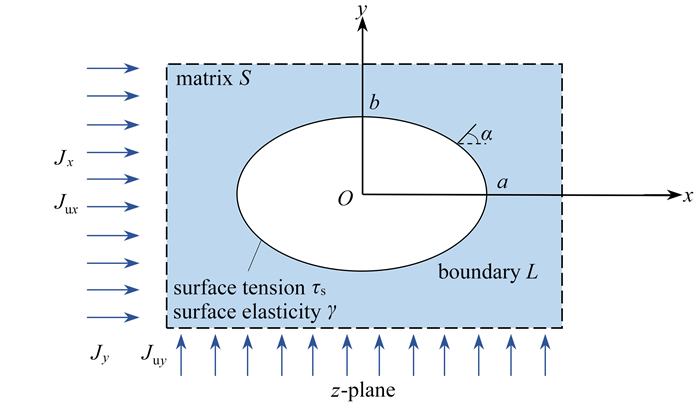
摘要: 基于完整Gurtin-Murdoch(G-M)低阶表面能模型,进一步探讨了纳米尺度下表面效应的影响. 建立了合理考虑构型变化的应力边界条件,实现了研究尺度从宏观到微观的转变. 利用复变函数理论和保角映射技术,构建了用于纳米尺度下的热-电-力理论框架模型,得到了热电基体中纳米孔周围热场、温度场以及应力场的半解析解. 数值结果表明,相对于完整G-M模型,简化G-M模型(忽略孔洞构型变化的影响)往往会高估表面效应和远场热电载荷对热应力分布的影响. 此外,表面效应的存在将在一定程度上缓解纳米孔周围的热应力集中.
-
关键词:
- 热电材料 /
- 完整Gurtin-Murdoch模型 /
- 表面效应 /
- 复变函数理论 /
- 纳米孔
Abstract: Based on the complete Gurtin-Murdoch (G-M) low-order surface energy model, the surface effects at nanoscale were further explored. The transition from macroscale to microscale was achieved through construction of reasonable stress boundary conditions in view of the change of hole geometry configuration. With the series expansion techniques and complex variable methods, the semi-analytic solutions for the electric field, the temperature field, and the full stress field in the vicinity of the nanohole within the thermoelectric matrix were derived eventually with a built thermal-electrical-force theoretical framework model at nanoscale. Numerical results show that, compared with the complete G-M model, the simplified G-M model (neglecting the effects of nanohole geometry changes) would overestimate the surface effects and far-field thermoelectric loading effects on the thermal stress distributions. In addition, the surface effects can relieve the thermal stress concentration around the nanohole to some extent. -
表 1 Bi2Te3和PbTe的材料性能
Table 1. Properties of the Bi2Te3 material and the PbTe material
δ/(S/m) E/GPa ε/(V/K) κ/(W/(m·K)) λ/K-1 ν Bi2Te3 1.1×105 47 2×10-4 1.6 2.7×10-5 0.4 PbTe 1×104 58 3×10-4 1.5 2×10-5 0.29 表 2 不同表面弹性与表面张力共同作用下的环向应力值(单位:MPa)
Table 2. Hoop stresses under the combined actions of different surface elasticities and surface tensions (unit: MPa)
surface elasticity γ/(N/m) δtt/MPa τs=0.2 N/m τs=0.6 N/m τs=1.0 N/m 0 138.587 0 136.587 0 134.587 0 0.2 138.573 3 136.573 3 134.573 4 0.6 138.545 8 136.546 0 134.546 1 1.0 138.518 3 136.518 6 134.518 9 -
[1] BISWAS K, HE J Q, BLUM I D, et al. High-performance bulk thermoelectrics with all-scale hierarchical architectures[J]. Nature, 2012, 489: 414-418. doi: 10.1038/nature11439 [2] ZHAO L D, LO S H, ZHANG Y S, et al. Ultralow thermal conductivity and high thermoelectric figure of merit in SnSe crystals[J]. Nature, 2014, 508: 373-377. doi: 10.1038/nature13184 [3] MARTIN-GONZALEZ M, CABALLERO-CALERO O, DIAZ-CHAO P. Nanoengineering thermoelectrics for 21st century: energy harvesting and other trends in the field[J]. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2013, 24: 288-305. [4] LIU W S, YAN X, CHEN G, et al. Recent advances in thermoelectric nanocomposites[J]. Nano Energy, 2012, 1(1): 42-56. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2011.10.001 [5] DRESSELHAUS M S, CHEN G, TANG M Y, et al. New directions for low-dimensional thermoelectric materials[J]. Advanced Materials, 2007, 19(8): 1043-1053. doi: 10.1002/adma.200600527 [6] WU Y H, ZHAI R S, ZHU T J, et al. Enhancing room temperature thermoelectric performance of n-type polycrystalline bismuth-telluride-based alloys via Ag doping and hot deformation[J]. Materials Today Physics, 2017, 2: 62-68. doi: 10.1016/j.mtphys.2017.09.001 [7] WANG Y, LIU W D, GAO H, et al. High porosity in nanostructured n-type Bi2Te3 obtaining ultralow lattice thermal conductivity[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(34): 31237-31244. [8] XU B A, FENG T L, AGNE M T, et al. Highly porous thermoelectric nanocomposites with low thermal conductivity and high figure of merit from large-scale solution-synthesized Bi2Te2.5Se0.5 hollow nanostructures[J]. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition, 2017, 56(13): 3546-3551. doi: 10.1002/anie.201612041 [9] TARKHANYAN R H, NIARCHOS D G. Reduction of thermal conductivity in porous "gray" materials[J]. APL Materials, 2014, 2(7): 076107. doi: 10.1063/1.4886220 [10] DUAN H L, WANG J, KARIHALOO B L, et al. Nanoporous materials can be made stiffer than non-porous counterparts by surface modification[J]. ACTA Materialia, 2006, 54(11): 2983-2990. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2006.02.035 [11] YU C B, YANG H B, SONG K, et al. Stress concentration around an arbitrarily-shaped hole in nonlinear fully coupled thermoelectric materials[J]. Journal of Mechanics of Materials and Structures, 2019, 14(2): 259-276. doi: 10.2140/jomms.2019.14.259 [12] 崔春丽, 徐耀玲. 预测纳米纤维复合材料有效弹性性能的界面模型和界面相模型[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2022, 43(8): 877-887. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.420231CUI Chunli, XU Yaoling. The interface model and the interphase model for predicting the effective elastic properties of nano-fiber composites[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2022, 43(8): 877-887. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.420231 [13] GURTIN M E, MURDOCH A I. A continuum theory of elastic material surfaces[J]. Archive for Rational Mechanics Analysis, 1975, 57(4): 291-323. doi: 10.1007/BF00261375 [14] DAI M, GAO C F, RU C Q. Surface tension-induced stress concentration around a nanosized hole of arbitrary shape in an elastic half-plane[J]. Meccanica, 2014, 49(12): 2847-2859. doi: 10.1007/s11012-014-0030-y [15] WANG S, YANG H B, GAO C F, et al. In-plane stress analysis of two nanoscale holes under surface tension[J]. Archive of Applied Mechanics, 2020, 90(6): 1363-1372. doi: 10.1007/s00419-020-01672-9 [16] 冯国益, 肖俊华, 苏梦雨. 考虑表面效应时孔边均布径向多裂纹Ⅲ型断裂力学分析[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2020, 41(4): 376-385. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.400177FENG Guoyi, XIAO Junhua, SU Mengyu. Fracture mechanics analysis of mode-Ⅲ fadial multi cracks on the edge of a hole with surface effects[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2020, 41(4): 376-385. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.400177 [17] WANG S, DAI M, RU C Q, et al. Surface tension-induced interfacial stresses around a nanoscale inclusion of arbitrary shape[J]. Zeitschrift fur Angewandte Mathematik und Physik, 2017, 68(6): 127. doi: 10.1007/s00033-017-0876-7 [18] WANG S, LI X Y, YI X, et al. Morphological changes of nanofiber cross-sections due to surface tension[J]. Extreme Mechanics Letters, 2021, 44: 101211. doi: 10.1016/j.eml.2021.101211 [19] 黄汝超, 陈永强. 残余界面应力对粒子填充热弹性纳米复合材料有效热膨胀系数的影响[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2011, 32(11): 1283-1293. doi: 10.3879/j.issn.1000-0887.2011.11.003HUANG Ruchao, CHEN Yongqiang. Effects of residual interface stress on effective thermal expansion coefficient of particle-filled composite[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2011, 32(11): 1283-1293. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3879/j.issn.1000-0887.2011.11.003 [20] SONG K, SONG H P, SCHIAVONE P, et al. The effects of surface elasticity on the thermal stress around a circular nano-hole in a thermoelectric material[J]. Mathematics and Mechanics of Solids, 2019, 24(10): 3156-3166. doi: 10.1177/1081286519837315 [21] DAI M, GHARAHI A, SCHIAVONE P. Note on the deformation-induced change in the curvature of a material surface in plane deformations[J]. Mechanics Research Communications, 2018, 94: 88-90. doi: 10.1016/j.mechrescom.2018.10.001 [22] DAI M, SCHIAVONE P. Deformation-induced change in the geometry of a general material surface and its relation to the Gurtin-Murdoch model[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics-Transactions of the ASME, 2020, 87(6): 061005. doi: 10.1115/1.4046635 [23] ZHANG A B, WANG B L. Explicit solutions of an elliptic hole or a crack problem in thermoelectric materials[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2016, 151: 11-21. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2015.11.013 [24] WANG P, WANG B L, WANG K F, et al. Analysis of inclusion in thermoelectric materials: the thermal stress field and the effect of inclusion on thermoelectric properties[J]. Composites (Part B): Engineering, 2019, 166: 130-138. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.11.120 [25] MOGILEVSKAYA S G, CROUCH S L, STOLARSKI H K. Multiple interacting circular nano-inhomogeneities with surface/interface effects[J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 2008, 56(6): 2298-2327. doi: 10.1016/j.jmps.2008.01.001 [26] DAI M, WANG Y J, SCHIAVONE P. Integral-type stress boundary condition in the complete Gurtin-Murdoch surface model with accompanying complex variable representation[J]. Journal of Elasticity, 2019, 134(2): 235-241. doi: 10.1007/s10659-018-9695-0 [27] PEI P Y, YANG H B, DAI M. Consistency of the boundary value problem of an elastic body involving surface tension in small deformations[J]. Mathematics and Mechanics of Solids, 2023, 28(6): 1488-1499. doi: 10.1177/10812865221122151 [28] MENG Q L, KONG S, HUANG Z W, et al. Simultaneous enhancement in the power factor and thermoelectric performance of copper sulfide by In2S3 doping[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2016, 4(32): 12624-12629. doi: 10.1039/C6TA03780A [29] DENNLER G, CHMIELOWSKI R, JACOB S, et al. Are binary copper sulfides/selenides really new and promising thermoelectric materials?[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2014, 4(9): 1301581. doi: 10.1002/aenm.201301581 [30] DAI M, LI M, SCHIAVONE P. Plane deformations of an inhomogeneity-matrix system incorporating a compressible liquid inhomogeneity and complete Gurtin-Murdoch interface model[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics-Transactions of the ASME, 2018, 85(12): 121010. doi: 10.1115/1.4041469 -





 下载:
下载:








 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号