A Cell-Based Smoothed Radial Point Interpolation Method for Upper Bound Limit Analysis
-
摘要: 基于极限分析的上限定理,建立了用区域光滑径向点插值法进行理想刚塑性结构极限分析的整套求解算法. 为了能方便地施加本质边界条件,采用径向点插值法构造机动容许的速度场. 通过引入广义梯度光滑技术,将复杂的域内积分转换为简单的光滑域边界积分,避免了对形函数的求导. 考虑了材料的塑性不可压条件,并针对平面应力和平面应变问题采用不同方式进行处理. 将极限上限分析问题归结为满足一系列等式约束的塑性耗散功率最小化问题,从而可采用标准的二阶锥规划对该问题进行求解,这样既提高了求解效率,又提高了求解精度. 数值算例结果表明,该文所提方法能对理想刚塑性结构的极限载荷乘子给出令人满意的结果,并且计算结果对网格畸变十分不敏感.
-
关键词:
- 无网格法 /
- 区域光滑径向点插值法 /
- 极限上限分析 /
- 广义梯度光滑技术 /
- 二阶锥规划
Abstract: Based on the upper bound theorem of limit analysis, a solution procedure for limit analysis of structures made of rigid-perfectly plastic material was proposed with the cell-based smoothed radial point interpolation method (CS-RPIM). To impose the essential boundary conditions directly, the RPIM was utilized to construct a kinematically admissible velocity field. The plastic incompressibility conditions of plane stress and plane strain problems were treated respectively with 2 different methods. The upper bound problem was formulated mathematically through minimization of the dissipation power subject to a set of equality constraints and this minimization problem can be transformed into a standard 2nd-order cone programming one, which can be easily solved with the primal-dual interior point method. Numerical examples demonstrate that, the proposed method can provide reasonable and satisfactory upper bound limit load multipliers for rigid-perfectly plastic structures. In addition, the computational results are very insensitive to the mesh distortion. -
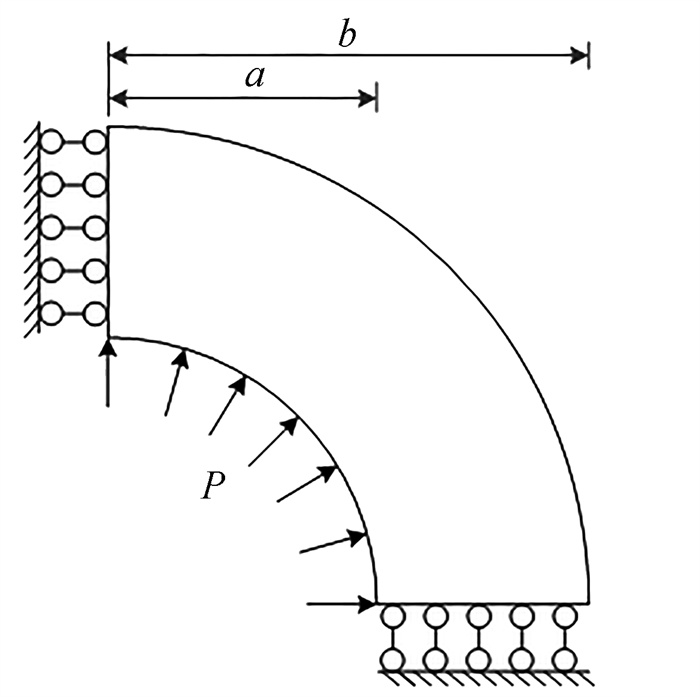
表 1 厚壁圆筒的极限载荷数值解
Table 1. Numerical limit loads for the cylinder
b/a analytical solution the present error/% 2.0 0.800 4 0.801 8 0.174 9 2.5 1.058 0 1.058 8 0.075 6 3.0 1.268 6 1.273 5 0.386 3 3.5 1.446 6 1.453 5 0.518 7 4.0 1.600 8 1.605 7 0.306 1 表 2 不同畸变系数下厚壁圆筒的极限载荷
Table 2. Limit loads of the cylinder with different irregularity factors
irregularity factor analytical solution the present error/% 0.1 0.801 8 0.174 9 0.2 0.803 5 0.387 3 0.3 0.800 4 0.806 6 0.774 6 0.4 0.807 5 0.887 1 0.5 0.808 3 0.987 0 -
[1] LIU F T, ZHAO J D. Upper bound limit analysis using radial point interpolation meshless method and nonlinear programming[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2013, 70: 26-38. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2013.01.017 [2] ZHOU S T, LIU Y H. Upper bound limit analysis based on the natural element method[J]. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 2012, 28 (5): 1398-1415. doi: 10.1007/s10409-012-0149-9 [3] YUAN S, DU J N. Upper bound limit analysis using the weak form quadrature element method[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2018, 56: 551-563. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2017.12.015 [4] YUAN S, DU J N. Effective stress-based upper bound limit analysis of unsaturated soils using the weak form quadrature element method[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2018, 98: 172-180. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2018.02.008 [5] ZHANG X F, LIU Y H, ZHAO Y N, et al. Lower bound limit analysis by the symmetric Galerkin boundary element method and the complex method[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2002, 191 (17/18): 1967-1982. [6] PANZECA T, PARLAVECCHIO E, ZITO L, et al. Lower bound limit analysis by BEM: convex optimization problem and incremental approach[J]. Engineering Analysis With Boundary Elements, 2013, 37 (3): 558-568. doi: 10.1016/j.enganabound.2012.11.016 [7] WANG L H, HU M H, ZHONG Z, et al. Stabilized Lagrange interpolation collocation method: a meshfree method incorporating the advantages of finite element method[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2023, 404: 115780. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2022.115780 [8] 陈卫, 汤智宏, 彭林欣. 基于分层法的功能梯度三明治壳线性弯曲无网格分析[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2024, 45 (5): 539-553. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.440262CHEN Wei, TANG Zhihong, PENG Linxin. Linear bending analysis of functionally graded sandwich shells with the meshless method based on the layer-wise theory[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2024, 45 (5): 539-553. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.440262 [9] 陈虹伶, 李小林. 分数阶Cable方程的有限点法分析[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2022, 43 (6): 700-706. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.420183 CHEN Hongling, LI Xiaolin. Analysis of the finite point method for fractional cable equations[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2022, 43 (6): 700-706. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.420183 [10] WU J, WANG D. An accuracy analysis of Galerkin meshfree methods accounting for numerical integration[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 375: 113631. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2020.113631 [11] 陈莘莘, 王崴. 基于自然单元法的轴对称结构极限上限分析[J]. 计算力学学报, 2020, 37 (2): 159-164.CHEN Shenshen, WANG Wei. Upper bound limit analysis of axisymmetric structures based on natural element method[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 2020, 37 (2): 159-164. (in Chinese) [12] CHEN S S, LIU Y H, CEN Z Z. Lower bound limit analysis by using the EFG method and nonlinear programming[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2008, 74: 391-415. doi: 10.1002/nme.2177 [13] LE C V, GILBERT M, ASKES H. Limit analysis of plates using the EFG method and second-order cone programming[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2009, 78 (13): 1532-1552. doi: 10.1002/nme.2535 [14] CHEN S S, XU M Y, ZHU X Y. A cell-based smoothed radial point interpolation method applied to kinematic limit analysis of thin plates[J]. Engineering Analysis With Boundary Elements, 2022, 143: 710-718. doi: 10.1016/j.enganabound.2022.07.021 [15] LE C V, HO P L H, NGUYEN P H, et al. Yield design of reinforced concrete slabs using a rotation-free meshfree method[J]. Engineering Analysis With Boundary Elements, 2015, 50: 231-238. doi: 10.1016/j.enganabound.2014.09.001 [16] CUI X Y, LIU G R, LI G Y. A cell-based smoothed radial point interpolation method (CS-RPIM) for static and free vibration of solids[J]. Engineering Analysis With Boundary Elements, 2010, 34 (2): 144-157. doi: 10.1016/j.enganabound.2009.07.011 [17] CUI X Y, LIU G R, LI G Y, et al. A thin plate formulation without rotation DOFs based on the radial point interpolation method and triangular cells[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2011, 85 (8): 958-986. doi: 10.1002/nme.3000 [18] LIU G R. A generalized gradient smoothing technique and smoothed bilinear form for Galerkin formulation of a wide class of computational methods[J]. International Journal of Computational Methods, 2008, 5 (2): 199-236. doi: 10.1142/S0219876208001510 [19] WANG J G, LIU G R. A point interpolation meshless method based on radial basis functions[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2002, 54 (11): 1623-1648. doi: 10.1002/nme.489 [20] 姚凌云, 于德介, 臧献国. 声学数值计算的分区光滑径向点插值无网格法[J]. 振动与冲击, 2011, 30 (10): 188-192. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2011.10.036YAO Lingyun, YU Dejie, ZANG Xianguo. Numerical computation for acoustic problems with a cell-based smoothed radial point interpolation method[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2011, 30 (10): 188-192. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2011.10.036 [21] TAO D S, ZHANG G Y, CHEN Z C, et al. A cell-based smoothed radial point interpolation method using condensed shape functions for free and forced vibration analysis of solids[J]. Engineering Analysis With Boundary Elements, 2019, 102: 29-38. doi: 10.1016/j.enganabound.2019.02.003 [22] WU G, ZHANG J, LI Y L, et al. Analysis of transient thermo-elastic problems using a cell-based smoothed radial point interpolation method[J]. International Journal of Computational Methods, 2016, 13 (5): 1650023. doi: 10.1142/S0219876216500237 [23] FENG S Z, LI A M. Analysis of thermal and mechanical response in functionally graded cylinder using cell-based smoothed radial point interpolation method[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2017, 65: 46-53. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2017.02.009 [24] TOOTOONCHI A, KHOSHGHALB A, LIU G R, et al. A cell-based smoothed point interpolation method for flow-deformation analysis of saturated porous media[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2016, 75: 159-173. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2016.01.027 [25] MITTELMANN H D. An independent benchmarking of SDP and SOCP solvers[J]. Mathematical Programming, 2003, 95 (2): 407-430. doi: 10.1007/s10107-002-0355-5 [26] LE C V, NGUYEN-XUAN H, ASKES H, et al. A cell-based smoothed finite element method for kinematic limit analysis[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2010, 83 (12): 1651-1674. doi: 10.1002/nme.2897 [27] CIRIA H, PERAIRE J, BONET J. Mesh adaptive computation of upper and lower bounds in limit analysis[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2008, 75 (8): 899-944. doi: 10.1002/nme.2275 -





 下载:
下载:







 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号