Intelligent Crack Recognition Based on XFEM and GA-BP Neural Networks
-
摘要:
基于扩展有限元法(XFEM)和经遗传算法(GA)优化的误差反向传播多层前馈(BP)神经网络(GA-BP)算法,建立了识别结构中裂纹的反演分析模型。模型通过XFEM正向分析获得的测点位移数据训练GA-BP神经网络,并在此基础上利用该网络进行裂纹反向识别。通过两个典型算例对模型的可行性和精度进行了验证,并探讨了网格密度、测点布置、输入数据噪声等对网络识别精度的影响。结果表明,该文的方法可反演线弹性断裂力学重点关注的直线裂纹的几何信息且具有较好的容噪性能,此外,GA-BP神经网络的预测精度较传统BP神经网络普遍更高。
Abstract:Based on the extended finite element method (XFEM) and the error back propagation (BP) multilayer feedforward neural network algorithm optimized by the genetic algorithm (GA), an inverse analysis model for identifying cracks in structures was established. The GA-BP neural network was trained by the displacement data of measuring points obtained by the XFEM forward analysis, and the network was used for crack inverse identification. The feasibility and accuracy of the model were verified with 2 typical examples, and the effects of the mesh density, the measuring point layout and the input data noise on the accuracy of network recognition were discussed. The results show that, the proposed method can invert the geometric information of straight cracks, which is the major focus of linear elastic fracture mechanics, and has good noise tolerance. Besides, the GA-BP neural network has higher accuracy than the traditional BP neural network in general.
-
Key words:
- extended finite element method /
- genetic algorithm /
- BP neural network /
- inverse analysis /
- crack
-
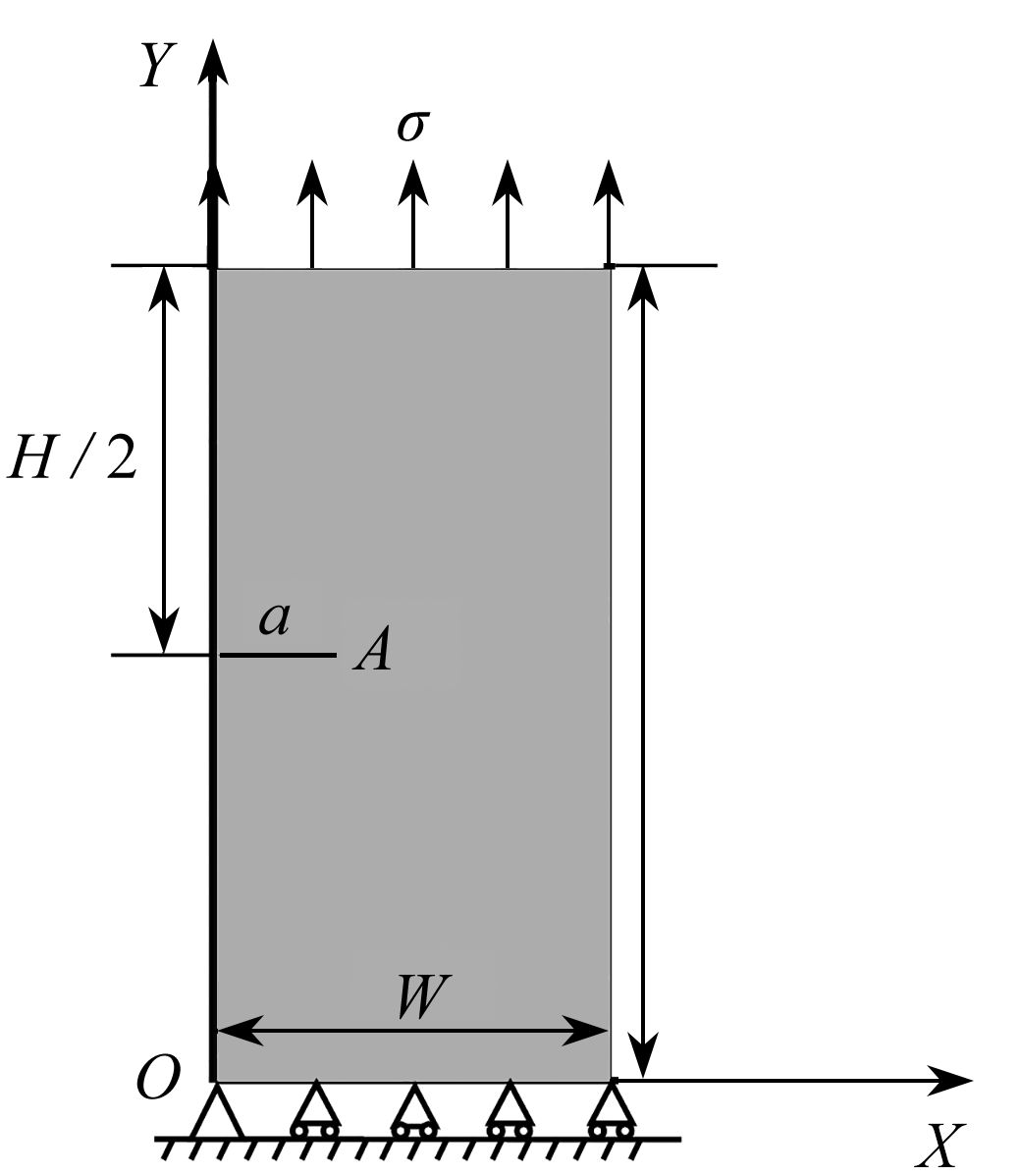
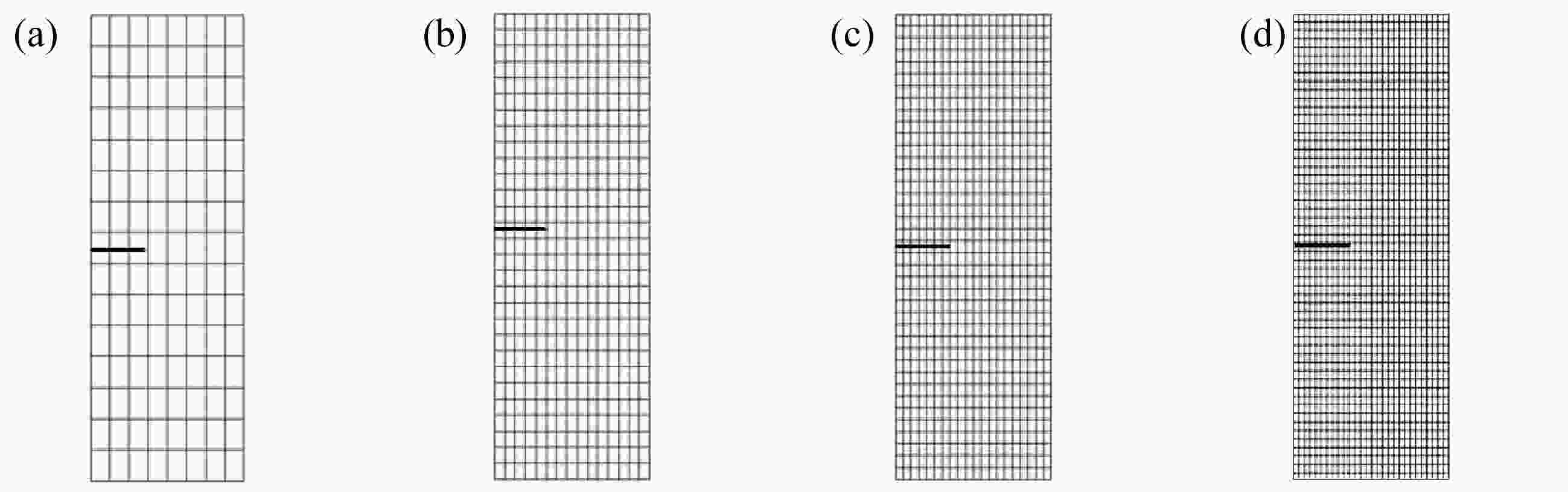
表 1 不同网格下的
$ {K_{\rm I}} $ (单位:MPa·m1/2)Table 1.
$ {K_{\rm I}} $ for different meshes (unit: MPa·m1/2)XFEM solution reference solution 120 elements 435 elements 780 elements 1540 elements 2.5743
(6.86%)2.6801
(3.03%)2.7209
(1.55%)2.7224
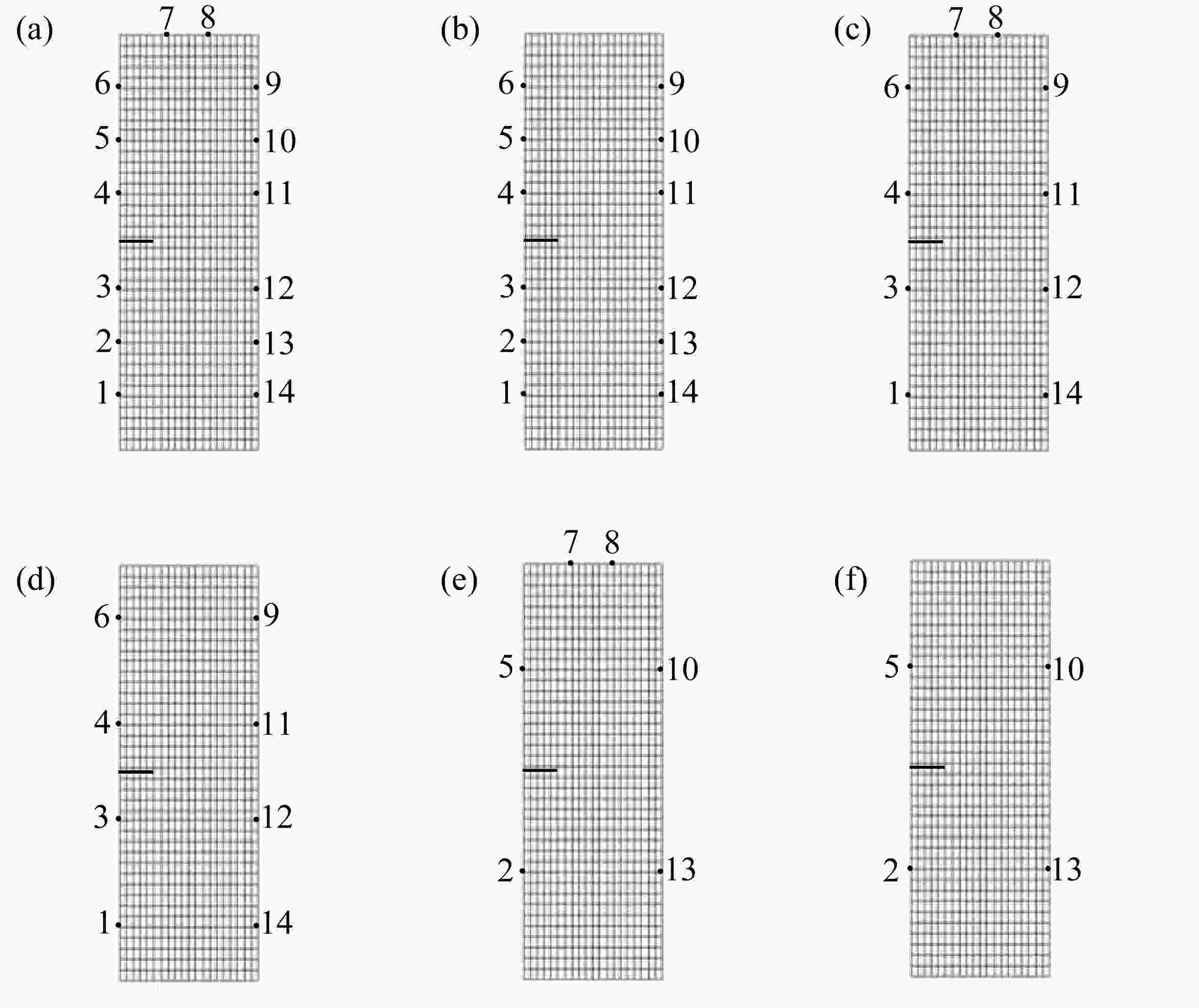
(1.50%)2.7639 表 2 测点坐标
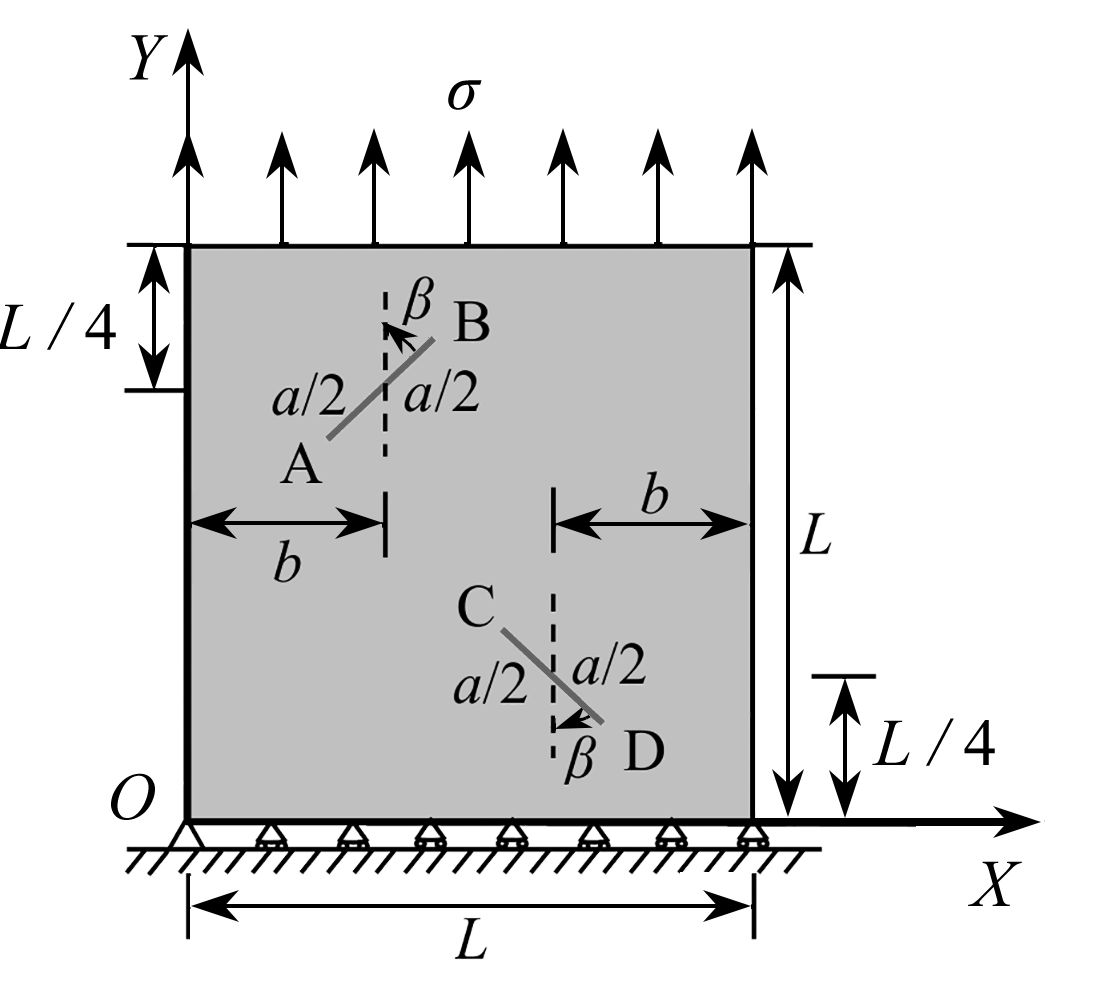
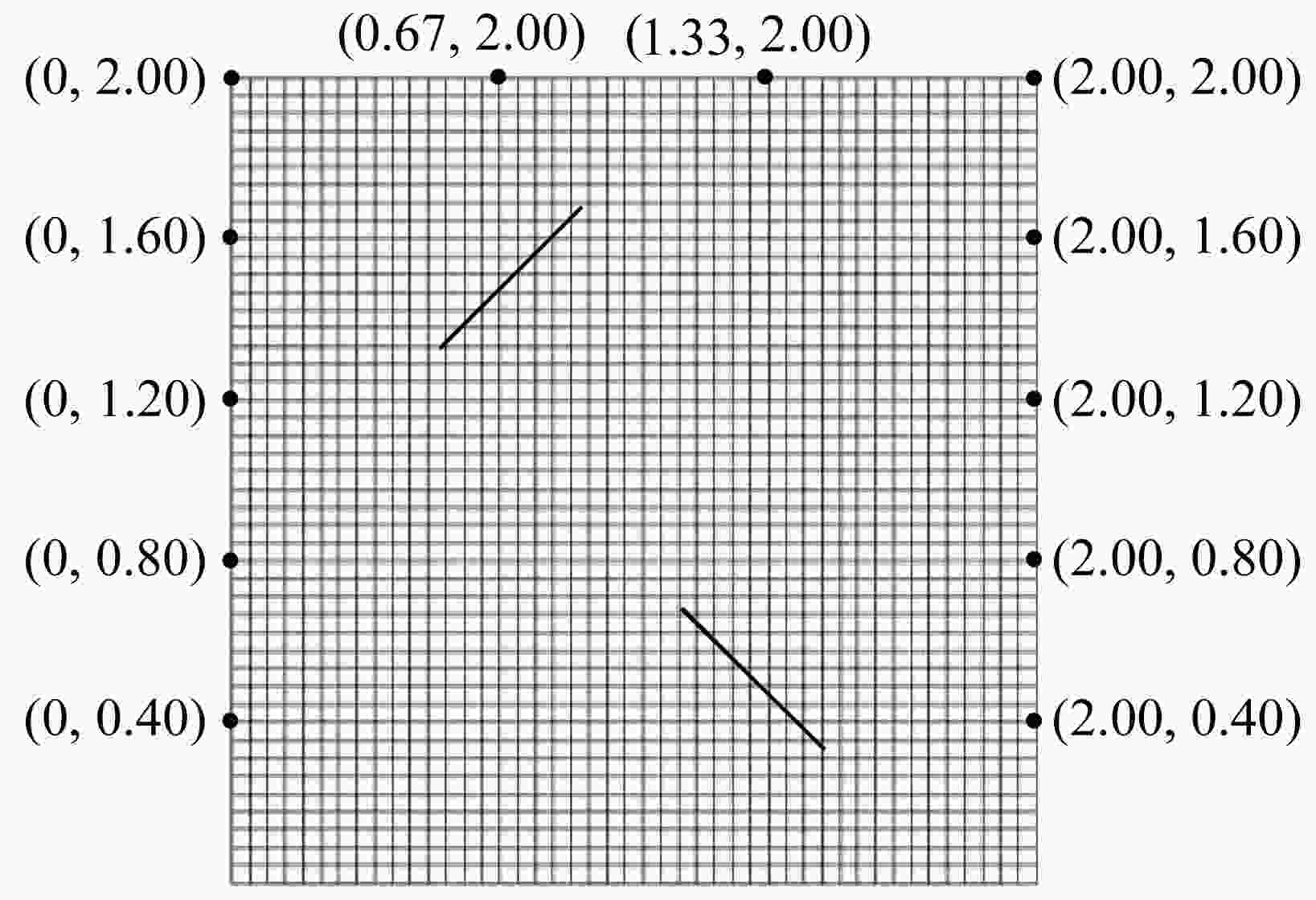
Table 2. Coordinates of measuring points
number X Y number X Y 1 0.0000 0.7692 8 1.3000 6.0000 2 0.0000 1.5385 9 2.0000 5.2308 3 0.0000 2.3077 10 2.0000 4.4615 4 0.0000 3.6923 11 2.0000 3.6923 5 0.0000 4.4615 12 2.0000 2.3077 6 0.0000 5.2308 13 2.0000 1.5385 7 0.7000 6.0000 14 2.0000 0.7692 表 3 GA-BP神经网络对XA的训练输出结果
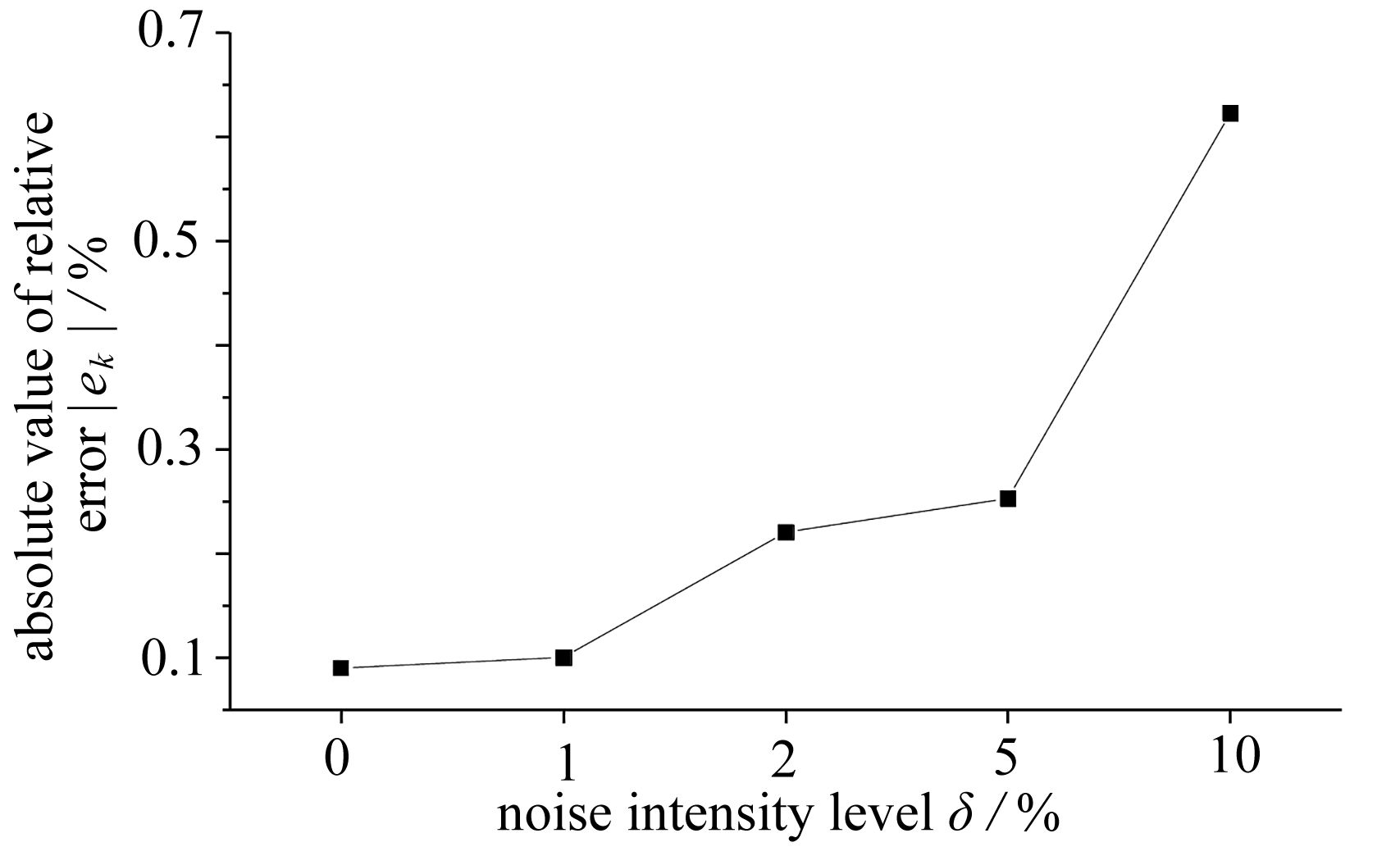
Table 3. Training results of the GA-BP neural network for XA
crack length a/m true XA training XA relative error ek/% 0.5 0.5000 0.5057 1.14 0.6 0.6000 0.6004 0.07 0.7 0.7000 0.6991 −0.13 0.8 0.8000 0.7996 −0.05 0.9 0.9000 0.9003 0.03 1.0 1.0000 1.0004 0.04 1.1 1.1000 1.0999 −0.01 1.2 1.2000 1.1994 −0.05 1.3 1.3000 1.2999 −0.01 1.4 1.4000 1.4010 0.07 表 4 BP与GA-BP神经网络预测的XA值
Table 4. Prediction of XA by BP and GA-BP neural networks
layout scheme of
measuring pointsnumber of
measuring pointsnumber of hidden
layer neuronstrue XA BP prediction
XArelative error
ek/%GA-BP prediction
XArelative error
ek/%1 14 4 1.5000 1.4756 1.63 1.4958 0.28 2 12 4 1.4968 0.21 1.4862 0.92 3 10 8 1.5977 6.51 1.4979 0.14 4 8 4 1.4911 0.59 1.4837 1.08 5 6 3 1.5210 1.40 1.4979 0.14 6 4 3 1.5518 3.45 1.4676 2.16 表 6 GA-BP神经网络对裂尖B坐标的训练值
Table 6. Training coordinates of crack tip B by the GA-BP neural network
crack length a/m true XB training XB true YB training YB 0.500 0.8768 0.8769 1.6768 1.6806 0.528 0.8868 0.8873 1.6868 1.6913 0.556 0.8968 0.8953 1.6968 1.6974 0.585 0.9068 0.9084 1.7068 1.7109 0.613 0.9168 0.9170 1.7168 1.7218 0.641 0.9268 0.9257 1.7268 1.7299 0.670 0.9368 0.9380 1.7368 1.7406 0.698 0.9468 0.9462 1.7468 1.7449 表 7 GA-BP神经网络对裂尖C坐标的训练值
Table 7. Training coordinates of crack tip C by the GA-BP neural network
crack length a/m true XC training XC true YC training YC 0.500 1.1232 1.1236 0.6768 0.6744 0.528 1.1132 1.1128 0.6868 0.6841 0.556 1.1032 1.1046 0.6968 0.6941 0.585 1.0932 1.0910 0.7068 0.7027 0.613 1.0832 1.0826 0.7168 0.7121 0.641 1.0732 1.0739 0.7268 0.7225 0.670 1.0632 1.0620 0.7368 0.7329 0.698 1.0532 1.0543 0.7468 0.7438 表 5 GA-BP神经网络对裂尖A坐标的训练值
Table 5. Training coordinates of crack tip A by the GA-BP neural network
crack length a/m true XA training XA true YA training YA 0.500 0.5232 0.5238 1.3232 1.3194 0.528 0.5132 0.5127 1.3132 1.3088 0.556 0.5032 0.5044 1.3032 1.3031 0.585 0.4932 0.4906 1.2932 1.2893 0.613 0.4832 0.4823 1.2832 1.2783 0.641 0.4732 0.4738 1.2732 1.2703 0.670 0.4632 0.4622 1.2632 1.2594 0.698 0.4532 0.4549 1.2532 1.2556 表 8 GA-BP神经网络对裂尖D坐标的训练值
Table 8. Training coordinates of crack tip D by the GA-BP neural network
crack length a/m true XD training XD true YD training YD 0.500 1.4768 1.4748 0.3232 0.3258 0.528 1.4868 1.4872 0.3132 0.3160 0.556 1.4968 1.4962 0.3032 0.3049 0.585 1.5068 1.5113 0.2932 0.2971 0.613 1.5168 1.5192 0.2832 0.2879 0.641 1.5268 1.5272 0.2732 0.2772 0.670 1.5368 1.5377 0.2632 0.2671 0.698 1.5468 1.5433 0.2532 0.2553 表 9 BP与GA-BP神经网络对裂尖A、B的预测值
Table 9. Prediction of crack tips A and B by BP and GA-BP neural networks
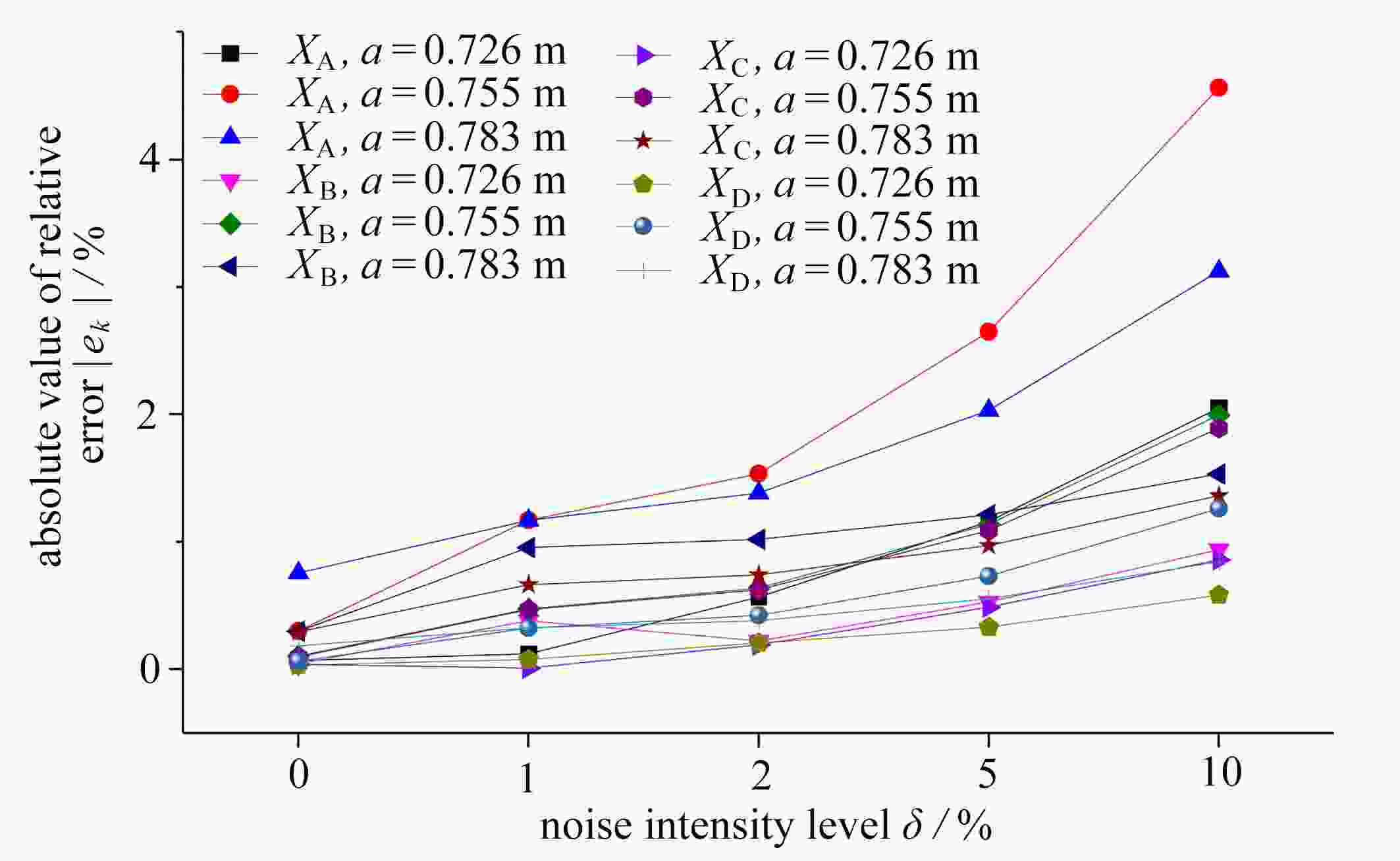
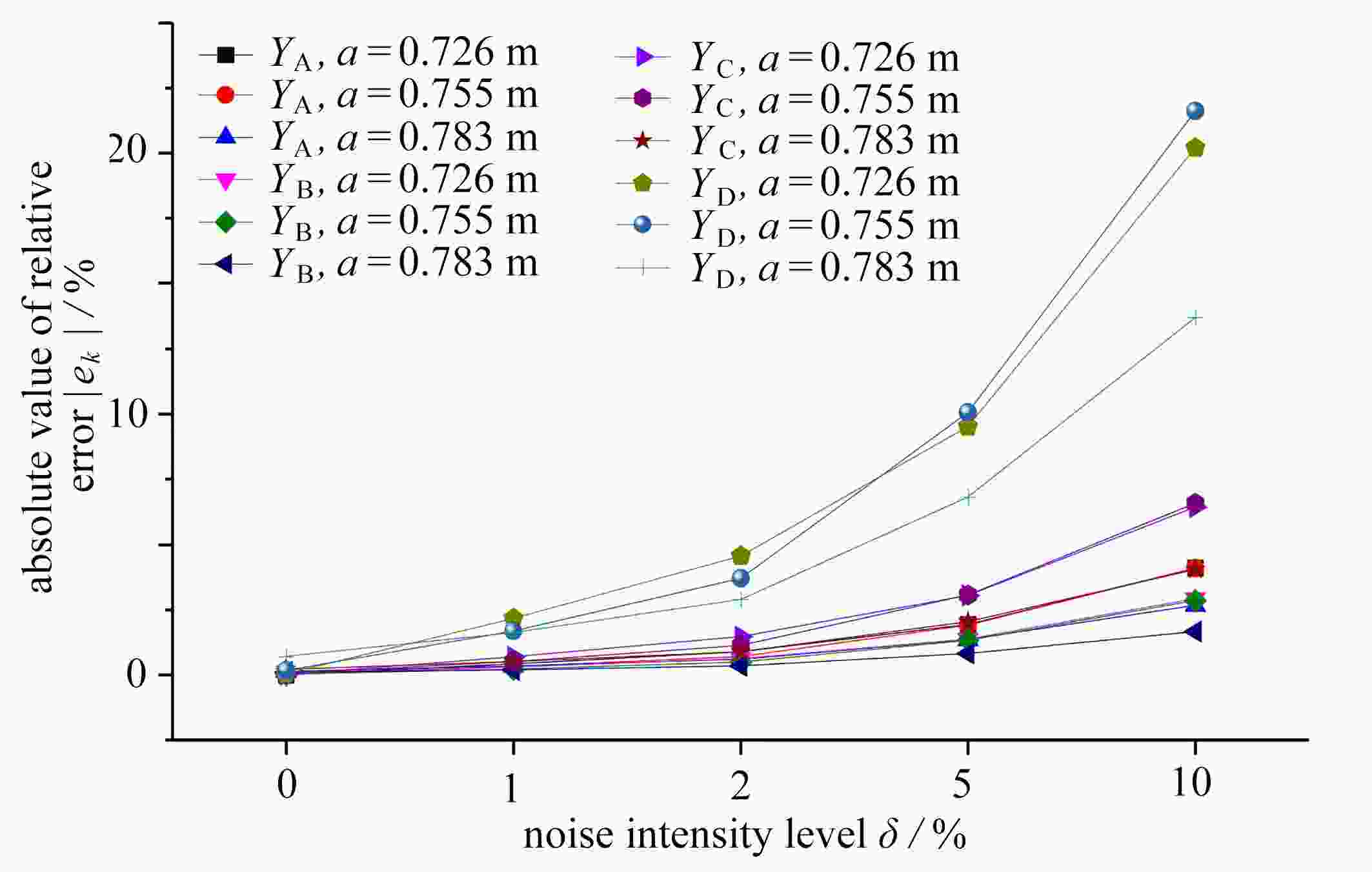
crack length a/m XA relative error ek/% YA relative error ek/% XB relative error ek/% YB relative error ek/% 0.726 true value 0.4432 − 1.2432 − 0.9568 − 1.7568 − BP 0.4465 0.74 1.2491 0.47 0.9558 0.11 1.7515 0.30 GA-BP 0.4435 0.07 1.2433 0.01 0.9564 0.04 1.7566 0.01 0.755 true value 0.4332 − 1.2332 − 0.9668 − 1.7668 − BP 0.4411 1.82 1.2534 1.64 0.9637 0.32 1.7482 1.05 GA-BP 0.4345 0.29 1.2336 0.03 0.9658 0.10 1.7663 0.03 0.783 true value 0.4232 − 1.2232 − 0.9768 − 1.7768 − BP 0.4350 2.79 1.2529 2.43 0.9729 0.40 1.7492 1.55 GA-BP 0.4264 0.77 1.2248 0.13 0.9739 0.30 1.7750 0.10 表 10 BP与GA-BP神经网络对裂尖C、D的预测值
Table 10. Prediction of crack tips C and D by BP and GA-BP neural networks
crack length a/m XC relative error ek/% YC relative error ek/% XD relative error ek/% YD relative error ek/% 0.726 true value 1.0432 − 0.7568 − 1.5568 − 0.2432 − BP 1.0454 0.22 0.7541 0.36 1.5492 0.49 0.2446 0.56 GA-BP 1.0436 0.04 0.7567 0.02 1.5563 0.03 0.2433 0.05 0.755 true value 1.0332 − 0.7668 − 1.5668 − 0.2332 − BP 1.0390 0.56 0.7656 0.16 1.5495 1.11 0.2306 1.10 GA-BP 1.0342 0.10 0.7664 0.05 1.5658 0.06 0.2336 0.17 0.783 true value 1.0232 − 0.7768 − 1.5768 − 0.2232 − BP 1.0318 0.84 0.7753 0.19 1.5492 1.75 0.2196 1.59 GA-BP 1.0262 0.29 0.7752 0.21 1.5739 0.19 0.2248 0.72 -
[1] KWAN A K H, MA F J. Crack width analysis of reinforced concrete under direct tension by finite element method and crack queuing algorithm[J]. Engineering Structures, 2016, 126(1): 618-627. [2] XIE G Z, ZHOU F L, LI H, et al. A family of non-conforming crack front elements of quadrilateral and triangular types for 3D crack problems using the boundary element method[J]. Frontiers of Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 14(3): 332-341. doi: 10.1007/s11465-019-0540-3 [3] 李录贤, 王铁军. 扩展有限元法(XFEM)及其应用[J]. 力学进展, 2005, 35(1): 5-20 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0992.2005.01.002LI Luxian, WANG Tiejun. The extended finite element method and its application: a review[J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2005, 35(1): 5-20.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0992.2005.01.002 [4] 王振, 余天堂. 模拟三维裂纹问题的自适应多尺度扩展有限元法[J]. 工程力学, 2016, 33(1): 32-38 doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2014.06.0483WANG Zhen, YU Tiantang. Adaptive multiscale extended finite element method for simulating three-dimensional crack problems[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2016, 33(1): 32-38.(in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2014.06.0483 [5] XIAO G Z, WEN L F, TIAN R. Arbitrary 3D crack propagation with improved XFEM: accurate and efficient crack geometries[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 377: 113659. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2020.113659 [6] LI Y M, XIA Y D, XIE D L, et al. Application of artificial bee colony algorithm for particle size distribution measurement of suspended sediment based on focused ultrasonic sensor[J]. Transactions of the Institute of Measurement and Control, 2021, 43(7): 1680-1690. doi: 10.1177/0142331221989115 [7] ALHADDAD W, HALABI Y, MEREE H, et al. Optimum design method for simplified model of outrigger and ladder systems in tall buildings using genetic algorithm[J]. Structures, 2020, 28: 2467-2487. doi: 10.1016/j.istruc.2020.09.066 [8] MOLDOVANU S, OBREJA C-D, BISWAS K C, et al. Towards accurate diagnosis of skin lesions using feedforward back propagation neural networks[J]. Diagnostics (Basel) , 2021, 11(6): 936. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11060936 [9] 王佳萍, 杜成斌, 王翔, 等. 基于XFEM和改进人工蜂群算法的结构内部缺陷反演[J]. 工程力学, 2019, 36(9): 25-31WANG Jiaping, DU Chengbin, WANG Xiang, et al. Inverse analysis of internal defects in structures using extended finite element method and improved artificial bee colony algorithm[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2019, 36(9): 25-31.(in Chinese) [10] DU C, ZHAO W, JIANG S, et al. Dynamic XFEM-based detection of multiple flaws using an improved artificial bee colony algorithm[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 365: 112995. doi: 10.1016/j.cma.2020.112995 [11] RABINOVICH D, GIVOLI D, VIGDERGAUZ S. XFEM-based crack detection scheme using a genetic algorithm[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2007, 71(9): 1051-1080. doi: 10.1002/nme.1975 [12] CHATZI E N, HIRIYUR B, WAISMAN H, et al. Experimental application and enhancement of the XFEM-GA algorithm for the detection of flaws in structures[J]. Computers and Structures, 2010, 89(7): 556-570. [13] 王佳萍, 杜成斌, 江守燕. 扩展有限元与遗传算法相结合的结构缺陷反演分析[J]. 力学与实践, 2017, 39(6): 591-596 doi: 10.6052/1000-0879-17-176WANG Jiaping, DU Chengbin, JIANG Shouyan. Analysis of structural defect inversion based on extended finite element and genetic algorithm[J]. Mechanics in Engineering, 2017, 39(6): 591-596.(in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/1000-0879-17-176 [14] 孟建军, 孟高阳, 李德仓. 基于SA-GA混合算法的动车组车辆轮重分配优化[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2021, 42(4): 363-372MENG Jianjun, MENG Gaoyang, LI Decang. Optimization of wheel weight distribution for EMU vehicles based on the SA-GA hybrid algorithm[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2021, 42(4): 363-372.(in Chinese) [15] WANG H Y, ZHANG Z X, LIU L M. Prediction and fitting of weld morphology of Al alloy-CFRP welding-rivet hybrid bonding joint based on GA-BP neural network[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2021, 63: 109-120. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.04.010 [16] WANG Z W, FEI Y, YE P X, et al. Crack characterization in ferromagnetic steels by pulsed eddy current technique based on GA-BP neural network model[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2020, 500: 166412. doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2020.166412 [17] 江守燕, 杜成斌. 基于扩展有限元的结构内部缺陷(夹杂)的反演分析模型[J]. 力学学报, 2015, 47(6): 1037-1045 doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-15-134JIANG Shouyan, DU Chengbin. Numerical model for identification of internal defect or inclusion based on extended finite elememt methods[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2015, 47(6): 1037-1045.(in Chinese) doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-15-134 [18] 张慧华. 典型不连续固体力学问题的数值求解[D]. 博士学位论文. 西安: 西安交通大学, 2009.ZHANG Huihua. Numerical solutions to typical discontinuous problems in solid mechanics[D]. PhD Thesis. Xi’an: Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2009. (in Chinese) [19] 茹忠亮, 朱传锐, 张友良, 等. 断裂问题的扩展有限元法研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2011, 32(7): 2171-2176 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2011.07.042RU Zhongliang, ZHU Chuanrui, ZHANG Youliang, et al. Study of fracture problem with extended finite element method[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2011, 32(7): 2171-2176.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2011.07.042 [20] 冉雨晴, 吴玮, 狄鑫. 基于遗传算法优化BP神经网络的管网漏失定位模型研究[J]. 水电能源科学, 2021, 39(5): 123-126RAN Yuqing, WU Wei, DI Xin. Study on leakage location model of water supply network based on bp neural network optimized by genetic algorithm[J]. Water Resources and Power, 2021, 39(5): 123-126.(in Chinese) [21] HOLLAND J H. Adaptation in Natural and Artificial Systems: an Introductory Analysis With Applications to Biology, Control, and Artificial Intelligence[M]. Cambridge : The MIT Press, 1992. [22] WANG X, AN S, XU Y Q, et al. A back propagation neural network model optimized by mind evolutionary algorithm for estimating Cd, Cr, and Pb concentrations in soils using vis-NIR diffuse reflectance spectroscopy[J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(1): 51. [23] 中国航空研究院. 应力强度因子手册[M]. 增订版. 北京: 科学出版社, 1993.Chinese Aeronautical Establishment. Stress Intensity Factor Manual[M]. revised and enlarged ed. Beijing: Science Press, 1993. (in Chinese) -




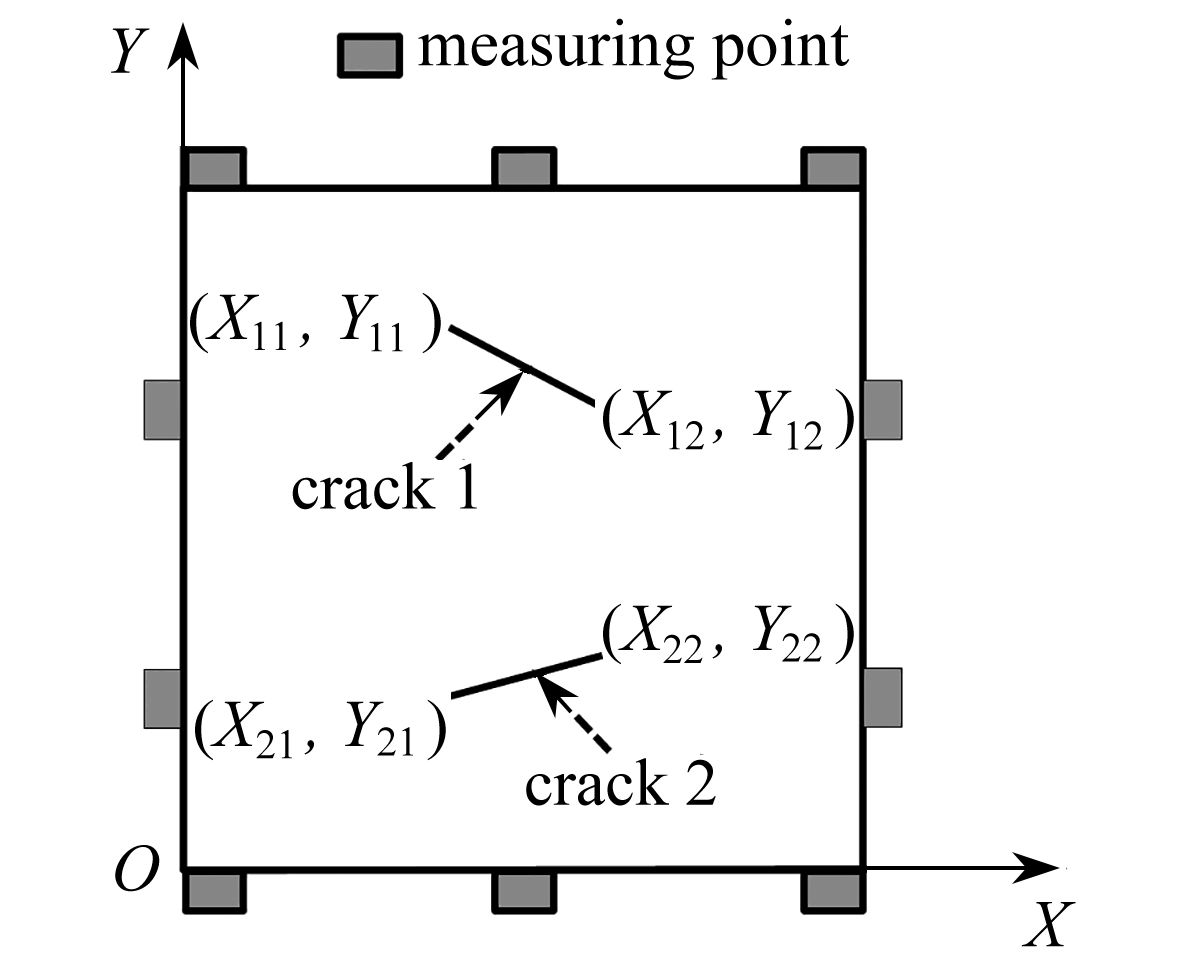
 下载:
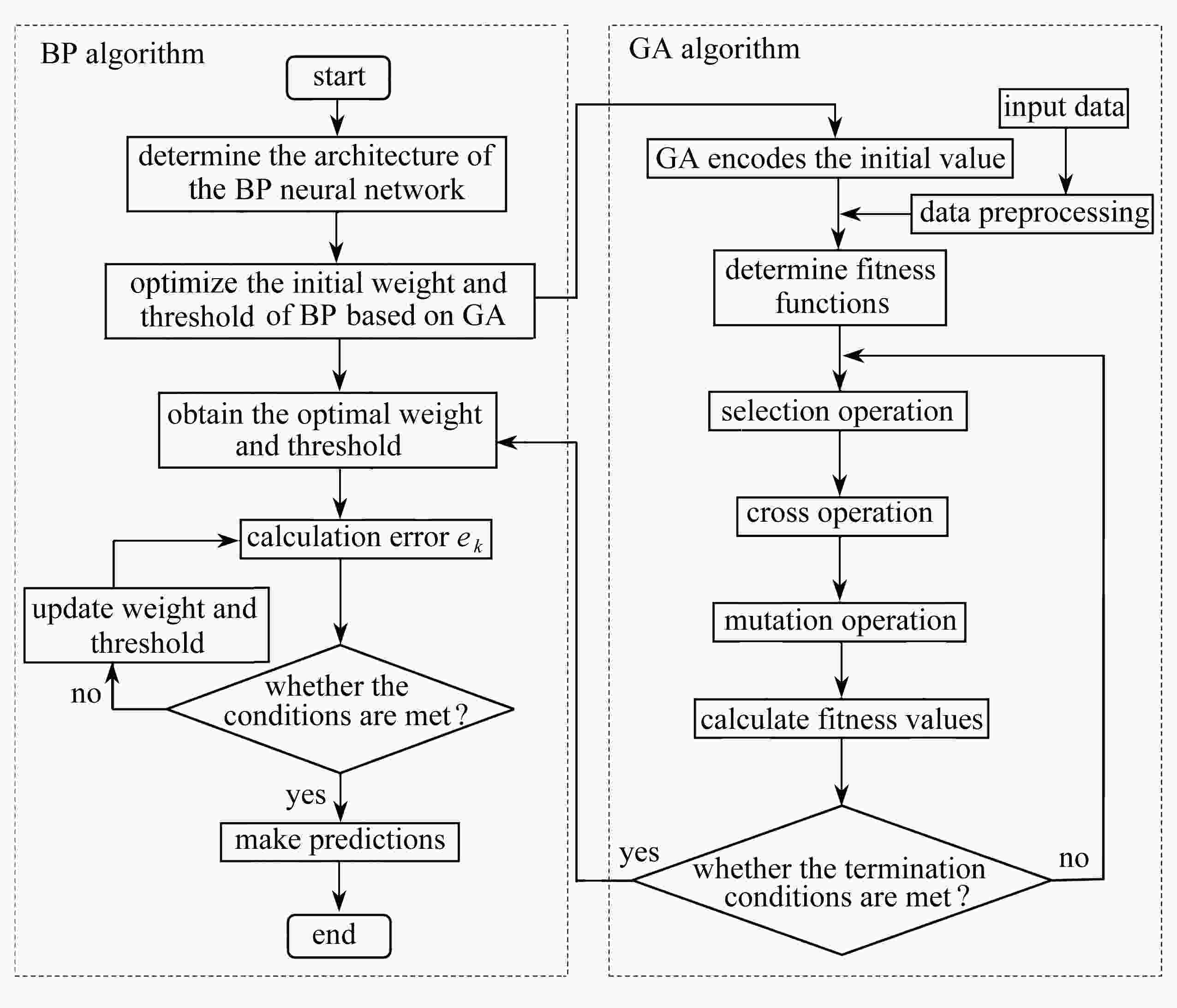
下载:
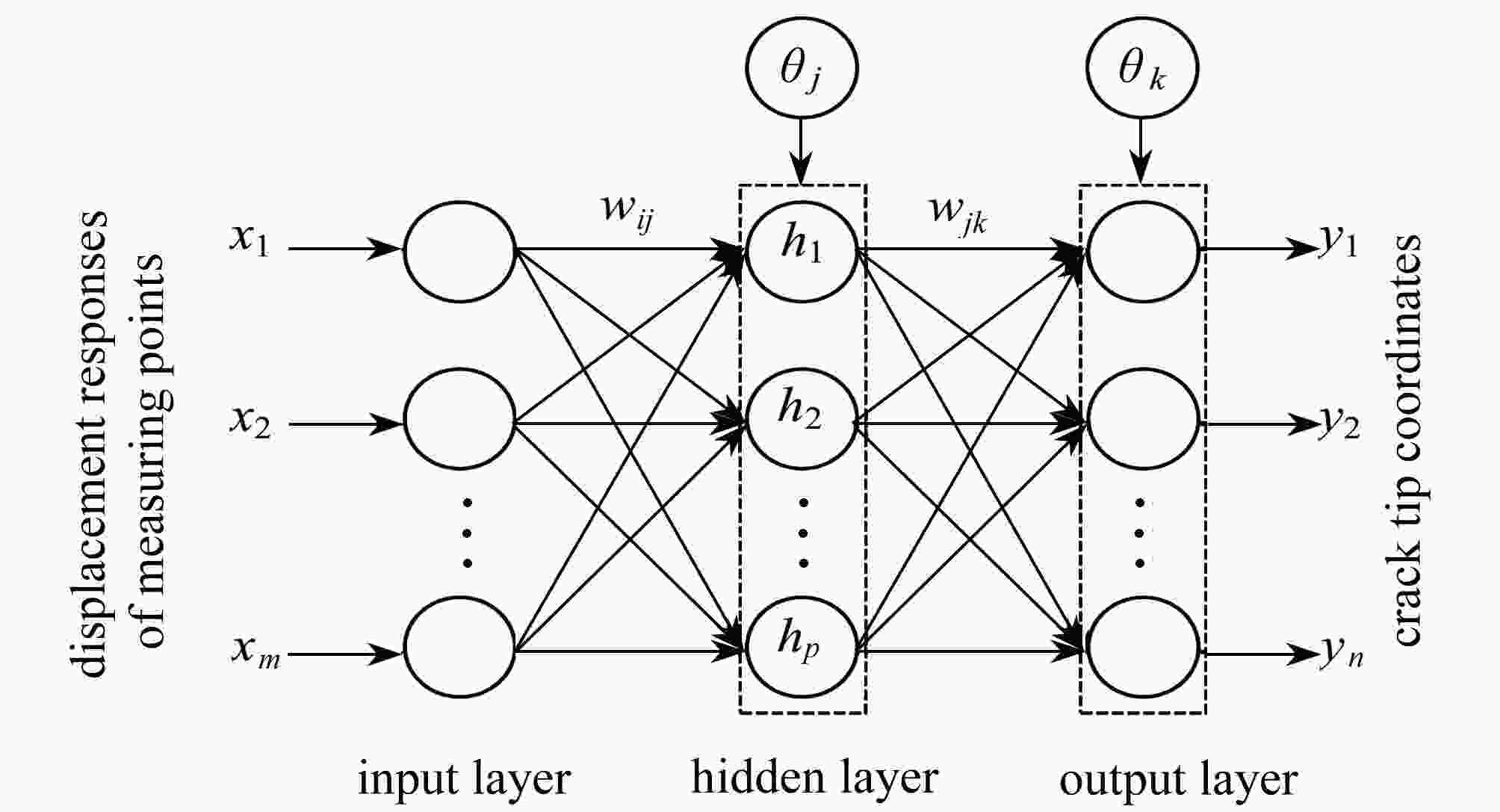
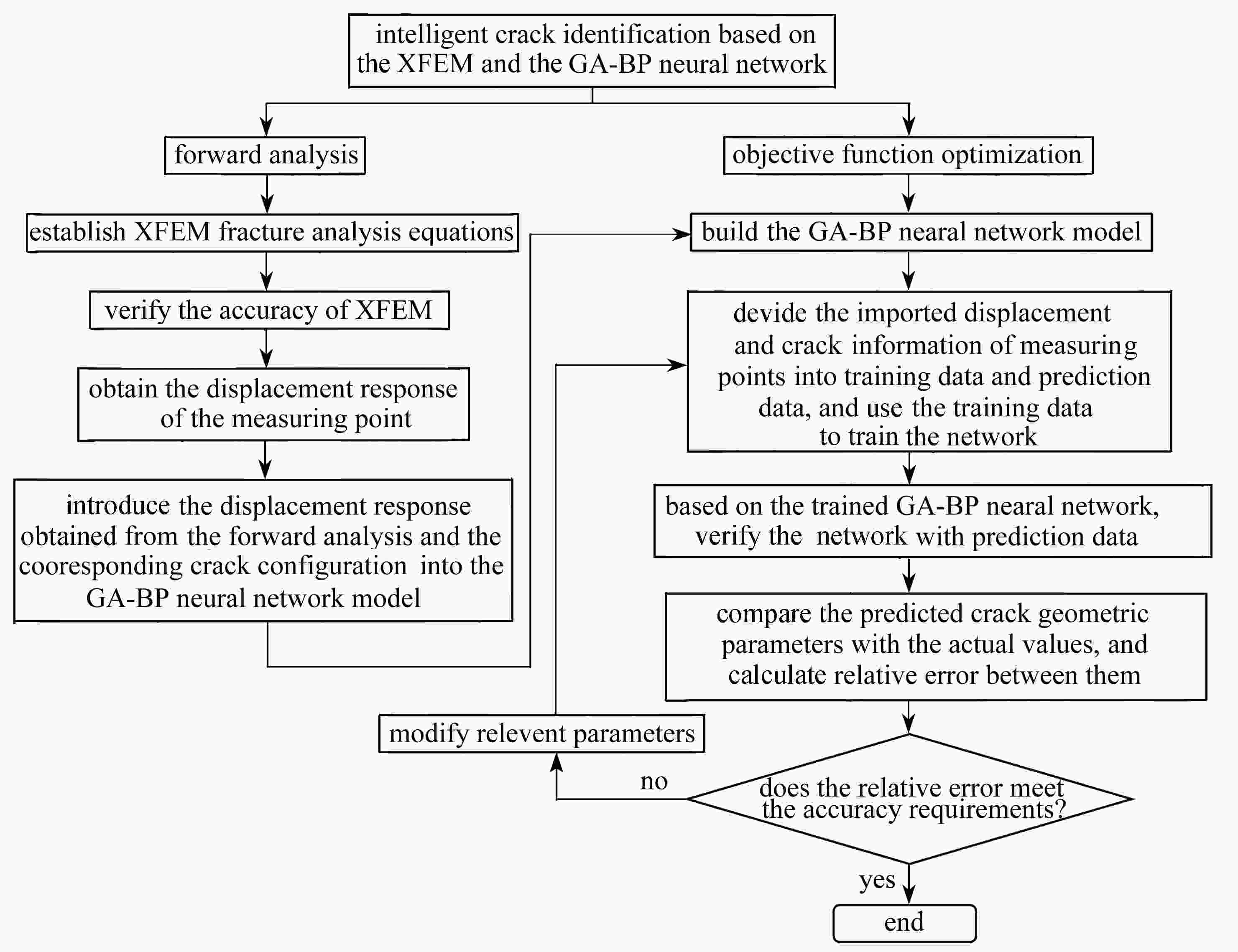



 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号