Dynamic Analyses of the Assembling Process of Ultra-Large Structures With Space Robots
-
摘要:
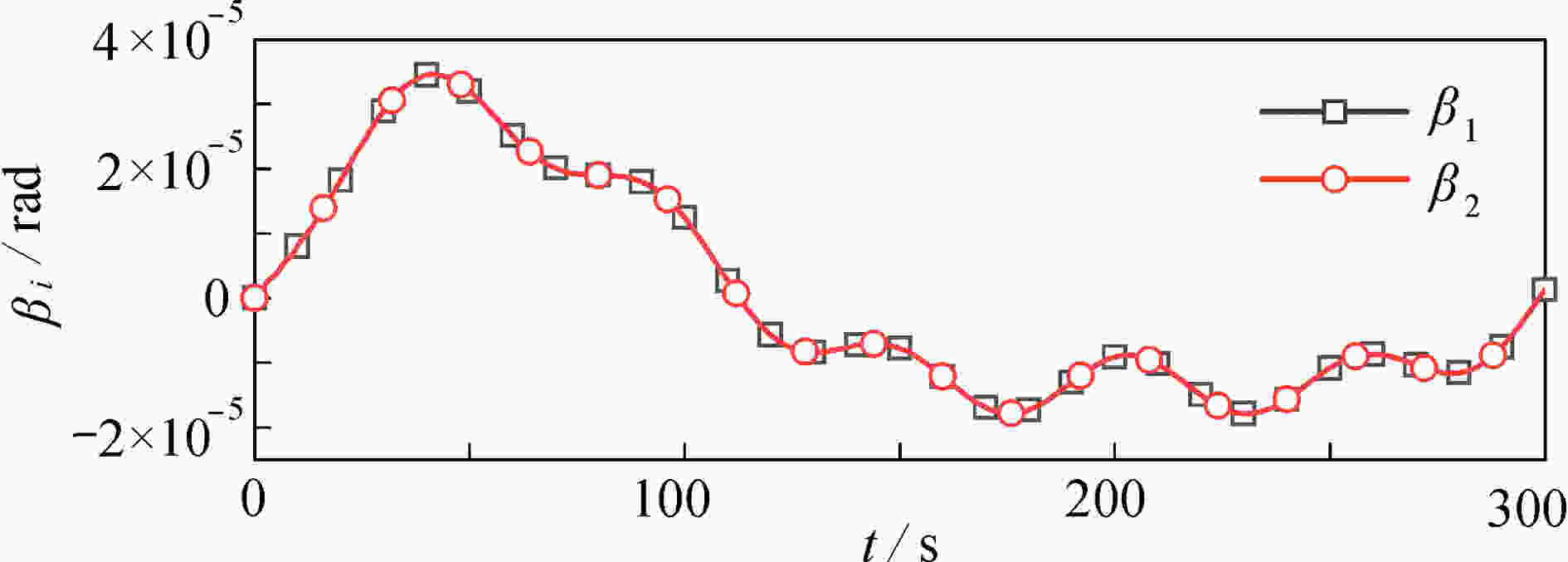
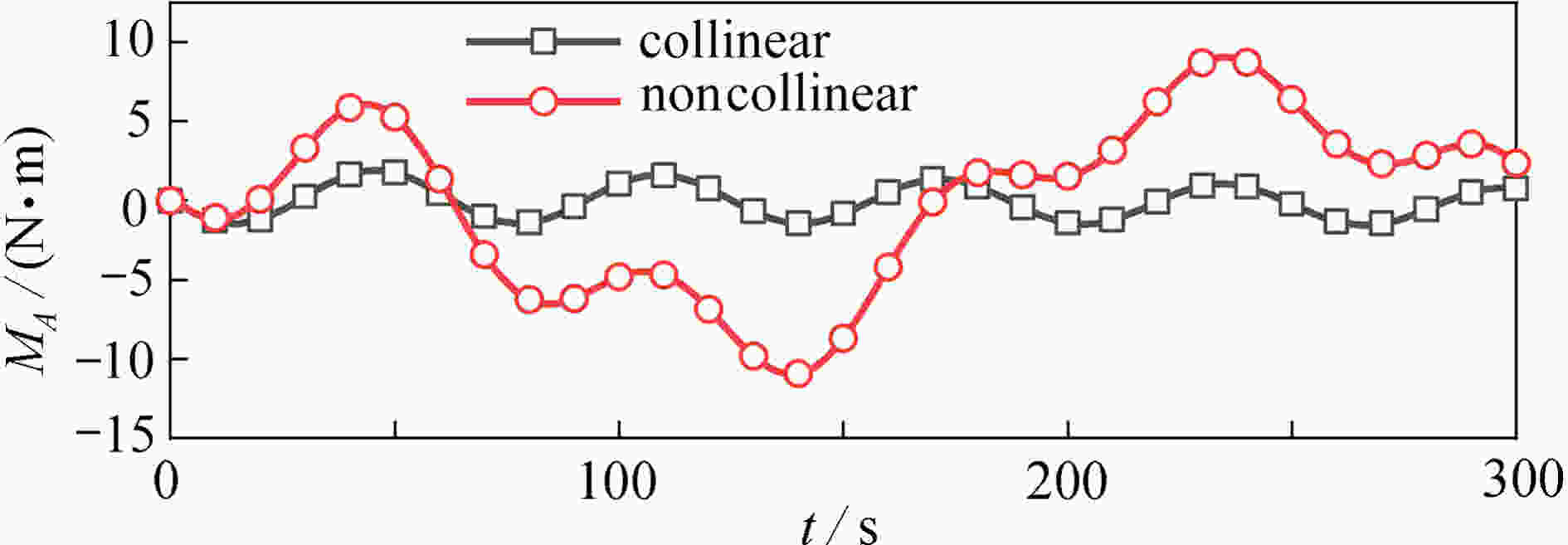
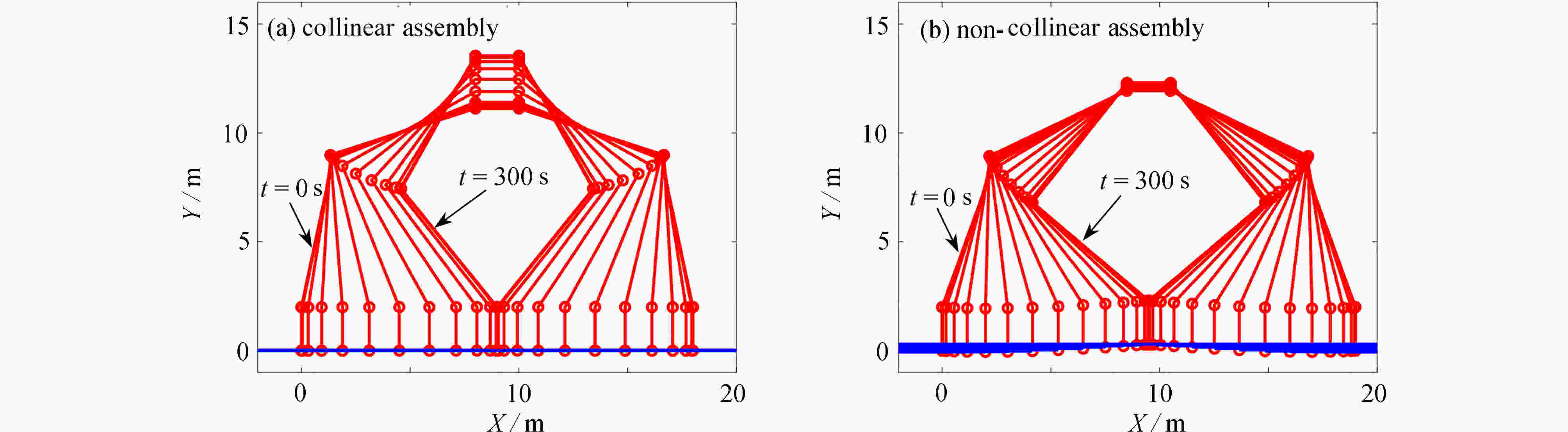
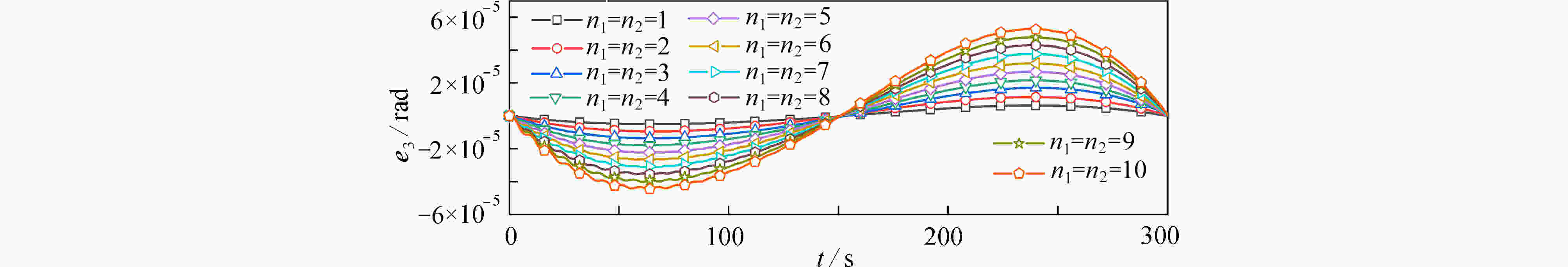
超大型航天结构具有超大柔性、超低固有频率的特点,空间机器人在轨组装时应尽可能避免激起超大型结构的柔性振动。空间机器人组装超大型结构模块的过程分成抓捕阶段、位姿调整与稳定阶段、安装阶段和爬行阶段。通过对安装阶段的动力学与控制研究,提出共线安装的轨迹规划方法,有效避免了柔性结构振动。首先,采用自然坐标法和绝对节点坐标法建立主结构-空间机器人-待组装结构的在轨组装系统动力学模型。然后,将共线安装的要求转化为空间机器人的轨迹规划约束,要求空间机器人质心到主结构/待组装结构的距离保持不变,实现共线安装的轨迹规划。数值仿真表明:提出的组装方法在组装过程中可有效避免超大型结构的横向运动,降低夹持力矩。最后,分析了系统参数对组装过程动力学响应的影响,为超大型航天器的在轨组装提供了参考。
Abstract:Structural vibrations of ultra-large structures during on-orbit assembly should be prevented to the maximum extent, given the extreme structural flexibility and low natural frequencies. The assembling process was divided into 4 stages: the grasping stage, the position-attitude adjusting and stabilizing stage, the mounting stage and the crawling stage. For the mounting stage, the dynamics and control were addressed, and a collinear assembly trajectory planning method was proposed to prevent structural vibrations. First, a dynamic model for the on-orbit assembly system including the main structure, the space robot and the assembling structure, was established based on natural coordinate formulation and absolute node coordinate formulation. Second, the requirements of collinear assembly were transformed into a trajectory planning problem of the space robot. The distance from the space robot mass center to the main structure should remain fixed, which is the main idea of the proposed collinear assembly method. Numerical simulation results show that, the proposed assembly method can effectively prevent the transverse motions of the ultra-large structure and reduce the required grasping moment. Finally, the influences of the system parameters on the dynamic responses during the assembly process were studied. The work provides a theoretical basis for the on-orbit assembly of ultra-large spacecraft.
-
表 1 刚体机械臂的参数
Table 1. Parameters of the rigid manipulator
parameter mechanical arms 1,4,7 mechanical arms 2,3,5,6 length l/m 2 7 density ρ/(kg/m³) 1000 1000 radius R/m 0.175 0.175 表 2 基本组装模块的参数
Table 2. Parameters of the basic assembly module
parameter meaning beam NM beam KI length l/m 100 100 cross sectional area A/m2 $0.011\;6$ $0.011\;6$ section second moment I/m4 $1.627\;9 \times {10^{ - 4} }$ $1.627\;9 \times {10^{ - 4} }$ density ρ/(kg/m³) 2 700 2 700 quality m/kg $3.132 \times {10^3}$ $3.132 \times {10^3}$ elastic modulus E/GPa 70 70 -
[1] 李庆军, 邓子辰, 王艳, 等. 空间太阳能电站的准对日定向姿态[J]. 宇航学报, 2019, 40(1): 29-40 doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2019.01.004LI Qingjun, DENG Zichen, WANG Yan, et al. Quasi-sun-pointing oriented attitude for solar power satellites[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2019, 40(1): 29-40.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2019.01.004 [2] 丁继锋, 高峰, 钟小平, 等. 在轨建造中的关键力学问题[J]. 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学, 2019, 49(2): 50-57DING Jifeng, GAO Feng, ZHONG Xiaoping, et al. The key mechanical problems of on-orbit construction[J]. Scientia Sinica: Physica, Mechanica & Astronomica, 2019, 49(2): 50-57.(in Chinese) [3] 沈晓凤, 曾令斌, 靳永强, 等. 在轨组装技术研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 载人航天, 2017, 23(2): 228-235 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5825.2017.02.016SHEN Xiaofeng, ZENG Lingbin, JIN Yongqiang, et al. Status and prospect of on-orbit assembly technology[J]. Manned Spaceflight, 2017, 23(2): 228-235.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5825.2017.02.016 [4] CHENG Z, HOU X, ZHANG X, et al. In-orbit assembly mission for the space solar power station[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2016, 129: 299-308. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2016.08.019 [5] 王恩美, 邬树楠, 吴志刚. 在轨组装空间结构面向主动控制的动力学建模[J]. 力学学报, 2020, 52(3): 805-816 doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-19-375WANG Enmei, WU Shunan, WU Zhigang. Active-control-oriented dynamic modelling for on-orbit assembly space structure[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2020, 52(3): 805-816.(in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-19-375 [6] CAO K, LI S, SHE Y, et al. Dynamics and on-orbit assembly strategies for an orb-shaped solar array[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2021, 178: 881-893. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2020.10.030 [7] WANG E, WU S, WU Z, et al. Distributed adaptive vibration control for solar power satellite during on-orbit assembly[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2019, 94: 105378. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2019.105378 [8] 荣吉利, 崔硕, 石文静, 等. 大型空间电站在轨展开与组装动力学与控制[J]. 宇航学报, 2021, 42(3): 295-304 doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2021.03.004RONG Jili, CUI Shuo, SHI Wenjing, et al. On-orbit deployment and assembly dynamics and control of large space power station[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2021, 42(3): 295-304.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2021.03.004 [9] CHEN T, WEN H, HU H, et al. Output consensus and collision avoidance of a team of flexible spacecraft for on-orbit autonomous assembly[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2016, 121: 271-281. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2015.11.004 [10] 周志成, 王兴龙, 曲广吉. 大型空间柔性组合航天器动力学建模与控制[J]. 中国科学: 物理学 力学 天文学, 2019, 49(2): 62-73ZHOU Zhicheng, WANG Xinglong, QU Guangji. Dynamic modeling and control of large flexible spacecraft combination[J]. Scientia Sinica: Physica, Mechanica & Astronomica, 2019, 49(2): 62-73.(in Chinese) [11] 朱安, 陈力. 配置柔顺机构空间机器人双臂捕获卫星操作力学模拟及基于神经网络的全阶滑模避撞柔顺控制[J]. 力学学报, 2019, 51(4): 1156-1169 doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-18-407ZHU An, CHEN Li. Mechanical simulation and full order sliding mode collision avoidance compliant control based on neural network of dual-arm space robot with compliant mechanism capturing satellite[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2019, 51(4): 1156-1169.(in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-18-407 [12] XU W, MENG D, CHEN Y, et al. Dynamics modeling and analysis of a flexible-base space robot for capturing large flexible spacecraft[J]. Multibody System Dynamics, 2014, 32(3): 357-401. doi: 10.1007/s11044-013-9389-0 [13] MENG D, LU W, XU W, et al. Vibration suppression control of free-floating space robots with flexible appendages for autonomous target capturing[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2018, 151: 904-918. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2018.07.044 [14] LU Y, HUANG Z, ZHANG W, et al. Experimental investigation on automated assembly of space structure from cooperative modular components[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2020, 171: 378-387. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2020.03.033 [15] DUBOWSKY S, BONING P. Coordinated control of space robot teams for the on-orbit construction of large flexible space structures[J]. Advanced Robotics, 2010, 24(3): 303-323. doi: 10.1163/016918609X12619993300665 [16] 王兴龙, 周志成, 王典军, 等. 面向空间近距离操作的机械臂与服务卫星协同控制[J]. 宇航学报, 2020, 41(1): 101-109 doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2020.01.012WANG Xinglong, ZHOU Zhicheng, WAGN Dianjun, et al. Cooperative control of manipulator and servicing satellite for spatial proximal operation[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2020, 41(1): 101-109.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2020.01.012 [17] 张凯锋, 周晖, 温庆平, 等. 空间站机械臂研究[J]. 空间科学学报, 2010, 30(6): 612-619 doi: 10.11728/cjss2010.06.612ZHANG Kaifeng, ZHOU Hui, WEN Qingping, et al. Review of the development of robotic manipulator for international space station[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2010, 30(6): 612-619.(in Chinese) doi: 10.11728/cjss2010.06.612 [18] ESCALONA J L, HUSSIEN H A, SHABANA A A. Application of the absolute nodal coordinate formulation to multibody system dynamics[J]. Journal of Sound & Vibration, 1998, 214(5): 833-851. [19] SHABANA A. Dynamics of Multibody Systems[M]. 4th ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2013. [20] 陶红武, 谭跃刚, 陈建文. 四足机器人单腿系统及其跳跃柔顺控制的研究[J]. 机械设计与制造, 2022(1): 290-294 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3997.2022.01.065TAO Hongwu, TAN Yuegang, CHEN Jianwen. Research on the design and jump compliance control of single leg system for a quadruped robot[J]. Machinery Design & Manufacture, 2022(1): 290-294.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3997.2022.01.065 -




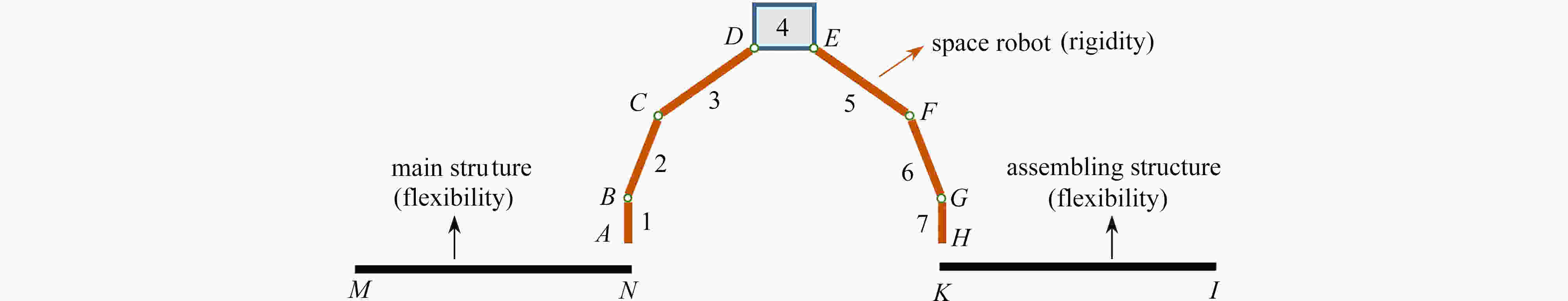
 下载:
下载:
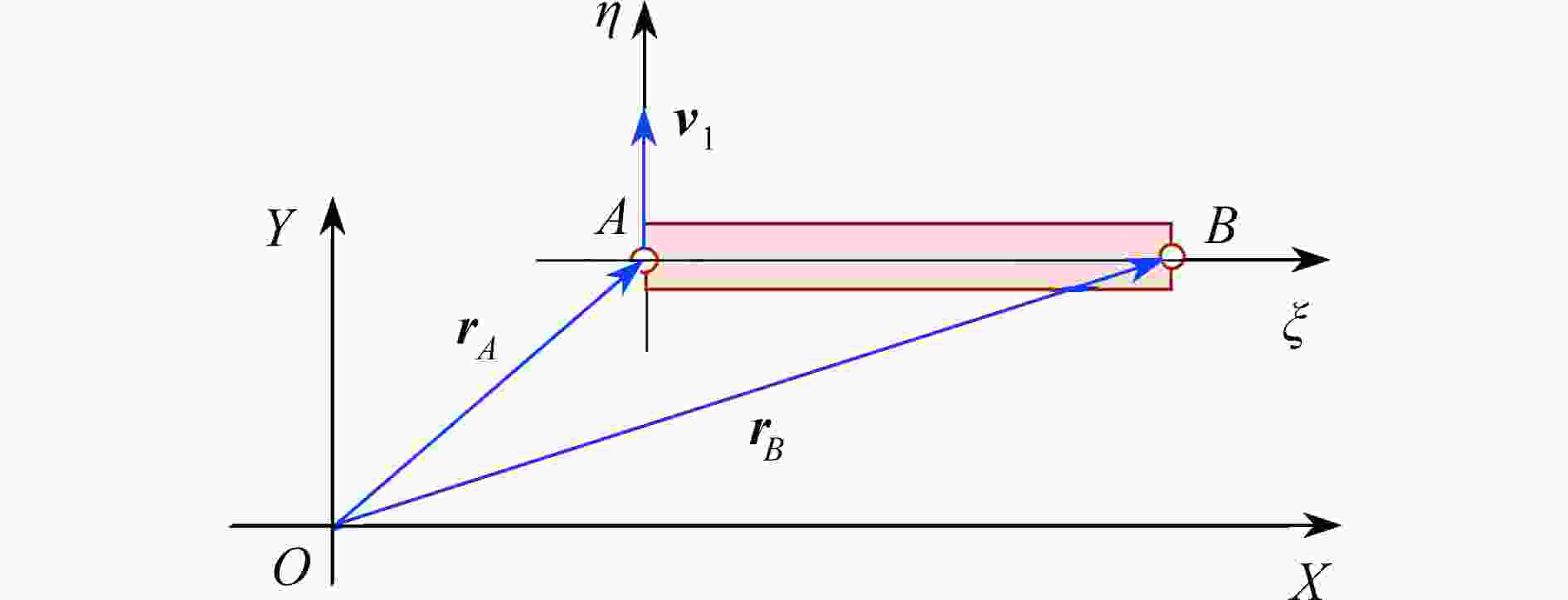
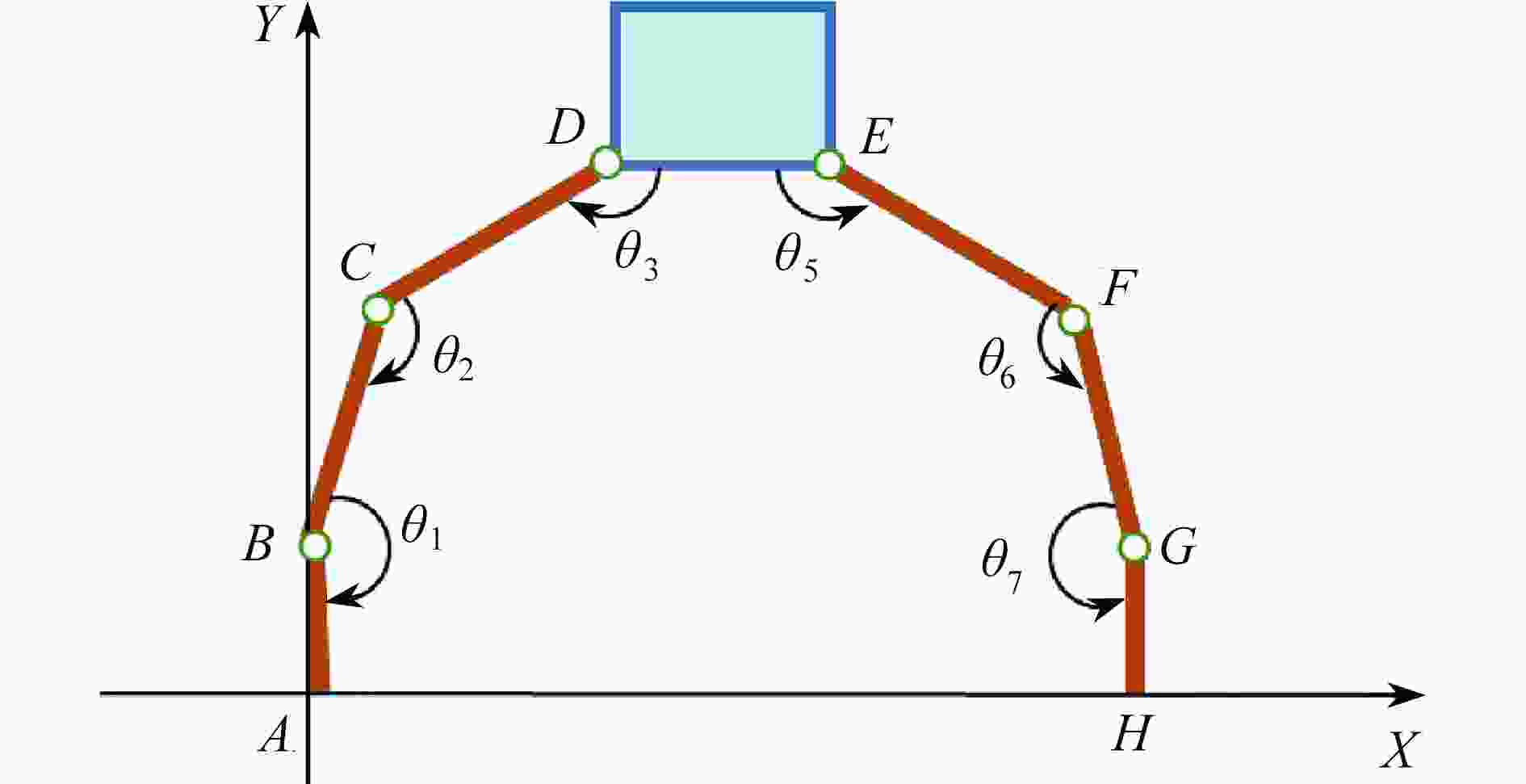
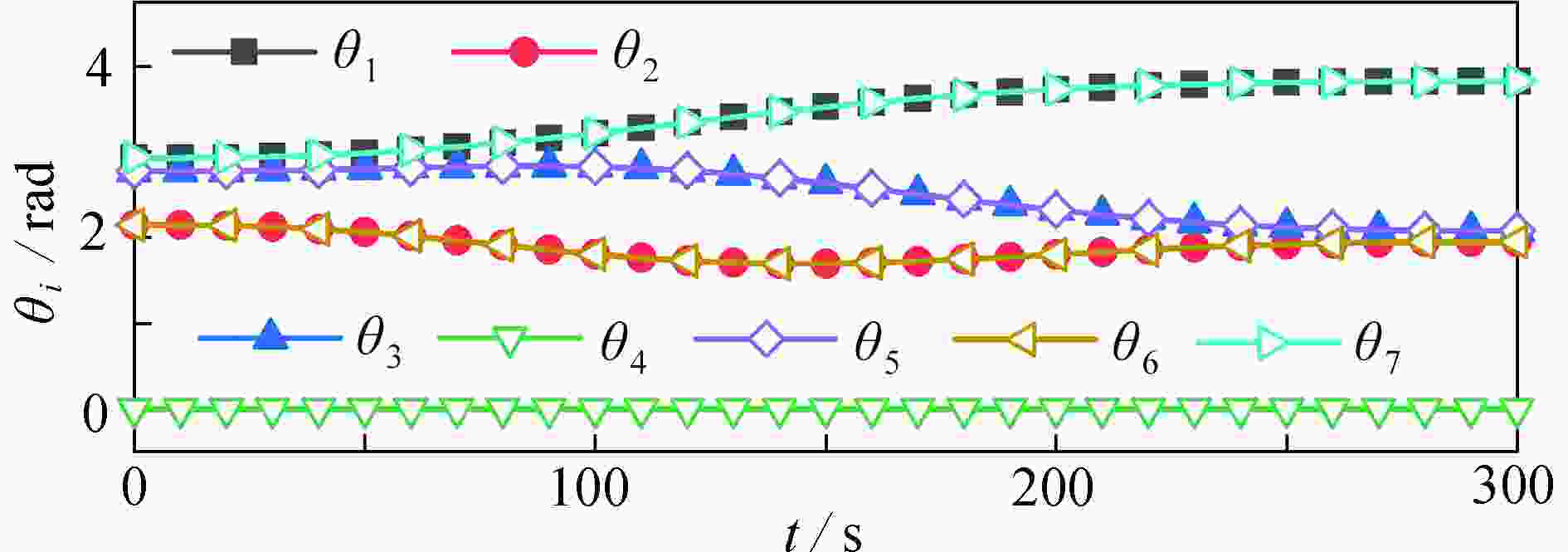
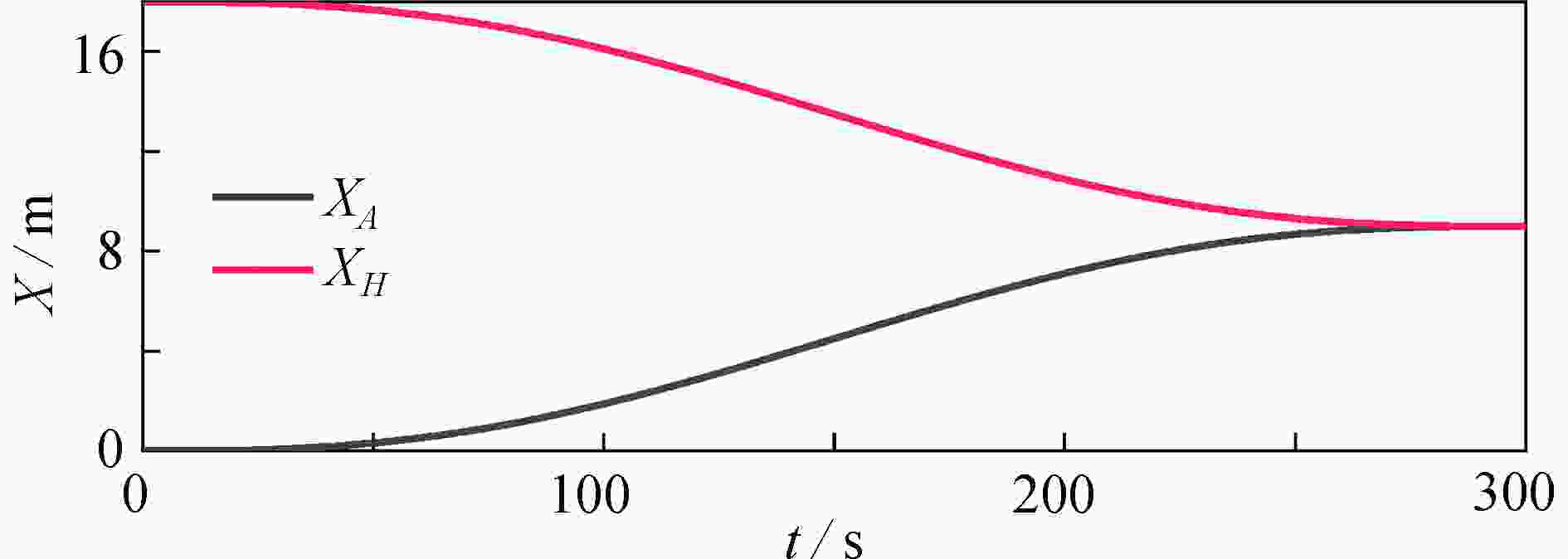
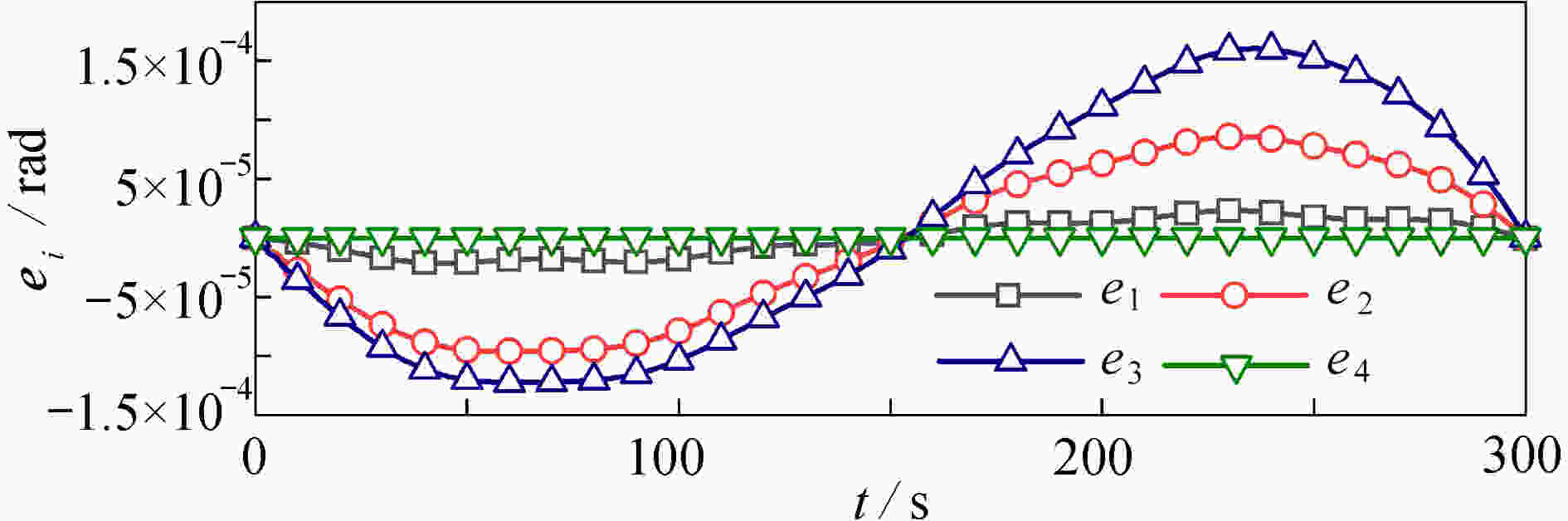

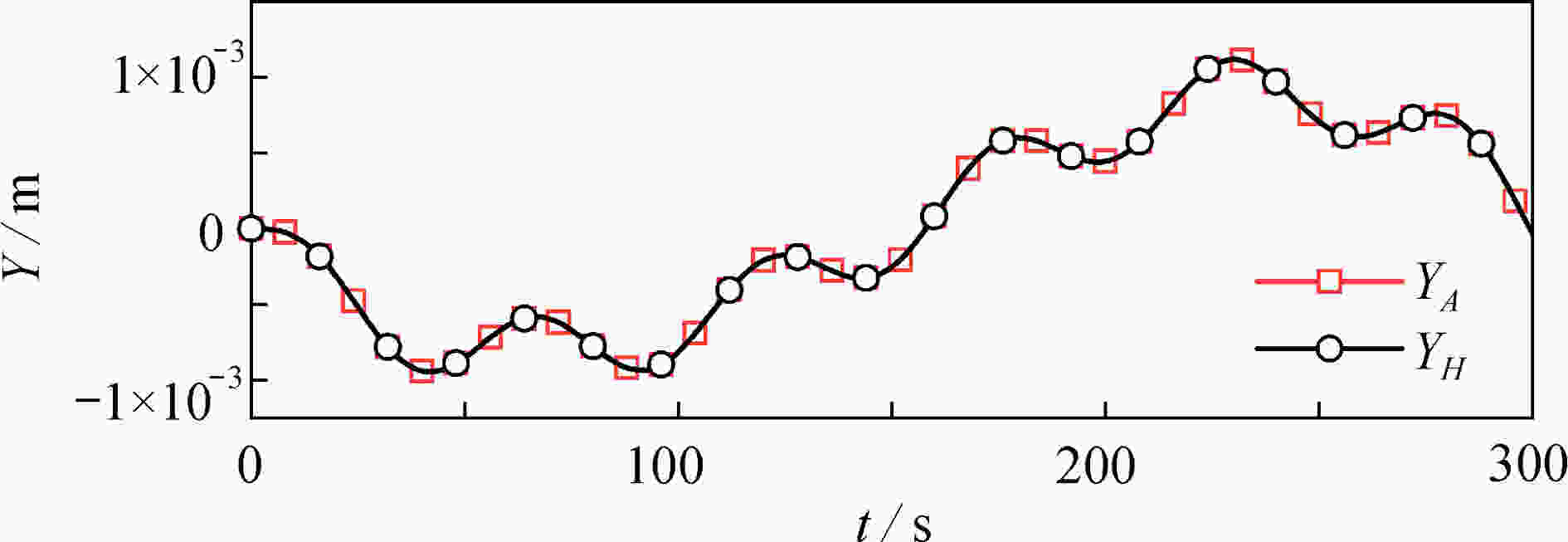


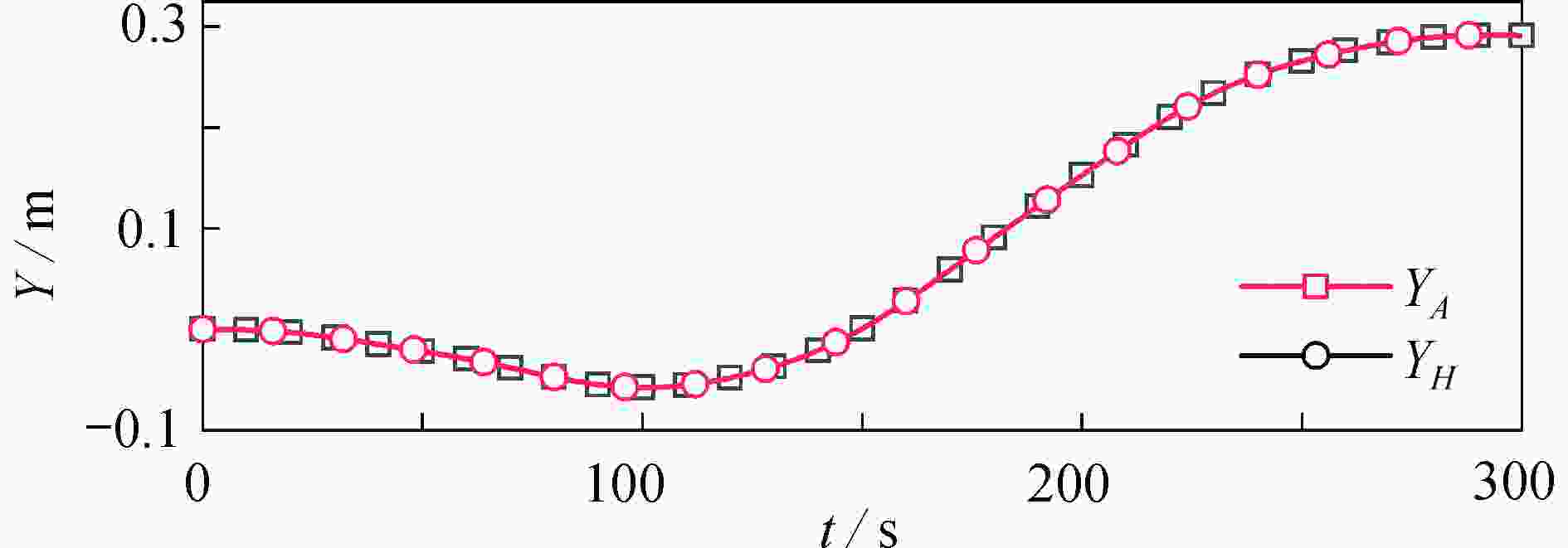


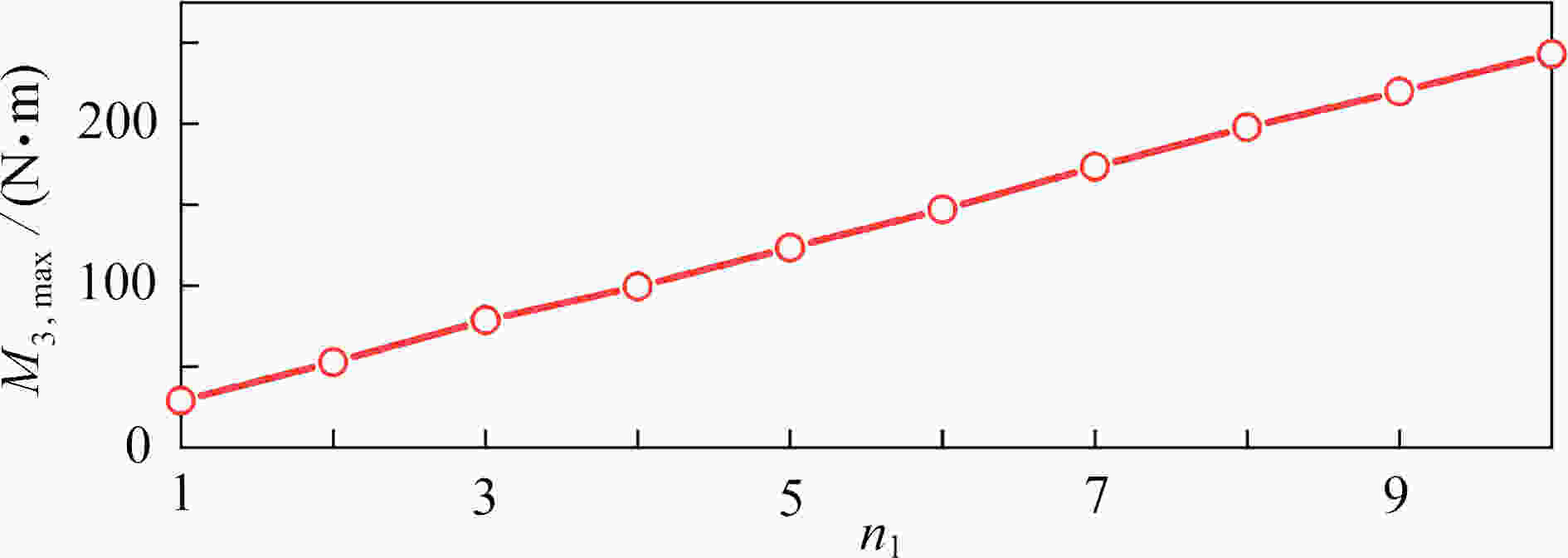


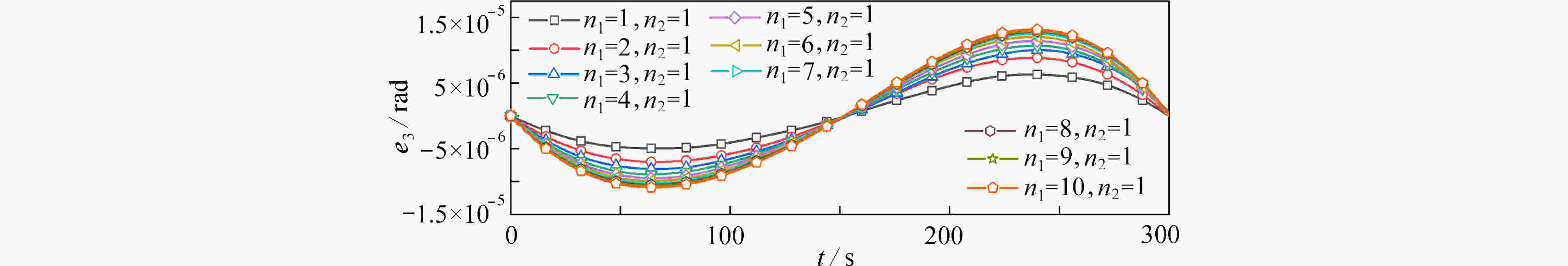


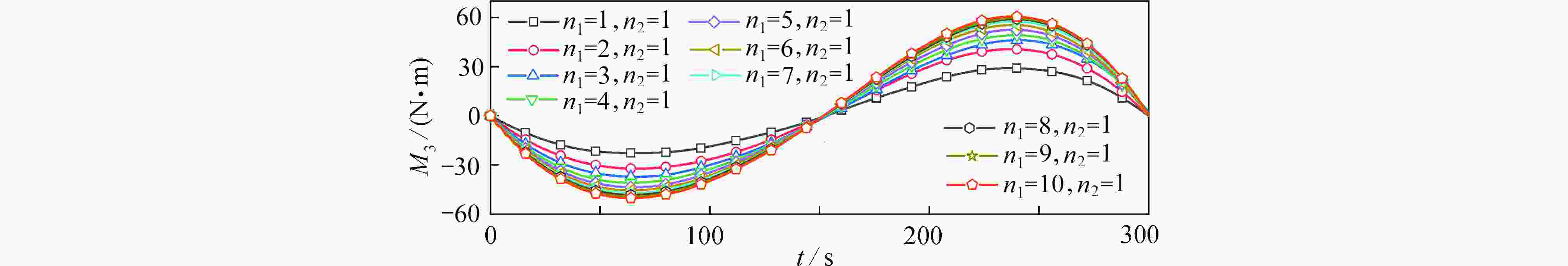










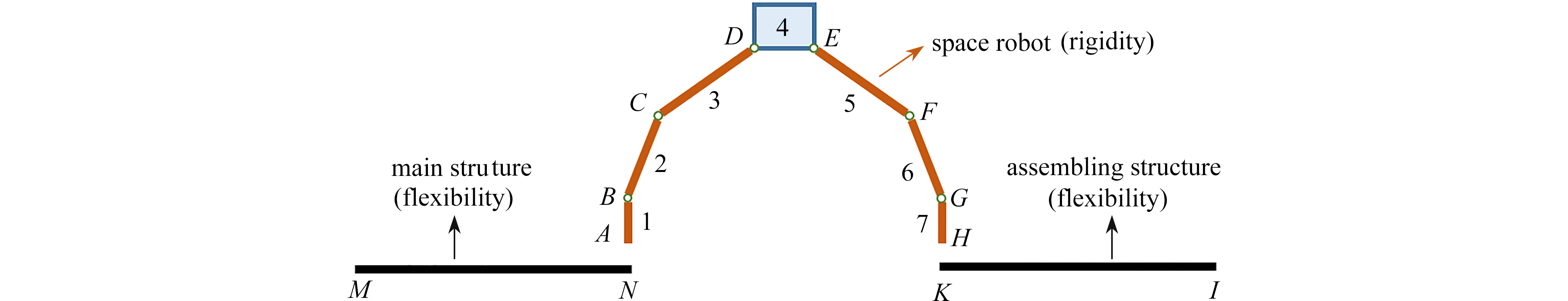

 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号