Dynamic Behavior of a Stochastic Predator Prey Model With the Gilpin-Ayala Growth
-
摘要:
该文研究了一类具有Gilpin-Ayala增长的随机捕食-食饵模型的动力学行为,证明了系统全局正解的存在性和唯一性,得到了灭绝性和持久性的充分条件。在此基础上,给出了控制捕食-食饵系统随机持久和灭绝的阈值,并且讨论了系统解的一些渐近性态。最后通过数值模拟,验证了结果的有效性。
-
关键词:
- Gilpin-Ayala增长 /
- 捕食-食饵模型 /
- Markov状态切换 /
- 脉冲扰动 /
- 持久性
Abstract:The dynamic behavior of a stochastic predator-prey model with the Gilpin-Ayala growth was studied. The existence and uniqueness of the global positive solution to the system were proved, and sufficient conditions for system extinction and persistence were obtained. On this basis, the thresholds for controlling the stochastic persistence and extinction of the predator-prey system were given, and some asymptotic behaviors of the solution were discussed. Finally, the effectiveness of the results was verified through numerical simulation.
-
Key words:
- Gilpin-Ayala growth /
- predator-prey model /
- Markov switching /
- impulsive disturbance /
- persistence
-
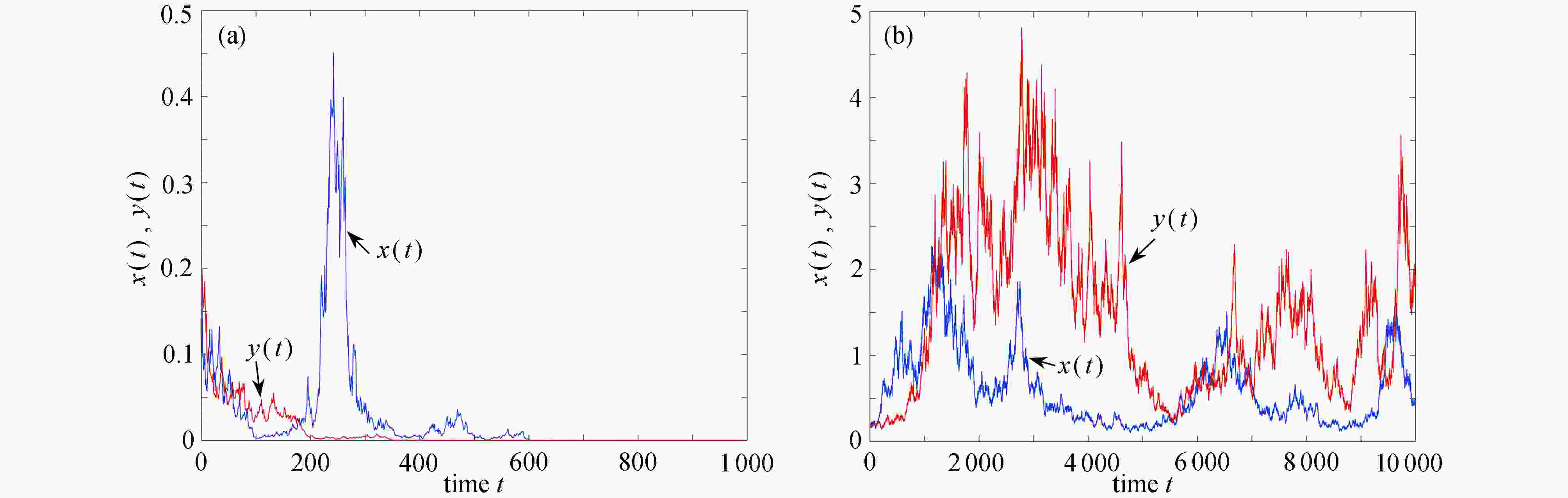
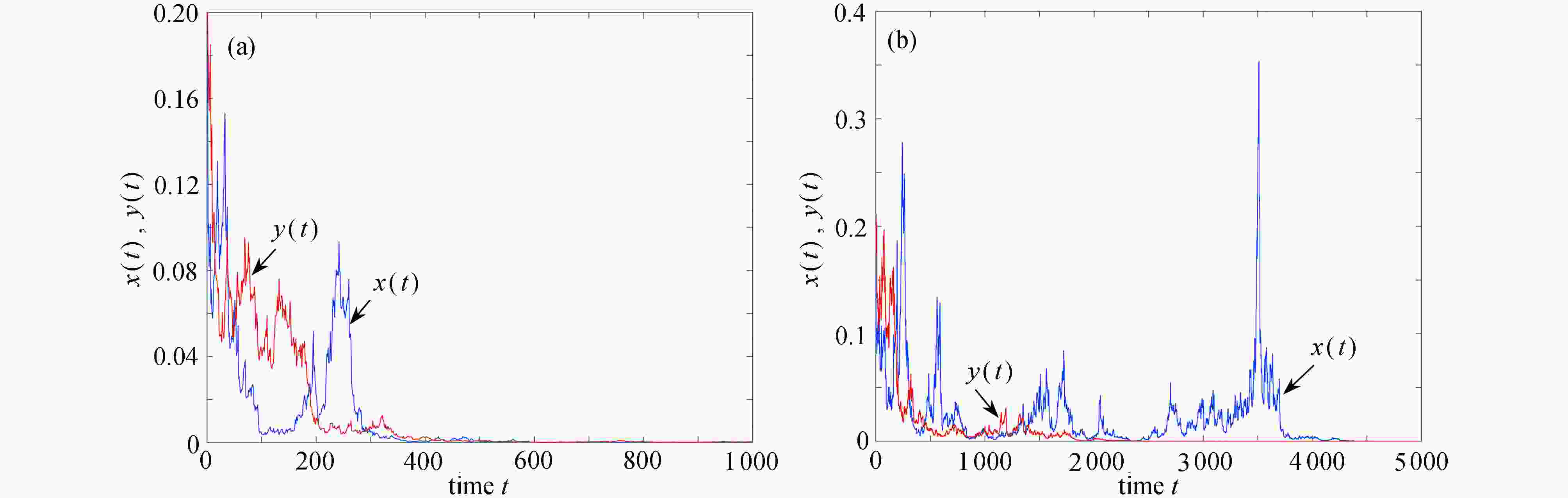
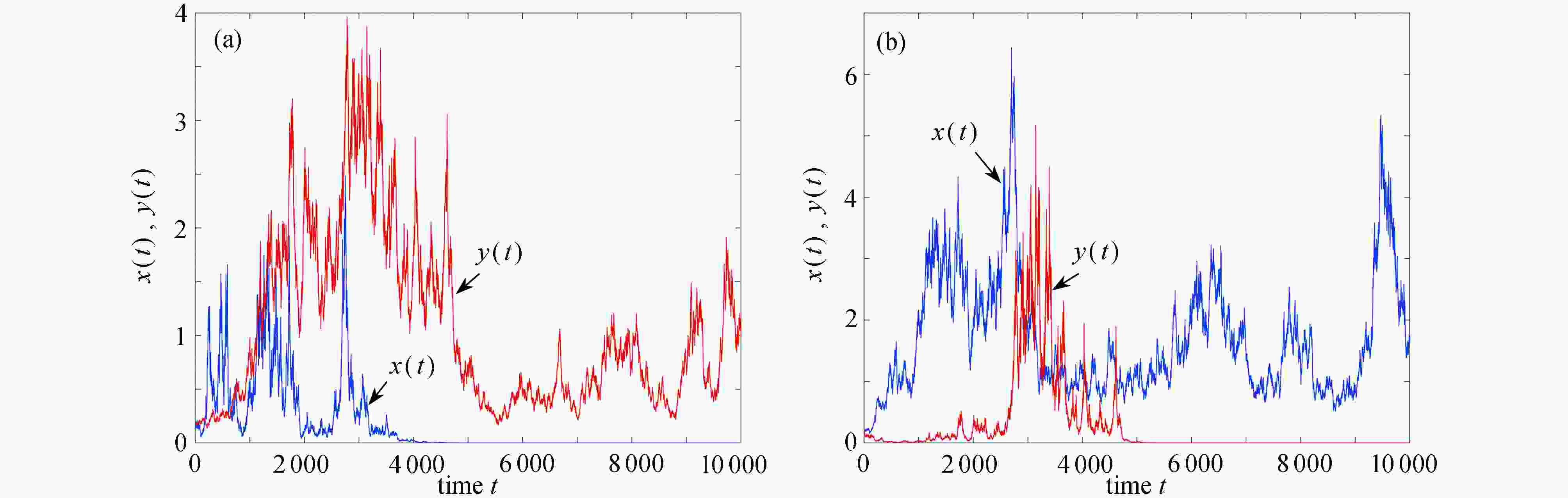
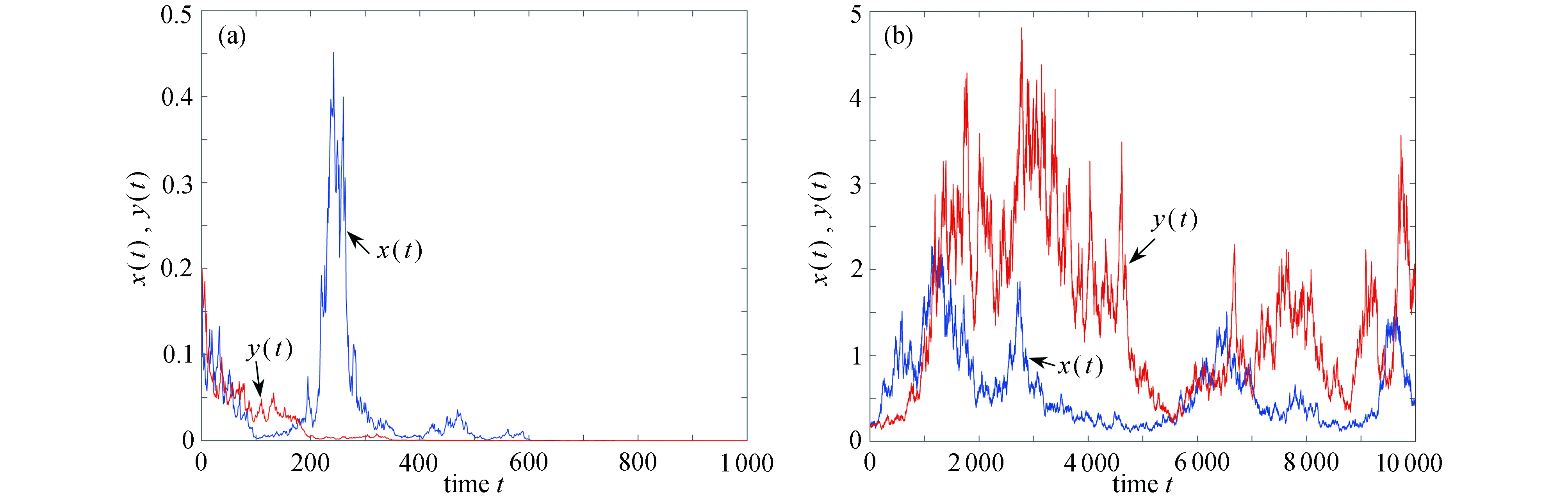
图 3 不考虑切换,例2参数下,两个子系统解的轨迹:(a) 子系统1,ξ(t)=1,(σ(1),σ(2))=
$ (\sqrt{0.12},\sqrt{0.82}) $ ;(b) 子系统2,ξ(t)=2,(σ(1),σ(2))=$ (\sqrt{0.82},\sqrt{0.12}) $ Figure 3. The trajectories of solutions to the 2 subsystems of example 2 without switching: (a) subsystem 1, ξ(t)=1, (σ(1), σ(2))=
$ (\sqrt{0.12},\sqrt{0.82}) $ ; (b) subsystem 2, ξ(t)=2, (σ(1), σ(2))=$ (\sqrt{0.82},\sqrt{0.12}) $ -
[1] BERRYMAN A A. The orgins and evolution of predator-prey theory[J]. Ecology, 1992, 73(5): 1530-1535. doi: 10.2307/1940005 [2] APPLETON D. Modelling biological populations in space and time[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society (Series C) : Applied Statistics, 1993, 42(2): 411-412. [3] 焦建军, 陈兰荪, 尼托 J J, 等. 连续收获捕食者与脉冲存放食饵的阶段结构捕食-食饵模型的全局吸引和一致持久[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2008, 29(5): 589-600. (JIAO Jianjun, CHEN Lansun, NIETO J J, et al. Permanence and global attractivity of a stage-structured predator-prey model with continuous harvesting on predator and impulsive stocking on prey[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2008, 29(5): 589-600.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3879/j.issn.1000-0887.2008.05.009 [4] 柳文清, 陈清婉. 捕食者食饵均染病的入侵反应扩散捕食系统中扩散的作用[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2019, 40(3): 321-331. (LIU Wenqing, CHEN Qingwan. Influence of diffusion on an invasion diffusion prey-predator model with disease infection in both populations[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2019, 40(3): 321-331.(in Chinese) doi: 10.1007/s10483-019-2443-9 [5] 刘荣, 刘桂荣. 周期环境中捕食者具有尺度结构的三物种捕食-食饵系统的最优收获[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2021, 42(5): 510-521. (LIU Rong, LIU Guirong. Optimal harvesting in a periodic 3-species predator-prey model with size structure in predators[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2021, 42(5): 510-521.(in Chinese) [6] WEI L, CHAO F, BOSHAN C. Hopf bifurcation for a predator-prey biological economic system with Holling type Ⅱ functional response[J]. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2011, 348(6): 1114-1127. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2011.04.019 [7] PERC M, SZOLNOKI A, SZABO G. Cyclical interactions with alliance-specific heterogeneous invasion rates[J]. Physical Review E, 2007, 75(5): 052102. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.75.052102 [8] PERC M, GRIGOLINI P. Collective behavior and evolutionary games: an introduction[J]. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2013, 56: 1-5. [9] HOLLING C S. The functional response of predators to prey density and its role in mimicry and population regulation[J]. Memoirs of the Entomological Society of Canada, 1965, 97(45): 1-60. [10] 陈兰荪, 陈键. 非线性生物动力系统[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1993.CHEN Lansun, CHEN Jian. Nonlinear Biological Dynamic System[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1993. (in Chinese) [11] 陈兰荪, 宋新宇, 陆征一. 数学生态学模型与研究方法[M]. 成都: 四川科学技术出版社, 2003.CHEN Lansun, SONG Xinyu, LU Zhengyi. Mathematical Models and Methods in Ecology[M]. Chengdu: Sichuan Science and Technology Press, 2004. (in Chinese) [12] 付胜男, 李祖雄. 一类具有状态脉冲控制的捕食-食饵模型的动力学研究[J]. 湖北民族大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 37(1): 45-49. (FU Shengnan, LI Zuxiong. Dynamical analysis of a predator-prey model with state impulsive controlling[J]. Journal of Hubei Minzu University (Natural Science Edition) , 2019, 37(1): 45-49.(in Chinese) [13] LIU Q, SHAO Y F, ZHOU S, et al. Dynamical behaviors of a three species predator-prey system with predator stage-structure and impulsive effects[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Mathematics, 2019, 36(2): 219-242. [14] 王克. 随机生物数学模型[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010.WANG Ke. Stochastic Biological Mathematical Model[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2010. (in Chinese) [15] KUMAR C P, REDDY K S, SRINIAVAS M. Dynamics of prey predator with Holling interactions and stochastic influences[J]. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 2017, 57(2): 1079-1086. [16] ZHANG X H, LI W X, LIU M, et al. Dynamics of a stochastic Holling Ⅱ one-predator two-prey system with jumps[J]. Physica A: Statical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2015, 421: 571-582. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2014.11.060 [17] JI C Y, JIANG D Q, SHI N Z. Analysis of a predator-prey model with modified Leslie-Gower and Holling-type Ⅱ schemes with stochastic perturbation[J]. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 2009, 359(2): 482-498. doi: 10.1016/j.jmaa.2009.05.039 [18] 张树文. 具Markov转换和脉冲扰动的捕食-食饵系统的动力学[J]. 数学物理学报, 2016, 36(3): 569-583. (ZHANG Shuwen. Dynamics behaviors of a predator-prey system with Markov switching and impulsive disturbance[J]. Acta Mathematica Scientia, 2016, 36(3): 569-583.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3998.2016.03.018 [19] JIANG X B, ZU L, JIANG D Q, et al. Analysis of a stochastic holling type Ⅱ predator-prey model under regime switching[J]. Bulletin of the Malaysian Mathematical Sciences Society, 2020, 43: 2171-2197. doi: 10.1007/s40840-019-00798-6 [20] AYALA F J, GILPIN M E, EHRENFELD J G. Competition between species: theoretical models and experimental tests[J]. Theoretical Population Biology, 1973, 4(3): 331-356. doi: 10.1016/0040-5809(73)90014-2 [21] GOPALSAMY K. Stability and Oscillations in Delay Differential Equations of Population Dynamics[M]. Mathematics and Its Applications, Vol 74. Berlin: Springer, 1992. [22] VASILOVA M. Asymptotic behavior of a stochastic Gilpin-Ayala predator-prey system with time-dependent delay[J]. Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 2013, 57(3/4): 764-781. [23] VASILOVA M, JOVANOVIC M. Stochastic Gilpin-Ayala competition model with infinite delay[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2011, 217(10): 4944-4959. doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2010.11.043 [24] JIANG Y, LIU Z J, YANG J, et al. Dynamics of a stochastic Gilpin-Ayala population model with Markovian switching and impulsive perturbations[J]. Advances in Difference Equations, 2020, 2020: 530. doi: 10.1186/s13662-020-02900-w [25] ANDERSON W J. Continuous-time Markov chains[J]. SIAM Review, 1994, 36(2): 316-317. doi: 10.1137/1036084 [26] LIU M, WANG K. Asymptotic properties and simulations of a stochastic logistic model under regime switching[J]. Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 2011, 54(9/10): 2139-2154. [27] LIU M, WANG K, WU Q. Survival analysis of stochastic competitive models in a polluted environment and stochastic competitive exclusion principle[J]. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology, 2011, 73(9): 1969-2012. doi: 10.1007/s11538-010-9569-5 [28] LIU M, WANG K. On a stochastic logistic equation with impulsive perturbations[J]. Computers and Mathematics With Applications: an International Journal, 2012, 63(5): 871-886. doi: 10.1016/j.camwa.2011.11.003 [29] MAO X R. Stochastic Differential Equations and Applications[M]. 2nd ed. Horwood Publishing Limited, 2007. [30] MAO X R, MARION G, RENSLAW E. Environmental Brownian noise suppresses explosions in population dynamics[J]. Stochastic Processes and Their Applications, 2002, 97(1): 95-110. doi: 10.1016/S0304-4149(01)00126-0 [31] PANG S L, DENG F Q, MAO X R. Asymptotic properties of stochastic population dynamics[J]. Dynamics of Continuous, Discrete and Impulsive Systems (Series A) : Mathematical Analysis, 2008, 15(5): 6386-6394. [32] ZHANG S Q, MENG X Z, TAO F, et al. Dynamics analysis and numerical simulations of a stochastic non-autonomous predator-prey system with impulsive effects[J]. Nonlinear Analysis: Hybrid Systems, 2017, 26: 19-37. doi: 10.1016/j.nahs.2017.04.003 -




 下载:
下载:





 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号