Study on Sound Insulation Characteristics of Thin Plate Acoustic Metamaterials With Flexoelectric Effects
edited-by
edited-by
(Contributed by MENG Han, M.AMM Youth Editorial Board)-
摘要: 区别于传统的压电效应,当结构尺寸减小到微纳米尺度时,一种新的力电耦合效应——挠曲电效应将无法被忽略. 该文利用变分原理推导了考虑挠曲电效应的薄板声学超材料结构隔声问题的控制方程和边界条件,基于Kirchhoff薄板理论预测了薄板质量块结构的隔声曲线,系统讨论了挠曲电效应、几何尺寸、质量密度等参数对结构隔声性能的影响. 结果表明,当结构尺寸减小到微纳米尺度时,挠曲电效应显著增加了隔声曲线的隔声谷值和峰值频率,因此考虑挠曲电效应是十分有必要的. 该文的工作有望为微机电系统的噪声控制研究提供理论基础.Abstract: When the structure size is reduced to the micro-and nano-scale, a new mechanoelectric coupling effect, the flexoelectric effect, cannot be ignored. The governing equations and boundary conditions for the sound insulation problem of thin plate acoustic metamaterial structure with the flexoelectric effects were derived by means of the variational principle. The sound insulation curves of thin plate mass blocks were predicted based on the Kirchhoff theory. The effects of flexural effects, geometric sizes and mass densities on the sound insulation performances of the structure were systematically discussed. The results show that, for the micro-and nano-scale structure sizes, the flexoelectric effect significantly increases the sound insulation valley values and peak frequencies of the sound insulation curves, so it is necessary to consider the flexoelectric effects. This work provides a theoretical basis for the research of noise control in MEMS.edited-byedited-by1) (我刊青年编委孟晗来稿)
-
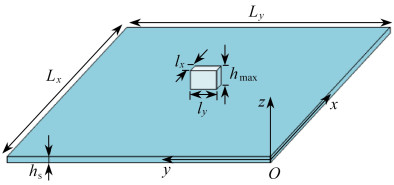
parameter value plate length Lx=500 nm plate width Ly=500 nm plate density ρs=7 500 kg/m3 plate thickness hs=10 nm mass block length lx=50 nm mass block width ly=50 nm mass block density ρmass=7 550 kg/m3 mass block thickness hmass=100 nm elasticity modulus c11=c22=1.26×1011 N/m2, c12=7.95×1010 N/m2, c66=2.325×1010 N/m2 piezoelectric coefficient e311=e322=-6.5 C/m2 flexoelectricity coefficient f3113=f3223=1×10-7 C/m dielectric constant a33=1.302×10-8 C/(V·m) -
[1] 田源, 葛浩, 卢明辉, 等. 声学超构材料及其物理效应的研究进展[J]. 物理学报, 2019, 68(19): 194301. doi: 10.7498/aps.68.20190850TIAN Yuan, GE Hao, LU Minghui, et al. Research advances in acoustic metamaterials[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2019, 68(19): 194301. (in Chinese) doi: 10.7498/aps.68.20190850 [2] MA G, YANG M, YANG Z, et al. Low-frequency narrow-band acoustic filter with large orifice[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2013, 103(1): 011903. doi: 10.1063/1.4812974 [3] PARK J J, KWAK J H, SONG K. Ultraslow medium with an acoustic membrane-like undamped dynamic vibration absorber for low-frequency isolation[J]. Extreme Mechanics Letters, 2021, 43: 101203. doi: 10.1016/j.eml.2021.101203 [4] YAO S, ZHOU X, HU G. Investigation of the negative-mass behaviors occurring below a cut-off frequency[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2010, 12(10): 103025. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/12/10/103025 [5] MEI J, MA G, YANG M, et al. Dark acoustic metamaterials as super absorbers for low-frequency soun[J]. Nature Communications, 2012, 3: 756. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1758 [6] KALAEE M, MIRHOSSEINI M, DIETERLE P B, et al. Quantum electromechanics of a hypersonic crystal[J]. Nature Nanotechnology, 2019, 14(4): 334-339. doi: 10.1038/s41565-019-0377-2 [7] CUENOT S, FRÉTIGNY C, DEMOUSTIER-CHAMPAGNE S, et al. Surface tension effect on the mechanical properties of nanomaterials measured by atomic force microscopy[J]. Physical Review B: Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 2004, 69(16): 165410. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.69.165410 [8] WANG Z L, SONG J. Piezoelectric nanogenerators based on zinc oxide nanowire arrays[J]. Science, 2006, 312(5771): 242-246. doi: 10.1126/science.1124005 [9] WANG X, ZHOU J, SONG J, et al. Piezoelectric field effect transistor and nanoforce sensor based on a single ZnO nanowire[J]. Nano Letters, 2006, 6(12): 2768-2772. doi: 10.1021/nl061802g [10] JIANG X, HUANG W, ZHANG S. Flexoelectric nano-generator: materials, structures and devices[J]. Nano Energy, 2013, 2(6): 1079. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2013.09.001 [11] ZHANG Z, JIANG L. Size effects on electromechanical coupling fields of a bending piezoelectric nanoplate due to surface effects and flexoelectricity[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2014, 116: 134308. doi: 10.1063/1.4897367 [12] SHEN S, HU S. A theory of flexoelectricity with surface effect for elastic dielectrics[J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics Solids, 2010, 58(5): 665-677. doi: 10.1016/j.jmps.2010.03.001 [13] 王平, 黄庆安, 于虹. 纳机电系统阻尼及噪声研究进展[J]. 电子器件, 2004, 27(3): 527-532. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9490.2004.03.039WANG Ping, HUANG Qing'an, YU Hong. Research and ptogress of damping and noise in NEMS[J]. Chinese Journal of Electron Devices, 2004, 27(3): 527-532. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9490.2004.03.039 [14] 任树伟, 辛锋先, 卢天健. 考虑尺度效应的微平板声振耦合特性研究[J]. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2014, 44(2): 201-208.REN Shuwei, XIN Fengxian, LU Tianjian. Vibroacoustic characteristics of micro-plates considering scale effect[J]. Scientia Sinica: Technologica, 2014, 44(2): 201-208. (in Chinese) [15] 原庆丹, 郭俊宏. 一维纳米准晶层合梁的非局部振动、屈曲与弯曲研究[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2024, 45(2): 208-219.YUAN Qingdan, GUO Junhong. Nonlocal vibration, buckling and bending of 1D layered quasicrystal nanobeams[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2024, 45(2): 208-219. (in Chinese) [16] GHORBANPOUR A A, SOLTAN A A H, HAGHPARAST E. Flexoelectric and surface effects on vibration frequencies of annular nanoplate[J]. Indian Journal of Physics, 2021, 95(10): 2063-2083. doi: 10.1007/s12648-020-01854-9 -





 下载:
下载:








 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号