Influences of Attack Angles on Aerodynamic Derivatives and Flutter Characteristics of Flat Box Girders
-
摘要:
以南京第四长江大桥扁平箱梁为研究对象,通过节段模型自由振动风洞试验详细测试了模型在不同风攻角下的颤振响应,探讨了系统非稳态及稳态临界振幅随风速的演化规律。首先,基于颤振响应振幅包络,结合Hilbert变换,识别了系统振幅依存的模态阻尼,并初步阐释了颤振形态随风攻角转变的机理。其次,提取了系统在不同风攻角下的模态参数,基于双模态耦合闭合解法,识别了断面在不同风攻角下的非线性颤振导数,研究了关键颤振导数振幅依存性随风攻角变化的规律及对断面颤振形态和特性的潜在影响。最后,通过逐项拆解模态阻尼,深入剖析了风攻角对非耦合及耦合气动阻尼的影响,并阐明了分项阻尼导致系统颤振性能差异性的动力学机理。
Abstract:The flutter responses of the Nanjing No.4 bridge flat box girder under different wind attack angles were tested in detail through sectional model tests. The evolution of unsteady and steady critical amplitudes at different wind speeds was discussed. Based on the amplitude envelope of the flutter response and the Hilbert transform, the amplitude-dependent modal damping of the system was identified, and the mechanism of the flutter mode change with the wind angle of attack was initially explained. Secondly, the modal parameters of the system under different wind attack angles were extracted. With the bimodal coupled flutter analysis method, the nonlinear flutter derivatives of the section under different wind attack angles were identified, and the change law for the amplitude dependence of the key flutter derivatives on the wind attack angle and the potential influence on the section flutter morphology and characteristics, were studied. Finally, the effects of the wind attack angle on the uncoupled and coupled aerodynamic damping were analyzed through analyses of the modal damping subterms one by one, and the dynamic mechanism of the differential flutter performance caused by fractional damping was illustrated.
-
Key words:
- flat box girder /
- soft flutter /
- flutter derivative /
- aerodynamic damping
-
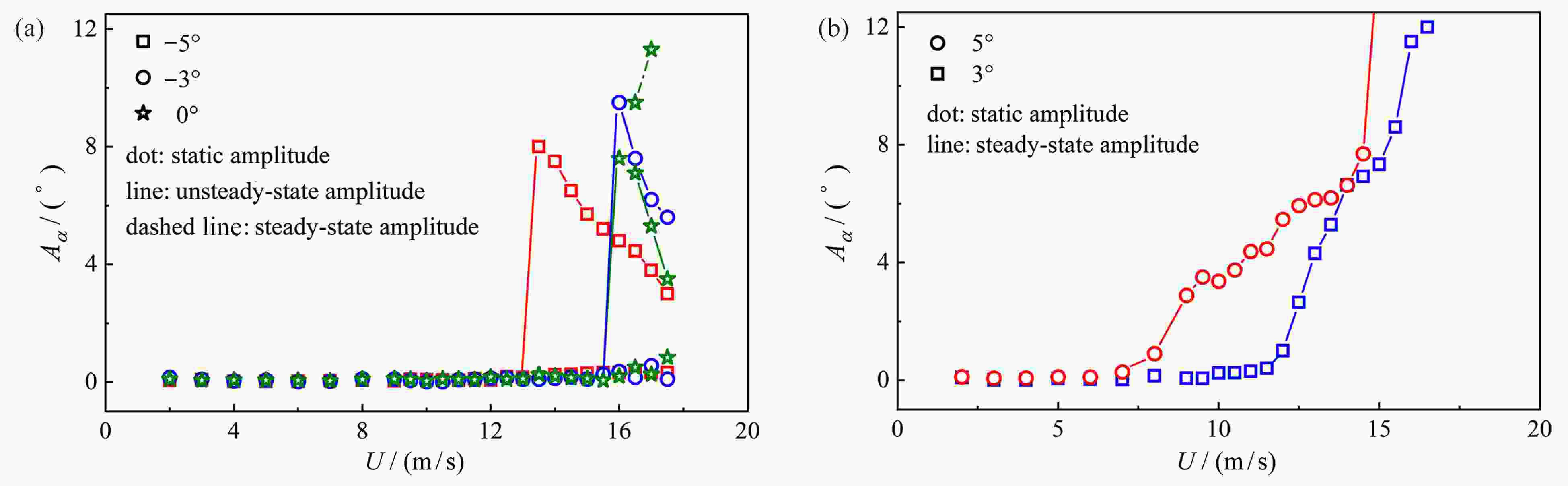
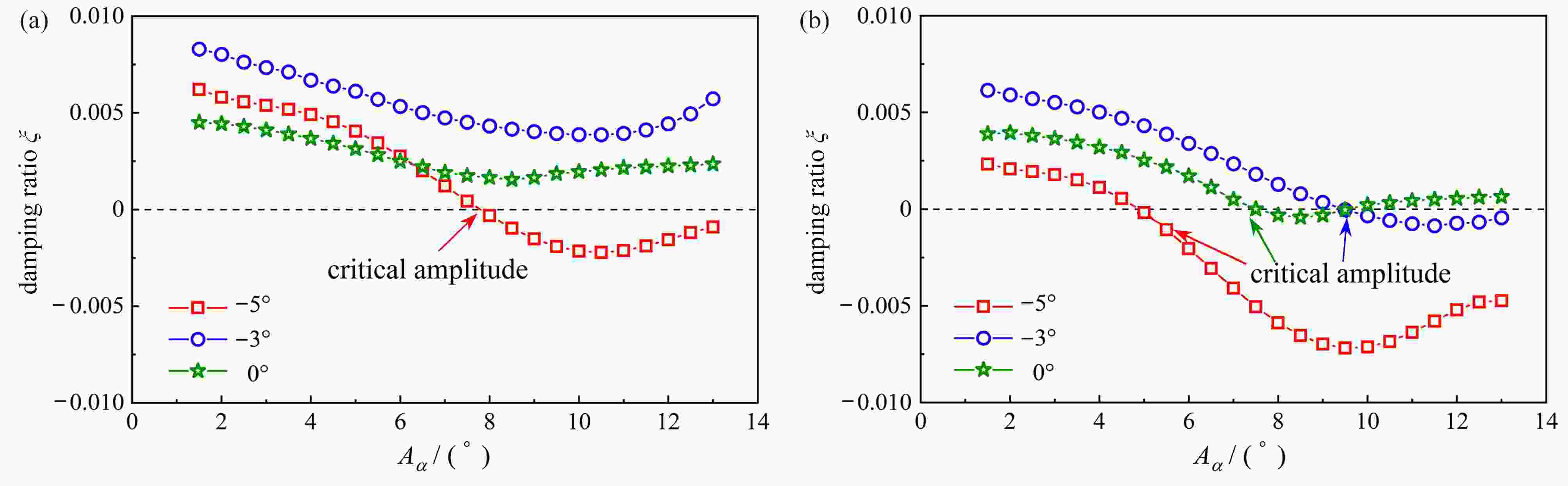
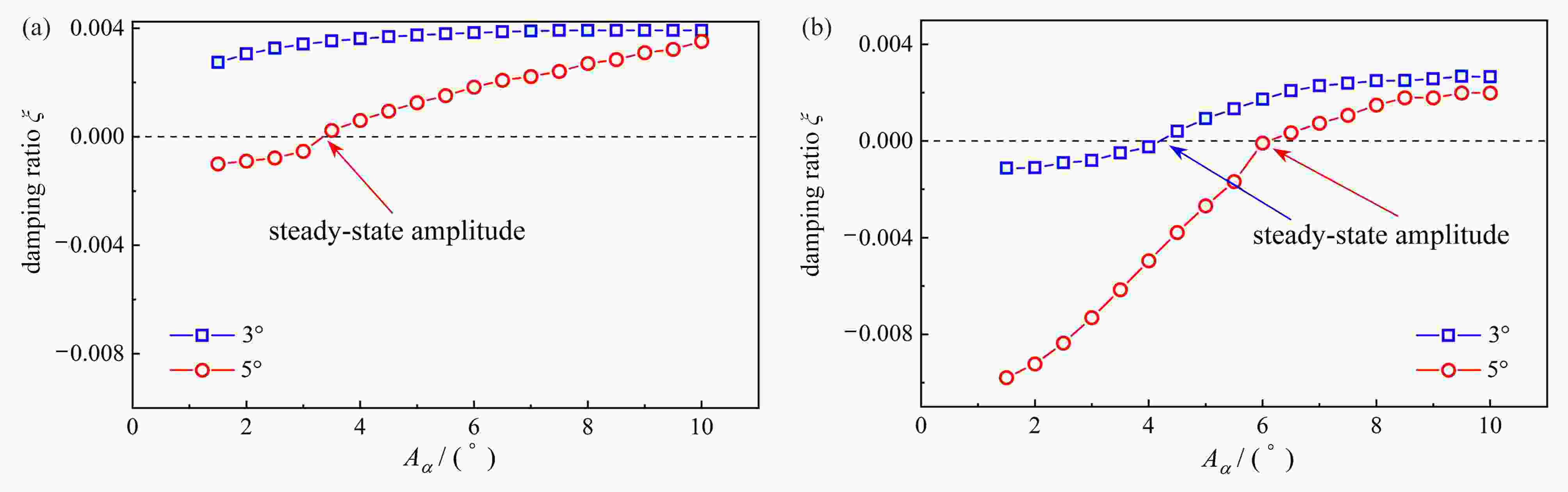
图 3 不同攻角下稳态振幅随风速的变化曲线:(a) 非正攻角下临界振幅随风速的变化曲线;(b) 正攻角下稳态振幅随风速的变化曲线
Figure 3. Curves of amplitude varying with the wind speed at different angles of attack: (a) curves of critical amplitude varying with the wind speed at non-positive angles of attack; (b) curves of steady-state amplitude varying with the wind speed at positive angles of attack
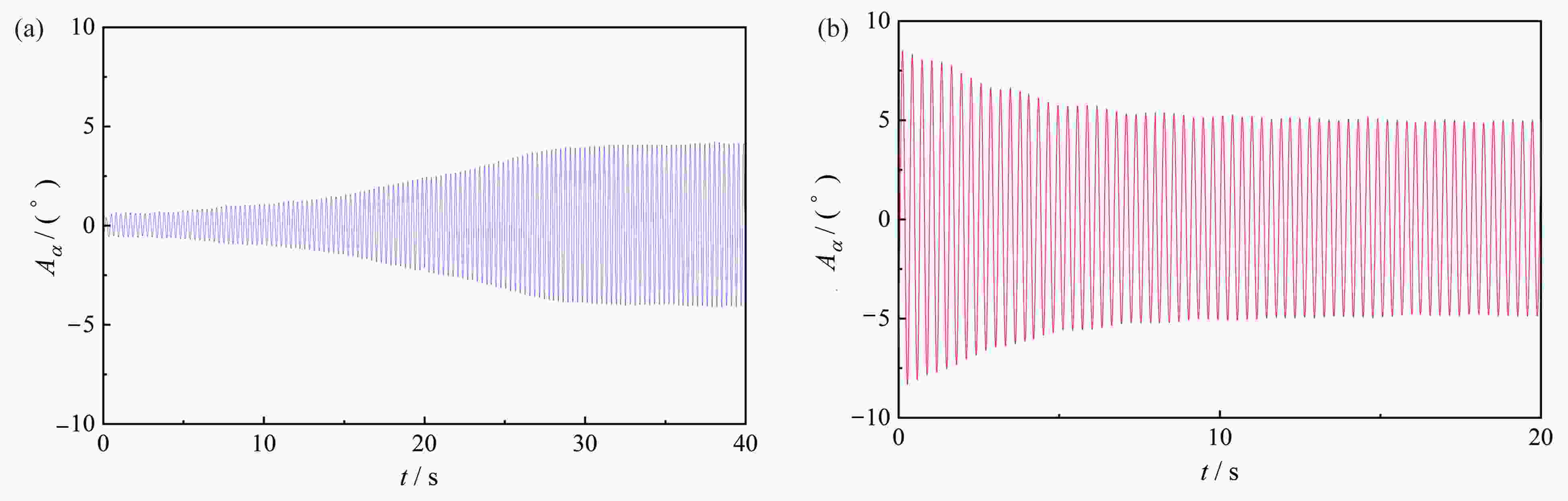
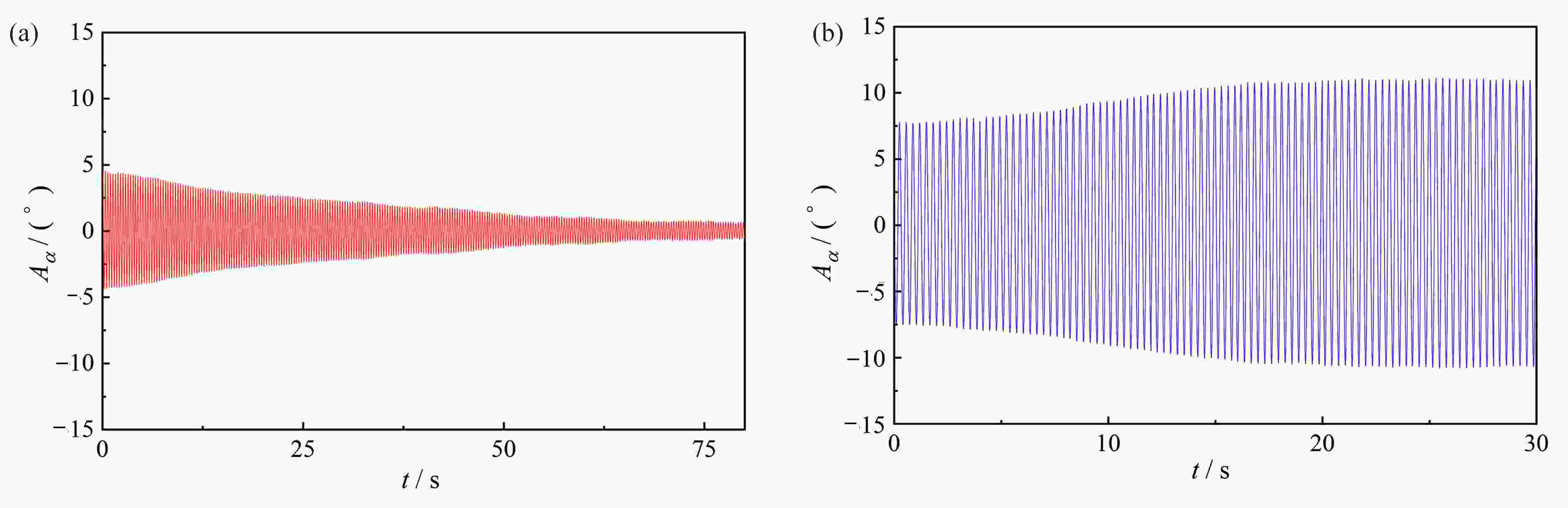
图 5 不同激励下的时程发展曲线(5°攻角,U=11.5 m/s):(a) 无激励下增长至稳定的时程曲线;(b) 大激励下衰减至稳定的时程曲线
Figure 5. Time history development curves under different excitations (attack angle of 5°, U=11.5 m/s): (a) the growth-to-stability time history curve without excitation; (b) the damping-to-stability time curve under the large excitation
图 6 不同激励下的时程发展曲线(0°攻角,U=17 m/s):(a)小激励下衰减至零的时程曲线;(b)大激励下增长至稳定的时程曲线
Figure 6. Time history development curves under different excitations (attack angle of 0°, U=17 m/s): (a) the damped time history curve under the small excitation; (b) the growth-to-stability time history curve under the large excitation
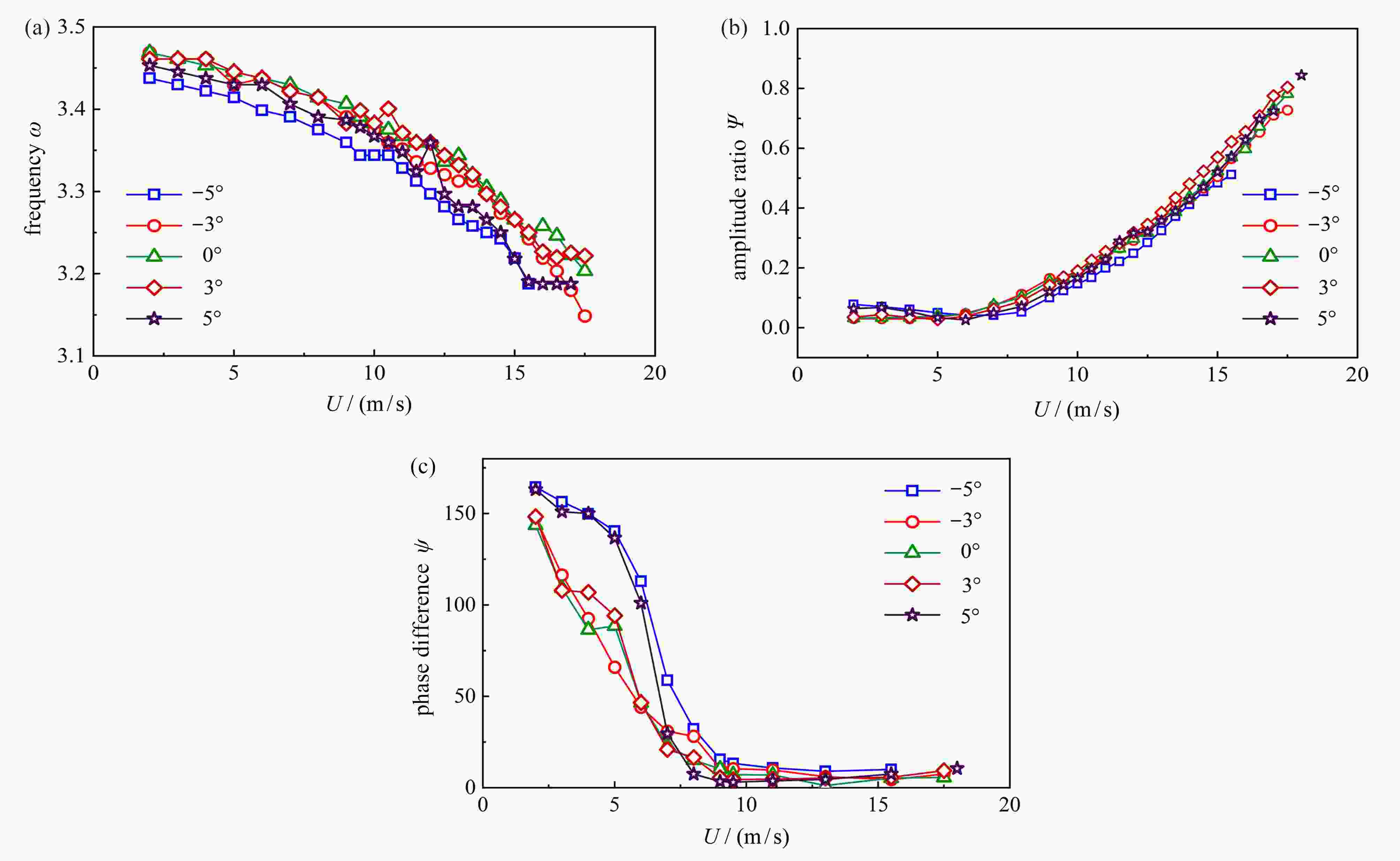
图 10 非耦合颤振导数识别结果:(a) −5°攻角下的颤振导数
$ A_2^* $ ;(b) −3°攻角下的颤振导数$ A_2^* $ ;(c) 0°攻角下的颤振导数$ A_2^* $ ;(d) 3°攻角下的颤振导数$ A_2^* $ ;(e) 5°攻角下的颤振导数$ A_2^* $ ;(f) 不同攻角下的颤振导数$ A_3^* $ Figure 10. Evolution of uncoupled flutter derivatives: (a)
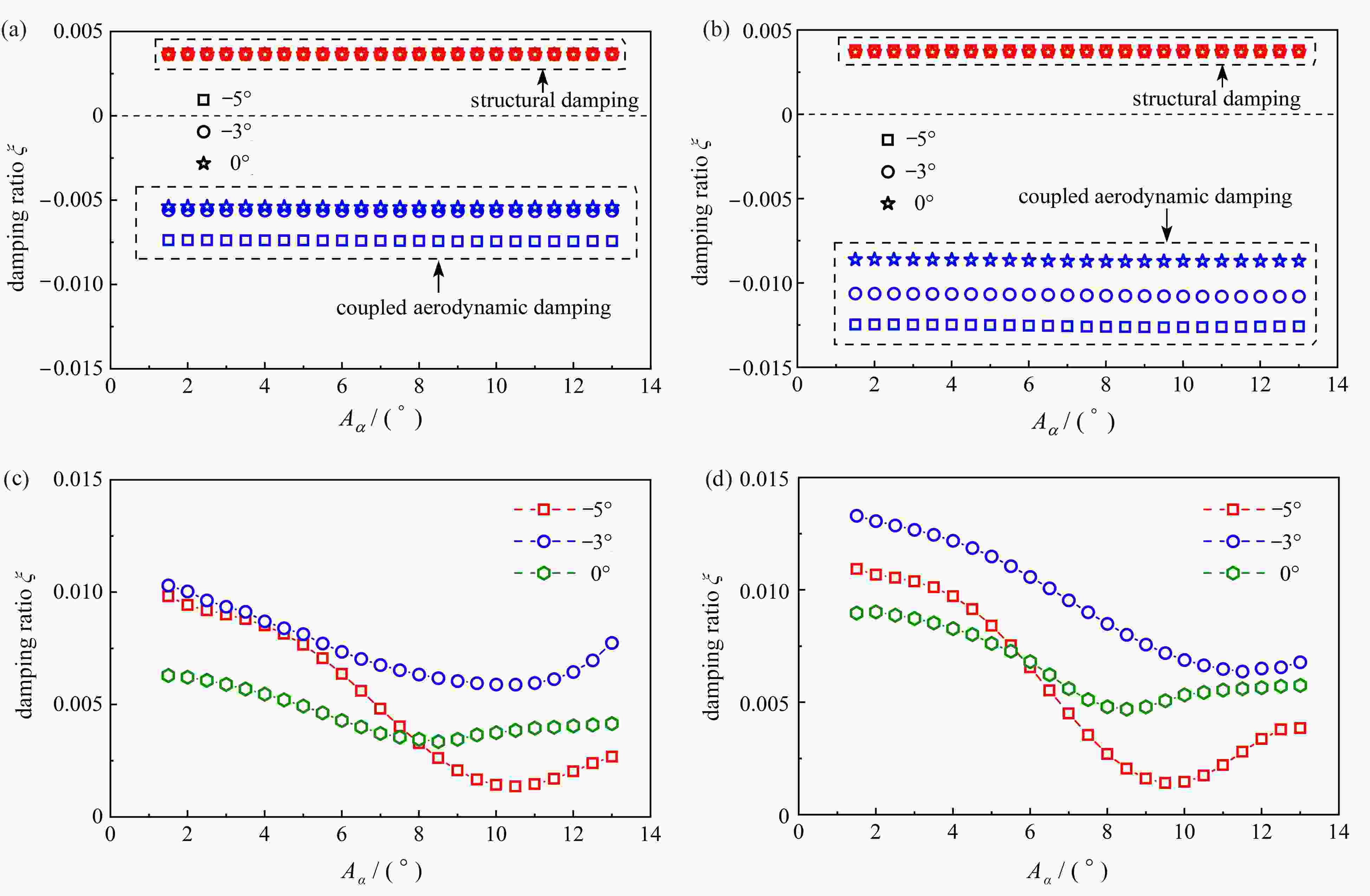
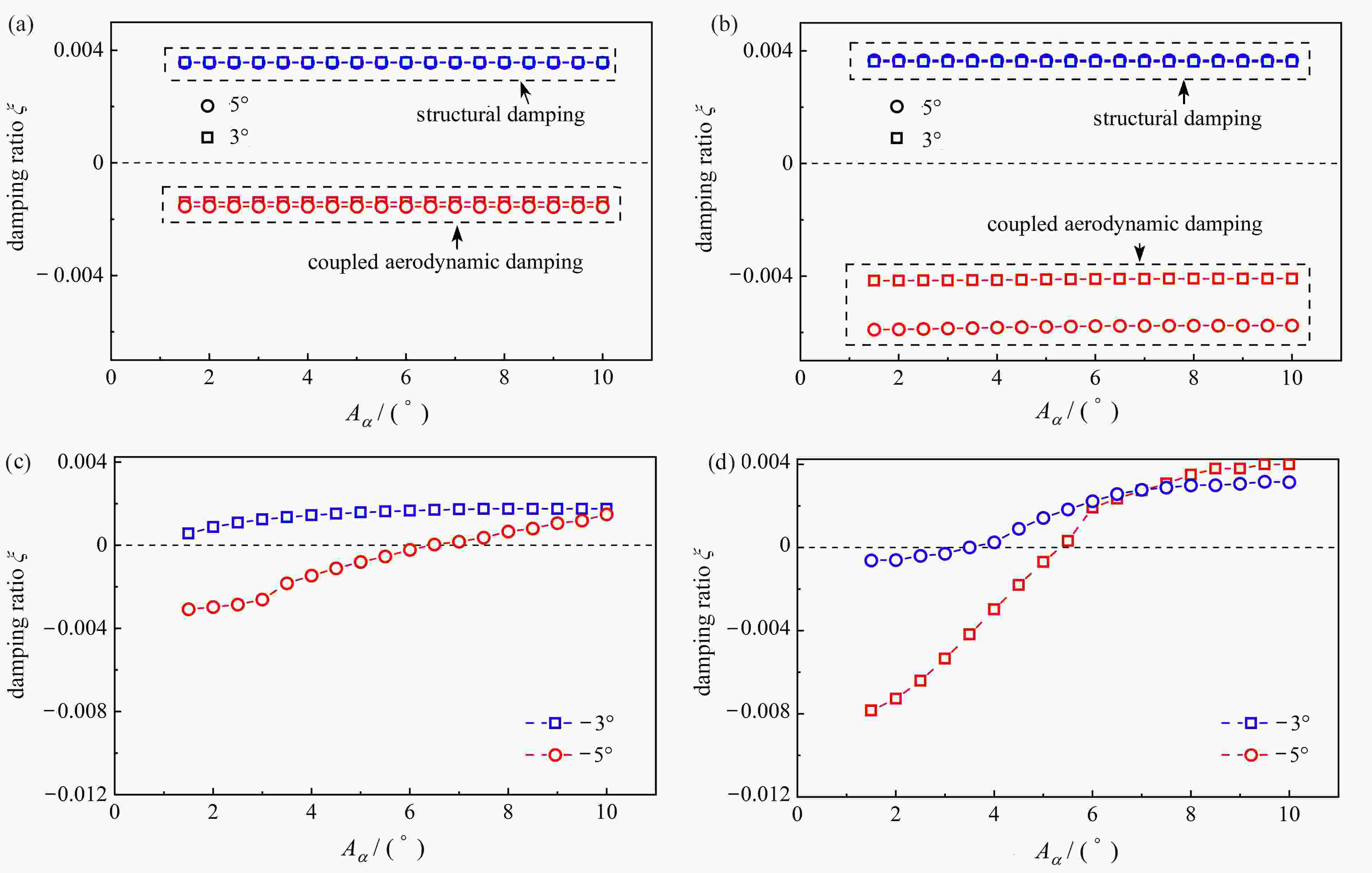
$ A_2^* $ under a wind attack angle of −5°; (b)$ A_2^* $ under a wind attack angle of −3°; (c)$ A_2^* $ under a wind attack angle of 0°; (d)$ A_2^* $ under a wind attack angle of 3°; (e)$ A_2^* $ under a wind attack angle of 5°; (f)$ A_3^* $ at different wind attack angles图 12 非正攻角下各阻尼项随振幅变化曲线:(a) 14 m/s下不同攻角的耦合气动阻尼和结构阻尼;(b) 16 m/s下不同攻角的耦合气动阻尼和结构阻尼;(c) 14 m/s下不同攻角的非耦合气动阻尼;(d) 16 m/s下不同攻角的非耦合气动阻尼
Figure 12. The damping term curves varying with the amplitude at non-positive angle of attack: (a) the coupled aerodynamic damping and the structural damping at different attack angles (U=14 m/s); (b) the coupled aerodynamic damping and the structural damping at different attack angles (U=16 m/s); (c) the uncoupled aerodynamic damping at different attack angles (U=14 m/s); (d) the uncoupled aerodynamic damping at different attack angles (U=16 m/s)
图 13 正攻角下各阻尼项随风速变化曲线:(a) 10 m/s不同攻角的耦合气动阻尼和结构阻尼;(b)13 m/s不同攻角的耦合气动阻尼和结构阻尼;(c) 10 m/s不同攻角的非耦合气动阻尼;(d) 13 m/s不同攻角的非耦合气动阻尼
Figure 13. The damping term curves varying with the amplitude under positive angles of attack: (a) the coupled aerodynamic damping and the structural damping at different attack angles (U=10 m/s); (b) the coupled aerodynamic damping and the structural damping at different attack angles (U=13 m/s); (c) the uncoupled aerodynamic damping at different attack angles (U=10 m/s); (d) the uncoupled aerodynamic damping at different attack angles (U=13 m/s)
表 1 基础试验参数
Table 1. Basic test parameters
$ m $/(kg/m) $ I $/(kg·m2/m) $ {\omega _{h0}} $/(rad/s) $ {\omega _{\alpha 0}} $/(rad/s) $ {\xi _{h0}} $ $ {\xi _{\alpha 0}} $ 9.29 0.345 14.20 37.20 0.0035 0.0030 表 2 不同攻角下
$ A_{\text{3}}^* $ 取值($ U/(fB) = 12 $ )Table 2.
$ A_{\text{3}}^* $ values at different angles of attack($ U/(fB) = 12 $ )attack angle −5° −3° 0° 3° 5° $ A_{\text{3}}^* $ 29 22 20.5 21.5 27.5 表 3 非正攻角下耦合气动阻尼各子项
Table 3. Sub-terms of the coupled aerodynamic damping at non-positive angles of attack
sub-term 14 m/s 16 m/s −5° −3° 0° −5° −3° 0° $ - 0.5\upsilon \mu $ −1.5E + 5 1.5E + 5 1.49E + 5 1.49E + 5 1.49E + 5 1.49E + 5 $ {\left( {\dfrac{{{\omega _2}}}{{{\omega _1}}}} \right)^2}{\left[ {1 - {{\left( {\dfrac{{{\omega _2}}}{{{\omega _1}}}} \right)}^2}} \right]^{ - 1}} $ 1.78 1.74 1.74 1.86 1.81 1.78 $ {[ {{{( {H_2^*} )}^2} + {{( {H_3^*} )}^2}} ]^{1/2}} $ 44.26 46.9 47.8 56.5 63.6 63.6 $ {[ {{{( {A_1^*} )}^2} + {{( {A_4^*} )}^2}} ]^{1/2}} $ 6.26 4.64 4.38 7.98 6.32 5.19 $\sin ( { {\psi ^\prime } } )$ 0.99 0.98 0.99 0.99 0.97 0.98 表 4 正攻角下耦合项气动阻尼各子项
Table 4. Sub-terms of the coupled aerodynamic damping at positive angles of attack
sub-term 10 m/s 13 m/s 3° 5° 3° 5° $ - 0.5\upsilon \mu $ −1.49E + 5 −1.49E + 5 −1.49E + 5 −1.49E + 5 $ {\left( {\dfrac{{{\omega _2}}}{{{\omega _1}}}} \right)^2}{\left[ {1 - {{\left( {\dfrac{{{\omega _2}}}{{{\omega _1}}}} \right)}^2}} \right]^{ - 1}} $ 1.68 1.69 1.72 1.76 $ {[ {{{( {H_2^*} )}^2} + {{( {H_3^*} )}^2}} ]^{1/2}} $ 21.5 18.77 42.6 39.0 $ {[ {{{( {A_1^*} )}^2} + {{( {A_4^*} )}^2}} ]^{1/2}} $ 2.56 3.30 3.75 5.60 $\sin ( { {\psi ^\prime } } )$ 0.99 0.99 0.99 0.99 -
[1] SCANLAN R. Amplitude and turbulence effects on bridge flutter derivatives[J]. Engineering Structures, 1997, 123(2): 232-236. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(1997)123:2(232) [2] NODA M, UTSUNOMIYA H, NAGAO F, et al. Effects of oscillation amplitude on aerodynamic derivatives[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2003, 91(1): 101-111. [3] XU F, YING X, ZHANG Z. Effects of exponentially modified sinusoidal oscillation and amplitude on bridge deck flutter derivatives[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2016, 21(5): 06016001. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)BE.1943-5592.0000884 [4] ZHANG M, XU F, YING X. Experimental investigations on the nonlinear torsional flutter of a bridge deck[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2017, 22(8): 04017048. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)BE.1943-5592.0001082 [5] ZHOU R, GE Y J, YANG Y X, et al. Wind-induced nonlinear behaviors of twin-box girder bridges with various aerodynamic shapes[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2018, 94: 1095-1115. doi: 10.1007/s11071-018-4411-y [6] WU B, CHEN X Z, WANG Q, et al, Characterization of vibration amplitude of nonlinear bridge flutter from section model to full bridge estimation[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2019, 197: 1040487. [7] 张博, 史天姿, 张贻林, 等. 旋转输液管动力稳定性理论分析[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2022, 43(2): 166-175ZHANG Bo, SHI Tianzi, ZHANG Yilin, et al. Theoretical analysis on dynamic stability of rotating pipes conveying fluid[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2022, 43(2): 166-175.(in Chinese) [8] 黄国庆, 彭留留, 廖海黎, 等. 普立特大桥桥位处山区风特性实测研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2016, 51(2): 349-356HUANG Guoqing, PENG Liuliu, LIAO Haili, et al. Field measurement study on wind characteristics at Puli great bridge site in mountainous area[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(2): 349-356.(in Chinese) [9] 于舰涵, 李明水, 廖海黎. 山区地形对桥位风场影响的数值模拟[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2016, 51(4): 654-662YU Jianhan, LI Mingshui, LIAO Haili. Numerical simulation of effect of mountainous topography on wind field at bridge site[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(4): 654-662.(in Chinese) [10] 赵林, 吴风英, 潘晶晶, 等. 强台风登陆过程大跨桥梁风特性特征及其抖振响应分析[J]. 空气动力学学报, 2016, 39(4): 654-662ZHAO Lin, WU Fengying, PAN Jingjing, et al. Wind field characteristics and wind-induced buffeting response of a long-span bridge during the landing of a strong typhoon[J]. Acta Aerodynamica Sinica, 2016, 39(4): 654-662.(in Chinese) [11] 朱乐东, 朱青, 郭震山. 风致静力扭角对桥梁颤振性能影响的节段模型试验研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2011, 30(5): 23-26ZHU Ledong, ZHU Qing, GUO Zhenshan. Effect of wind-induced static torsional angle on flutter performance of bridges via sectional model test[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2011, 30(5): 23-26.(in Chinese) [12] 欧阳克俭, 陈政清. 附加攻角效应对颤振稳定性能影响[J]. 振动与冲击, 2015, 34(2): 45-49OUYANG Kejian, CHEN Zhenqing. Influence of static wind additive attack angle on flutter performance of bridges[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2015, 34(2): 45-49.(in Chinese) [13] 伍波, 王骑, 廖海黎, 等. 双层桥面桁架梁软颤振特性风洞试验研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2020, 39(1): 191-198WU Bo, WANG Qi, LIAO Haili, et al. Wind tunnel tests for soft flutter characteristics of double-deck truss girder[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2020, 39(1): 191-198.(in Chinese) [14] 伍波, 王骑, 廖海黎, 等. 不同风攻角下薄平板断面颤振机理研究[J]. 振动工程学报, 2020, 33(4): 667-678WU Bo, WANG Qi, LIAO Haili, et al. Flutter mechanism of thin plate section under different wind attack angles[J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 2020, 33(4): 667-678.(in Chinese) [15] 李志国, 王骑, 伍波, 等. 不同攻角下扁平箱梁颤振机理[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2018, 53(4): 687-695LI Zhiguo, WANG Qi, WU Bo, et al. Flutter mechanism of flat box girder under different attack angles[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2018, 53(4): 687-695.(in Chinese) [16] 伍波, 王骑, 廖海黎. 扁平箱梁颤振后状态的振幅依存性研究[J]. 中国公路学报(自然科学版), 2019, 32(10): 96-106WU Bo, WANG Qi, LIAO Haili. Characteristics of amplitude dependence of a flat box grider in a post-flutter state[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2019, 32(10): 96-106.(in Chinese) [17] XU F, YANG J, ZHANG M, et al. Experimental investigations on post-flutter performance of a bridge deck sectional model using a novel testing device[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2021, 217: 104752. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2021.104752 [18] LI K, HAN Y, CAI C S, et al. Experimental investigation on post-flutter characteristics of a typical steel-truss suspension bridge deck[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2021, 216: 104724. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2021.104724 [19] 邓正科, 孙测世, 杨汝东. 不同索力斜拉索的主共振瞬时相频特性[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2021, 42(10): 1126-1135DENG Zhengke, SUN Ceshi, YANG Rudong. Transient primary resonance phase-frequency characteristics of stay cables with different tensions[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2021, 42(10): 1126-1135.(in Chinese) [20] SCANLAN R H, TOMKO J J. Airfoil and bridge deck flutter derivatives[J]. Journal of the Engineering Mechanics Division, 1971, 97(6): 1717-1737. [21] MATSUMOTO M. Aerodynamic damping of prisms[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1971, 56: 159-175. [22] MATSUMOTO M, KOBAYASHI Y, SHIRATO H. The influence of aerodynamic derivatives on flutter[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1996, 60: 227-239. doi: 10.1016/0167-6105(96)00036-0 [23] WANG Y F, CHEN X Z, LI Y L. Nonlinear self-excited forces and aerodynamic damping associated with vortex-induced vibration and flutter of long span bridges[J]. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2020, 204: 104207. doi: 10.1016/j.jweia.2020.104207 [24] CHEN X. Analysis of crosswind fatigue of wind-excited structures with nonlinear aerodynamic damping[J]. Engineering Structures, 2014, 74: 145-156. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2014.04.049 -




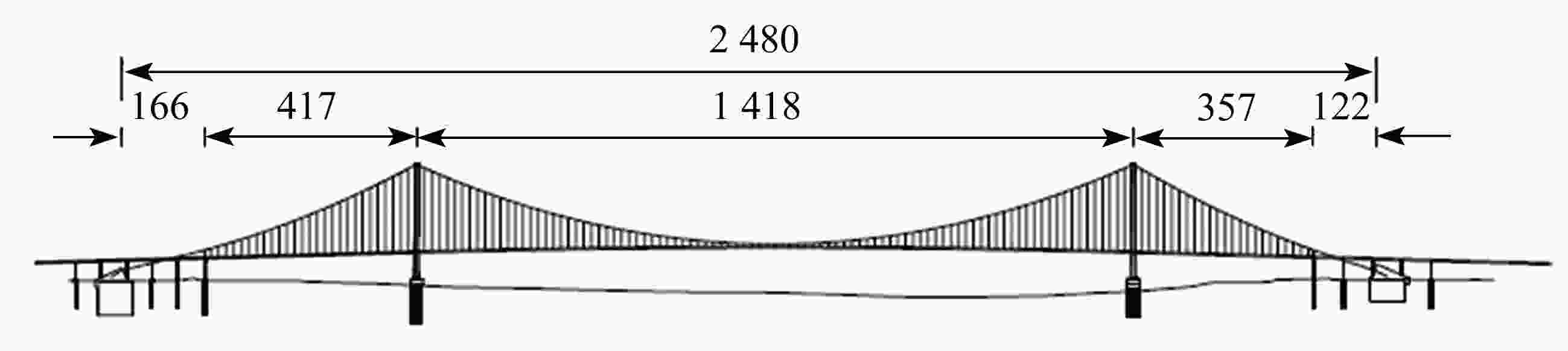
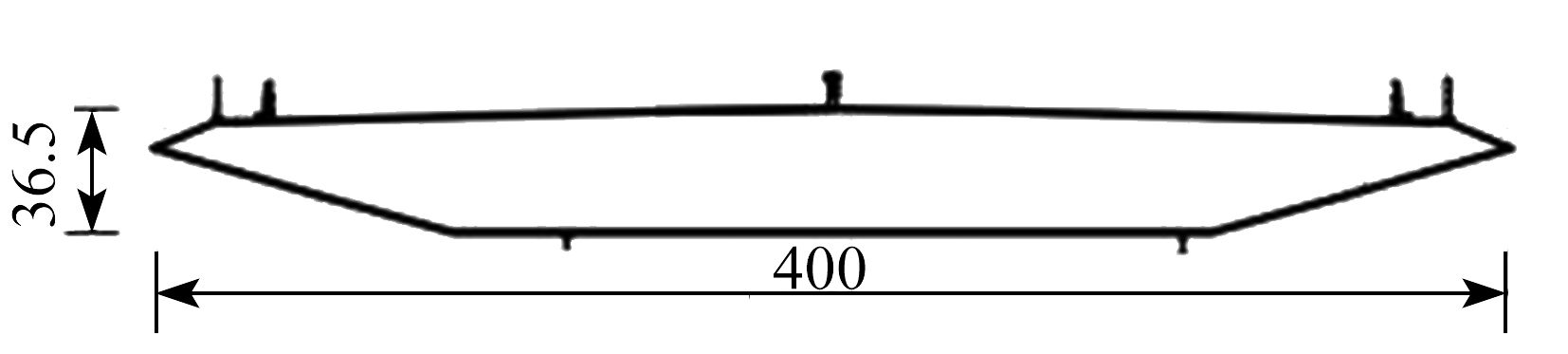
 下载:
下载:

























 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号