Study on Multiphase Pressure Wave Velocity Characteristics of Automatic Kill Annulus in Chuanyu Fractured Formation
-
摘要:
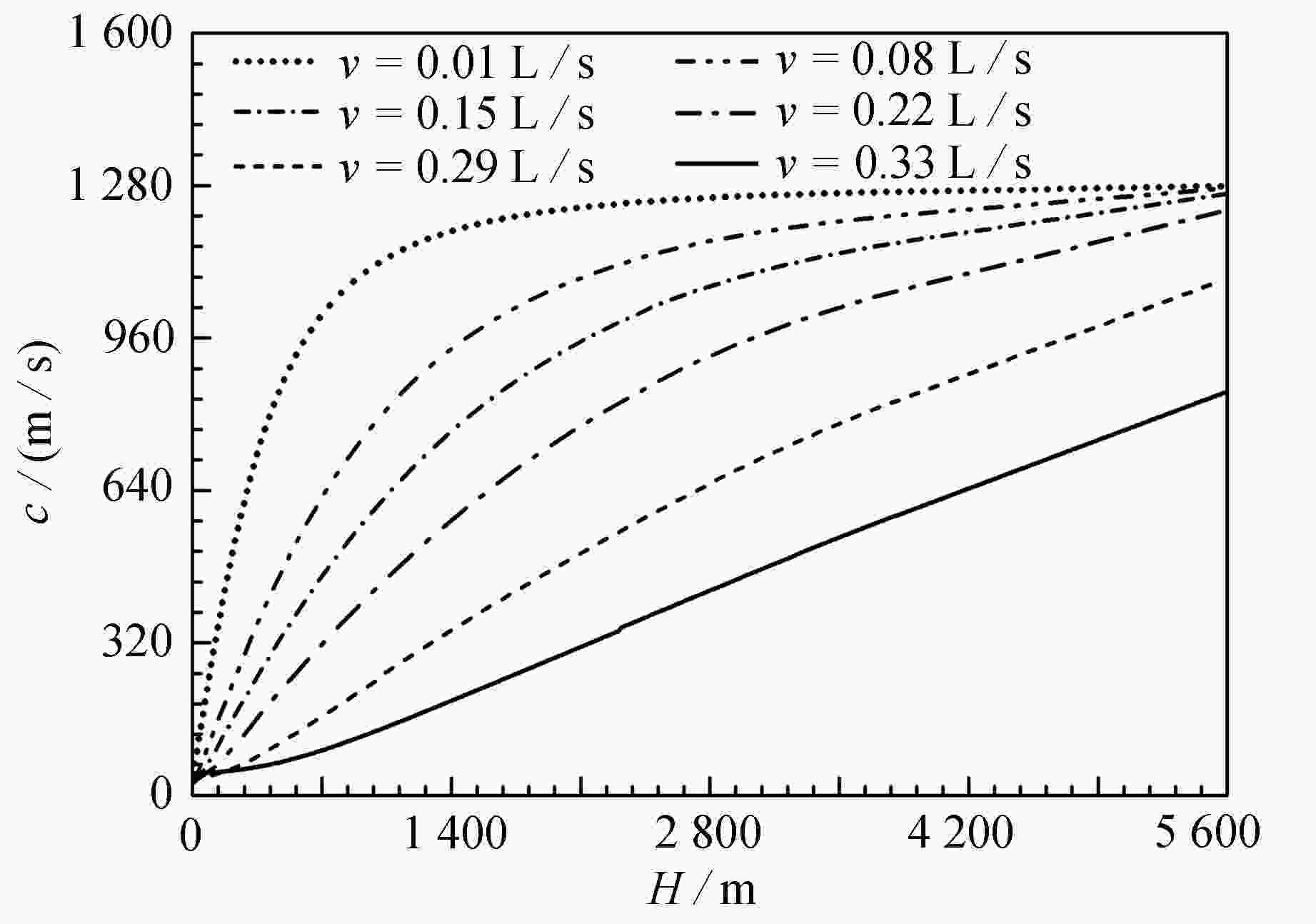
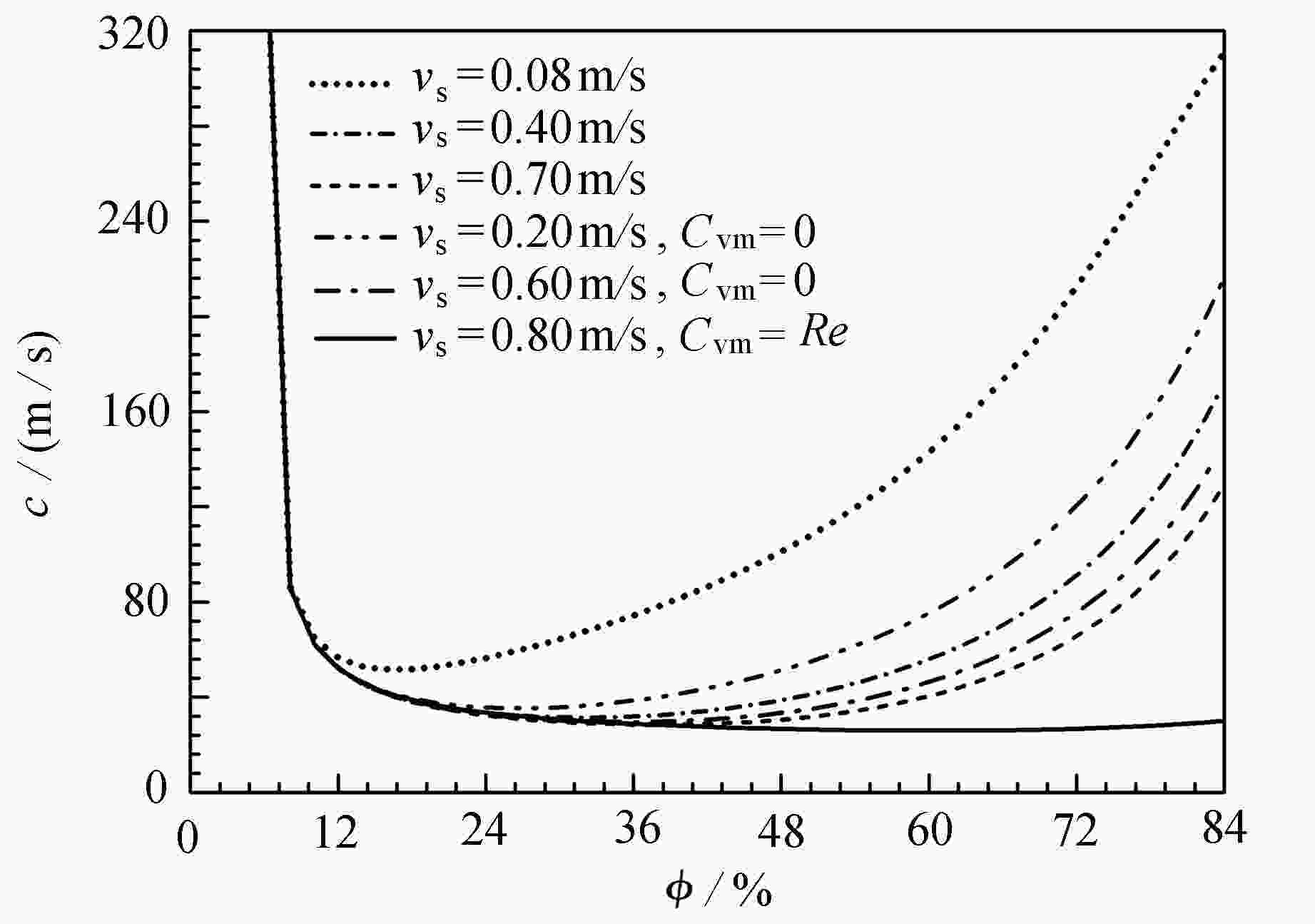
考虑虚拟质量力、环空沿程压力、气液相间阻力、气体滑脱、环空空隙率等因素,基于小扰动理论,提出了裂缝性地层自动压井环空多相压力波速数学模型,结合半显式差分方法,以彭州PZ-5-3D井(垂深5827 m)为实例,对模型编程求解。结果表明:裂缝性地层出气具有段塞流特点,随空隙率增大,压力波速呈现先减小后增大趋势;空隙率在0%至16%区间,压力波速以液弹为主,压力波速呈急剧下降趋势;空隙率在16%至40%区间,压力波速趋于平缓恒定值;空隙率在42%至100%区间,压力波速呈现增大趋势,压力波速以气弹为主;随环空井深减小,环空空隙率减小,压力波速整体呈现减小趋势;随压井循环排气井口回压增大,压力波速整体呈现增大趋势;环空空隙率在0%至13%区间内,气体滑脱速度对压力波速影响不大;环空空隙率在13%至85%区间内,随气体滑脱速度增大,压力波速呈现减小趋势;节流阀调阀时间间隔与井底压力响应时间具有跟随性,随井底压力响应时间增大,调阀时间间隔增大。
Abstract:In view of the virtual mass force, the annulus pressure, the gas-liquid resistance, the gas slippage, the annulus void fraction and other factors, the mathematical model for annular multiphase pressure wave velocities of automatic kill in fractured formation, was proposed based on the small perturbation theory. With the Pengzhou PZ-5-3D well (vertical depth 5 827 m) as an example, the model was solved programmatically with the semi-explicit difference method. The results show that, the gas from the fractured formation is characterized by the slug flow. With the increase of the void fraction, the pressure wave velocity first decreases and then increases. For a void fraction between 0% and 16%, the pressure wave velocity is mainly of liquid slug, and decreases sharply. For a void fraction between 16% and 40%, the pressure wave velocity tends to be flat and constant. For a void fraction between 42% and 100%, the pressure wave velocity shows an increasing trend, and is mainly of bubble slug. With the decrease of the annulus well depth, the void fraction decreases and the pressure wave velocity falls. The pressure wave velocity increases with the back pressure of the kill circulating exhaust wellhead. For an annular void fraction between 0% and 13%, the gas slippage velocity has little influence on the pressure wave velocity. For an annular void fraction between 13% and 85%, the pressure wave velocity decreases with the gas slippage velocity. The time interval of the throttle valve follows the response time of the bottom hole pressure, and increases with the response time.
-
Key words:
- fractured gas reservoir /
- automatic kill /
- annulus polyphase /
- pressure wave velocity /
- gas slippage
-
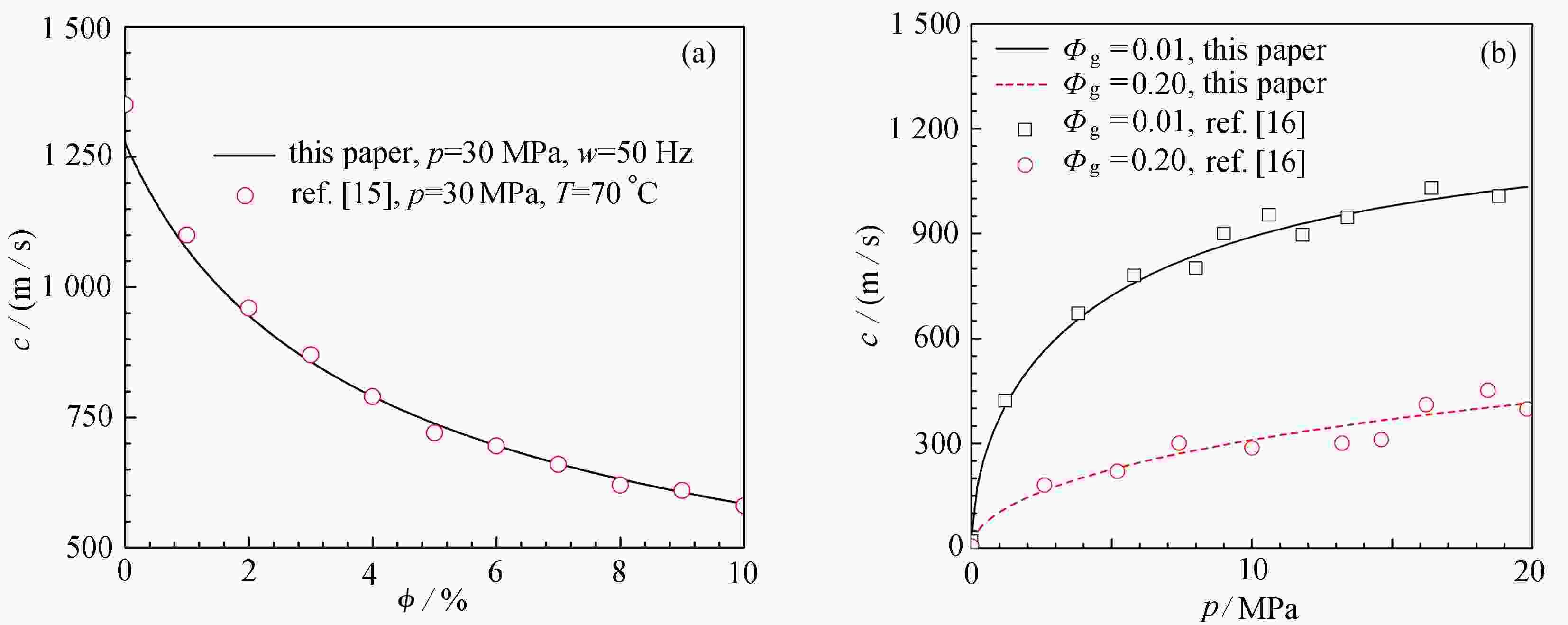
图 2 文献[15-16]的实验测试结果与本文模型计算压力波速对比:(a)30 MPa压力条件下压力波速对比结果;(b)含气率在1%及20%条件下波速对比结果
Figure 2. Comparisons between the experimental results of ref. [15-16] and the wave velocities calculated in this paper: (a) comparison of the wave velocity at a pressure of 30 MPa; (b) comparison of the wave velocity at gas contents of 1% and 20%
表 1 气体滑脱速度对压力波速影响数据表
Table 1. Effects of the gas slippage velocity on the pressure wave velocity
gas rate vs=0.08 m/s
Cvm=0vs=0.20 m/s
Cvm=0vs=0.40 m/s
Cvm=0vs=0.60 m/s
Cvm=0vs=0.70 m/s
Cvm=0vs=0.80 m/s
Cvm=Re6.1 372.18 372.16 372.15 372.13 372.12 372.10 13.1 51.56 41.88 41.16 40.97 40.89 40.61 23.1 59.02 35.31 32.39 31.55 31.20 30.34 33.1 74.55 38.64 31.88 29.54 28.49 28.12 43.1 96.16 48.64 37.08 32.21 29.74 26.92 53.1 127.09 65.87 48.94 40.75 36.03 26.04 63.1 173.82 94.36 70.62 58.27 50.57 26.14 73.1 244.94 145.00 111.09 92.65 80.68 27.50 83.1 325.26 241.65 196.06 168.26 149.18 31.08 93.1 349.51 344.27 334.70 322.83 310.25 41.06 98.1 349.99 349.99 349.99 349.99 349.99 87.31 -
[1] 姜海龙, 朱培旺, 徐东华. 考虑气体加速效应的高压气井产能方程推导及其应用[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2020, 41(2): 134-142JIANG Hailong, ZHU Peiwang, XU Donghua. Derivation and application of productivity equations for high-pressure gas reservoirs with gas acceleration effects[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2020, 41(2): 134-142.(in Chinese) [2] 伍贤柱, 胡旭光, 韩烈祥, 等. 井控技术研究进展与展望[J]. 天然气工业, 2022, 42(2): 133-142 doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2022.02.014WU Xianzhu, HU Xuguang, HAN Liexiang, et al. Progress and prospect of well control technology research[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(2): 133-142.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2022.02.014 [3] WILLIAM B. Consideration of Compressibility Effects for Applied-Back Pressure Dynamic Well Control Response to a Gas Kick in Managed Pressure Drilling Operations[M]. Master of Science in Mechanical Engineering, The University of Texas at Arlington, 2011. [4] 史爽, 敬加强, 孔祥伟. 大跨越管道油气混输压力波速及响应特性研究[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2016, 37(3): 290-300.SHI Shuang, JING Jiaqiang, KONG Xiangwei. Research of pressure wave velocity and response time for oil-gas mixing transportation in large span pipelines[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2016, 37(3): 290-300. (in Chinese) [5] 刘磊, 王跃社, 周芳德. 气液两相流压力波传播速度研究[J]. 应用力学学报, 1999, 16(3): 22-27, 150-151.LIU Lei, WANG Yueshe, ZHOU Fangde. Propagation speed of pressure wave in gas liquid two phase flow[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1999, 16(3): 22-27, 150-151. (in Chinese) [6] 黄飞, 白博峰, 郭烈锦. 水平管内气液两相泡状流压力波数学模型及其数值模拟[J]. 自然科学进展, 2004, 14(4): 344-349 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.2004.01.015HUANG Fei, BAI Bofeng, GUO Liejin. Mathematical model and numerical simulation of pressure wave in gas-liquid two-phase bubble flow in horizontal tube[J]. Progress in Natural Science, 2004, 14(4): 344-349.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.2004.01.015 [7] 白博峰, 黄飞, 王先元. 气液两相流压力波色散特性实验研究[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2005, 26(3): 447-450 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-231X.2005.03.026BAI Bofeng, HUANG Fei, WANG Xianyuan. Experimental study on pressure wave dispersion characteristics of gas-liquid two-phase flow[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2005, 26(3): 447-450.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-231X.2005.03.026 [8] 王海成. 天然气井压井与带压施工的实践与认识[J]. 中国石油和化工标准与质量, 2021, 41(10): 144-145.WANG Haicheng. Practice and understanding of natural gas well killing and pressure construction[J]. China Petroleum and Chemical Standards and Quality, 2021, 41(10): 144-145. (in Chinese) [9] SUROSO T, TRIYOSO W, PRIYONO A. Hydrocarbon identification by evaluating anisotropy parameters estimated from crosswell seismic data[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2021, 1943(1): 12030-12038. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1943/1/012030 [10] 袁凡, 吴望一. 脉象的血管位移波理论[J]. 应用数学和力学, 1989, 10(6): 469-476 doi: 10.1007/BF02017892YUAN Fan, WU Wangyi. The displacement wave theory of blood vessel[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 1989, 10(6): 469-476.(in Chinese) doi: 10.1007/BF02017892 [11] 刘小靖, 周又和, 王记增. 小波方法及其力学应用研究进展[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2022, 43(1): 1-13 doi: 10.1007/s10483-021-2795-5LIU Xiaojing, ZHOU Youhe, WANG Jizeng. Research progresses of wavelet methods and their applications in mechanics[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2022, 43(1): 1-13.(in Chinese) doi: 10.1007/s10483-021-2795-5 [12] 卫志军, 申利敏, 关晖, 等. 拓扑优化技术在抑制流体晃荡中的数值模拟研究[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2021, 42(1): 49-57WEI Zhijun, SHEN Limin, GUAN Hui, et al. Numerical simulation of topology optimization technique for tank sloshing suppression[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2021, 42(1): 49-57.(in Chinese) [13] MEHRDAD K, ABDORREZA K, MOHAMMAD N S, et al. Investigating the effects of transient flow in concrete-lined pressure tunnels, and developing a new analytical formula for pressure wave velocity[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology Incorporating Trenchless Technology Research, 2019, 11(91): 18-25. [14] MOSLAND E N, LOHNE K D, YSTAD B, et al. Pressure wave velocity in fluid-filled pipes with and without deposits in the low-frequency range[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2018, 144(10): 101-106. [15] LIU X, LI B, YUE Y. Transmission behavior of mud-pressure pulse along wellbore[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2007, 19(2): 236-240. doi: 10.1016/S1001-6058(07)60054-7 [16] 李相方, 管丛笑, 隋秀香, 等. 压力波气侵检测理论及应用[J]. 石油学报, 1997, 18(3): 128-133 doi: 10.7623/syxb199703021LI Xiangfang, GUAN Congxiao, SUI Xiuxiang, et al. The theory of gas influx detection of pressure wave and its application[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 1997, 18(3): 128-133.(in Chinese) doi: 10.7623/syxb199703021 -




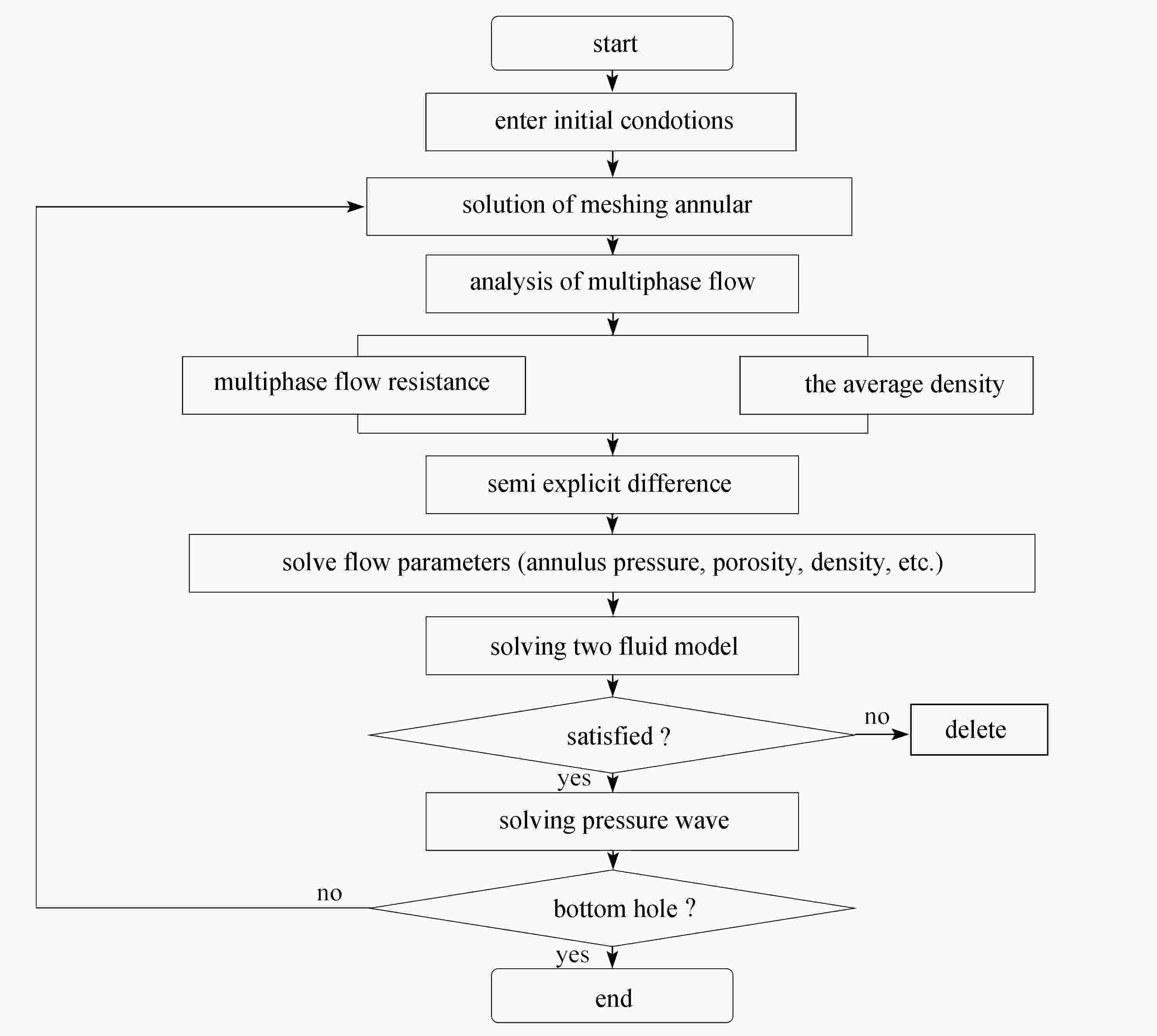
 下载:
下载:
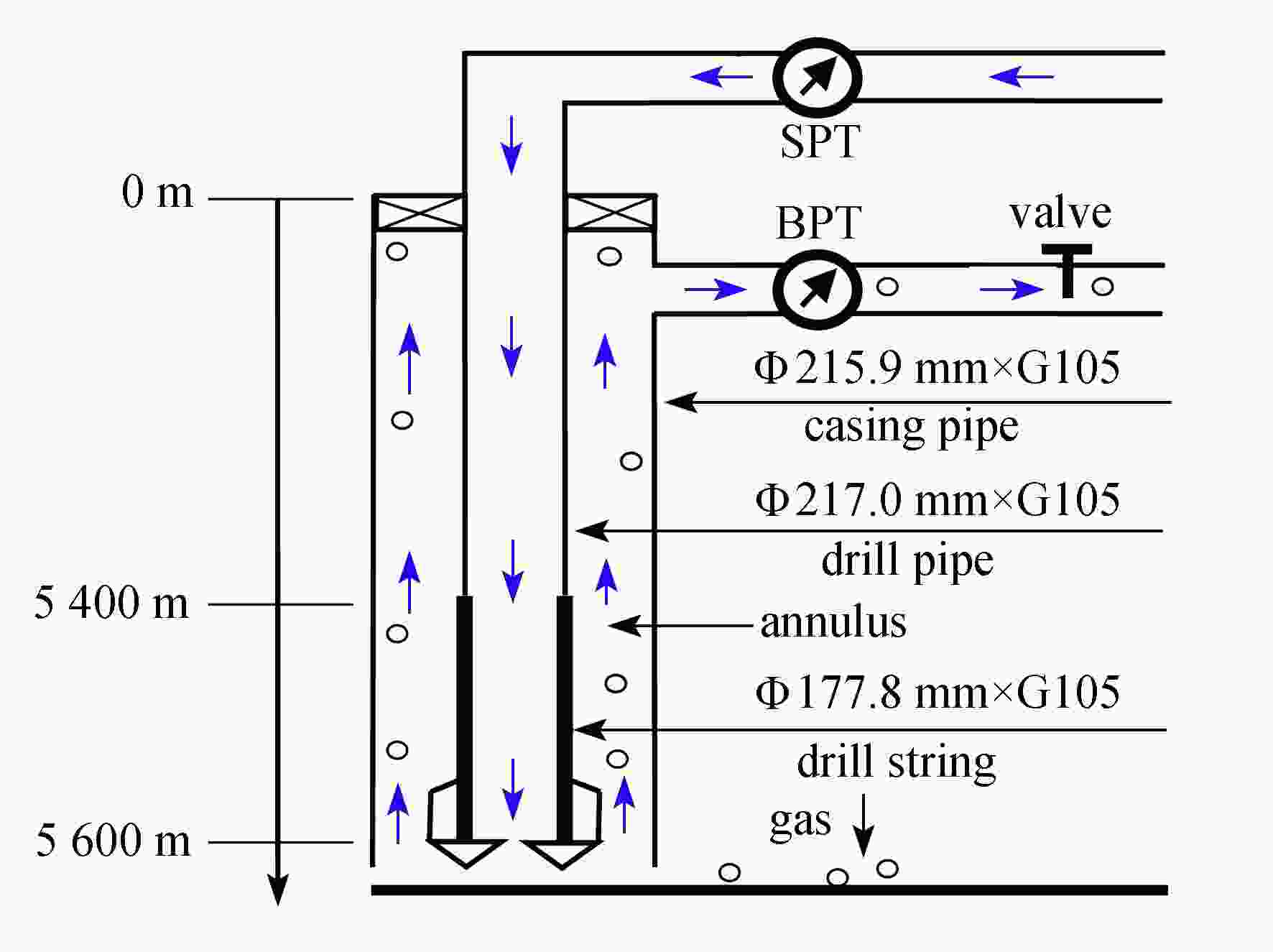
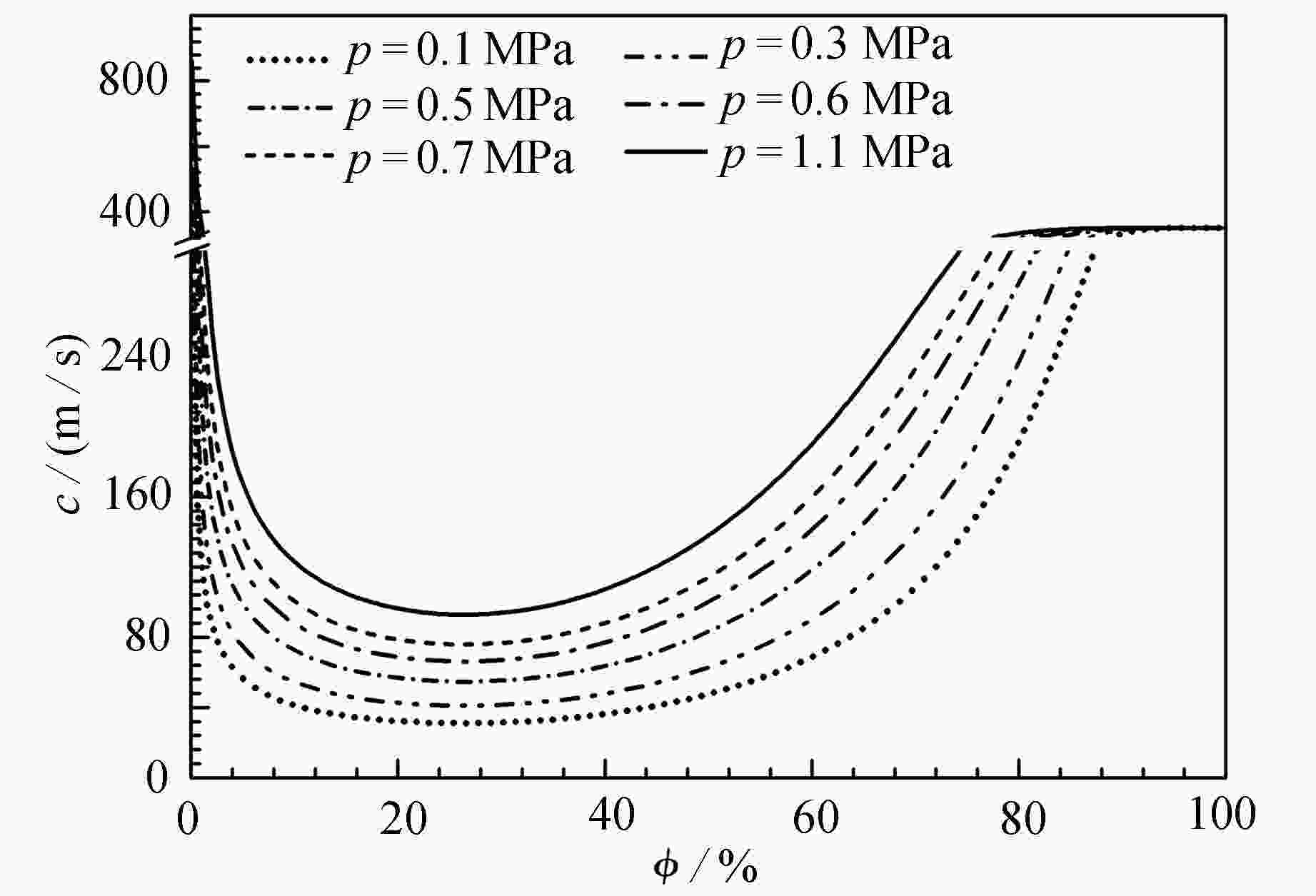




 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号