Numerical Investigation of Particle Focusing Patterns in Laminar Pipe Flow With High Reynolds Numbers
-
摘要:
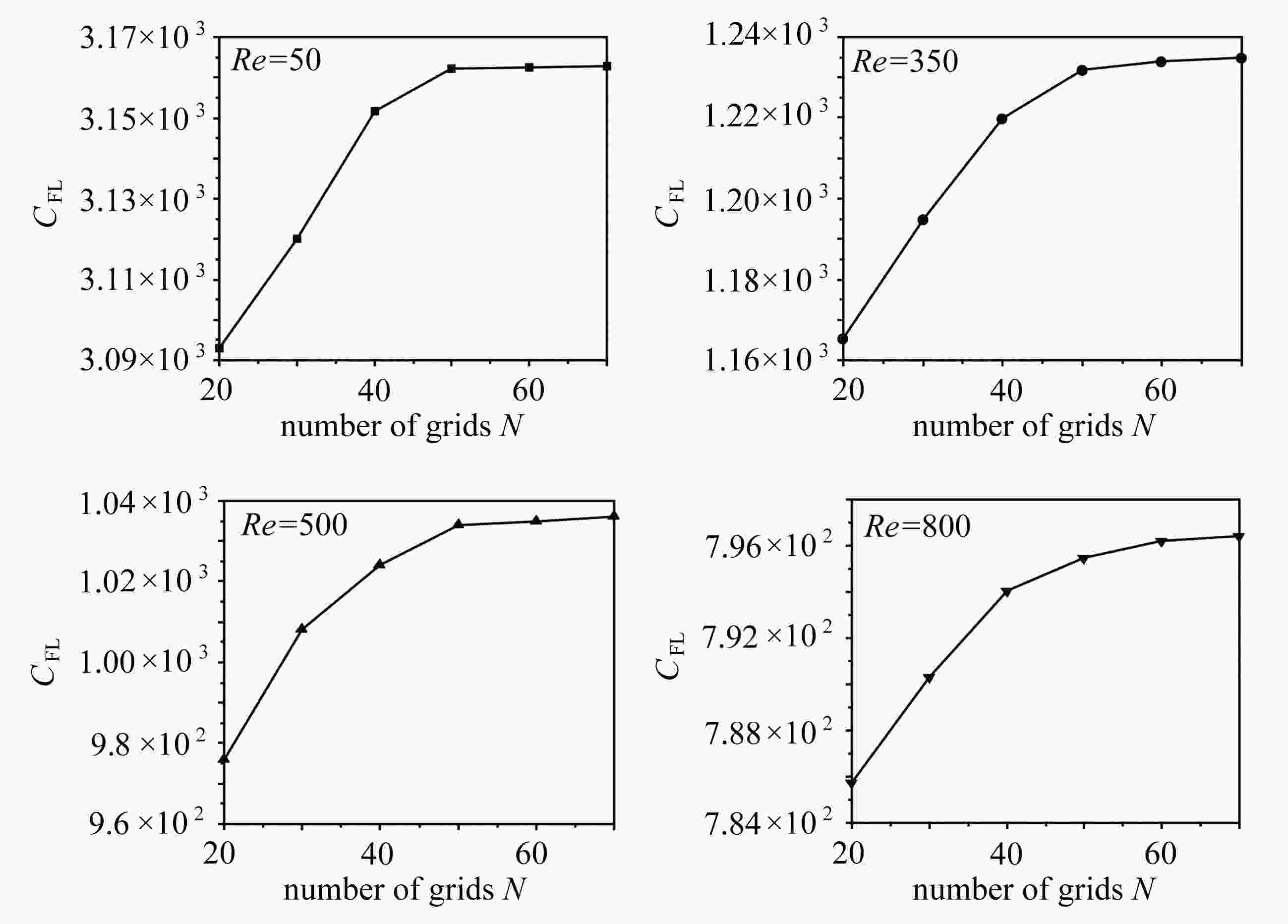
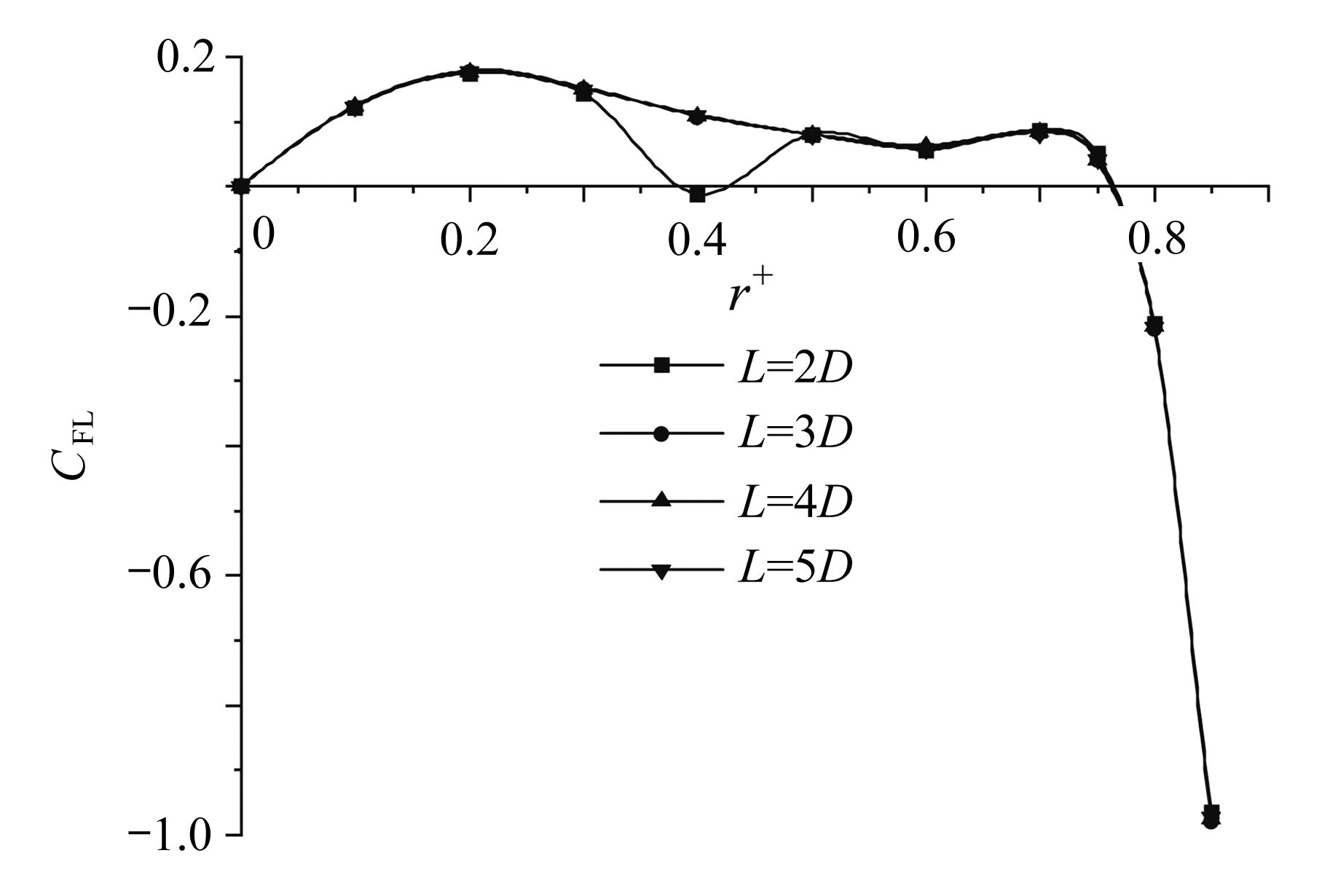
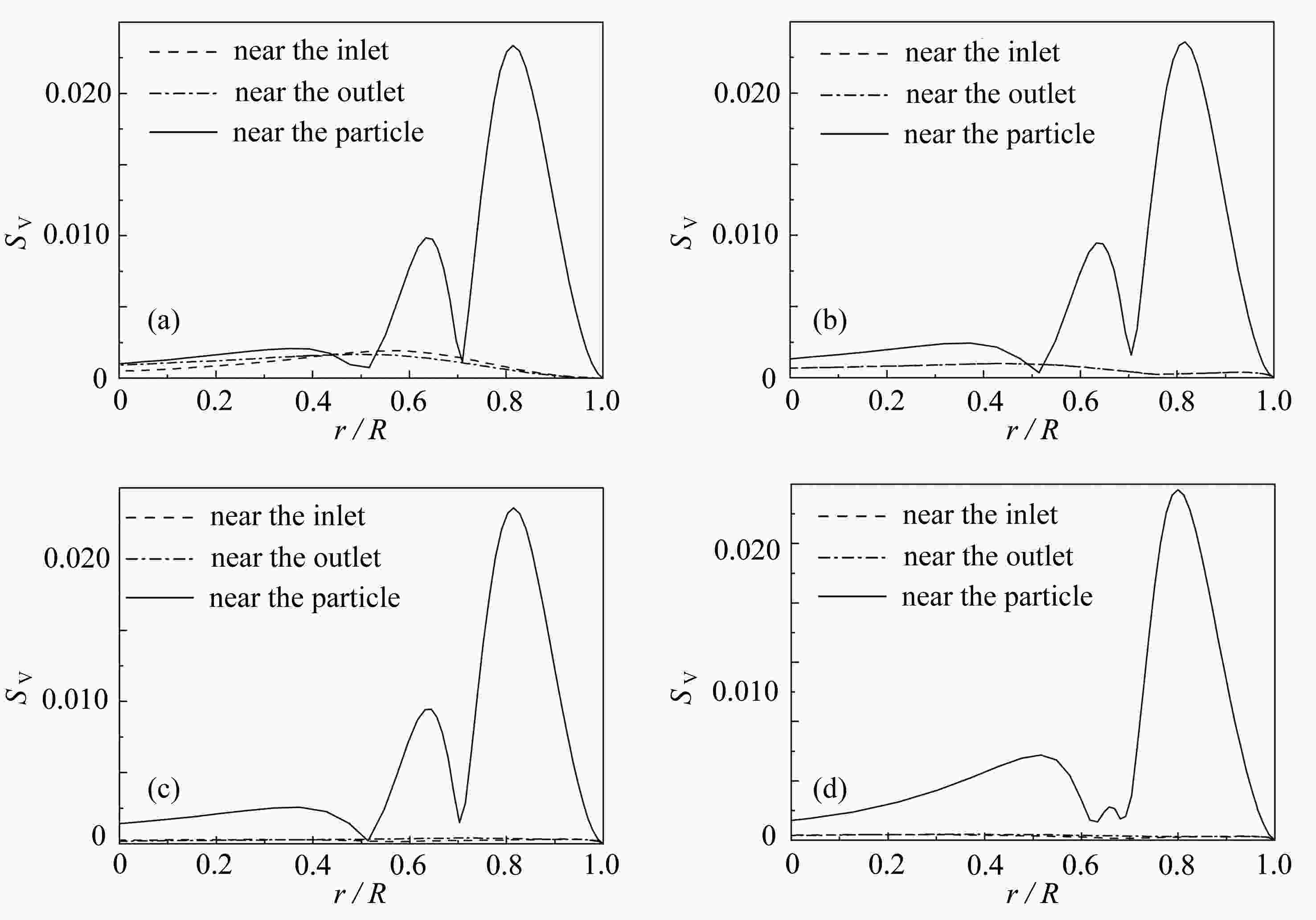
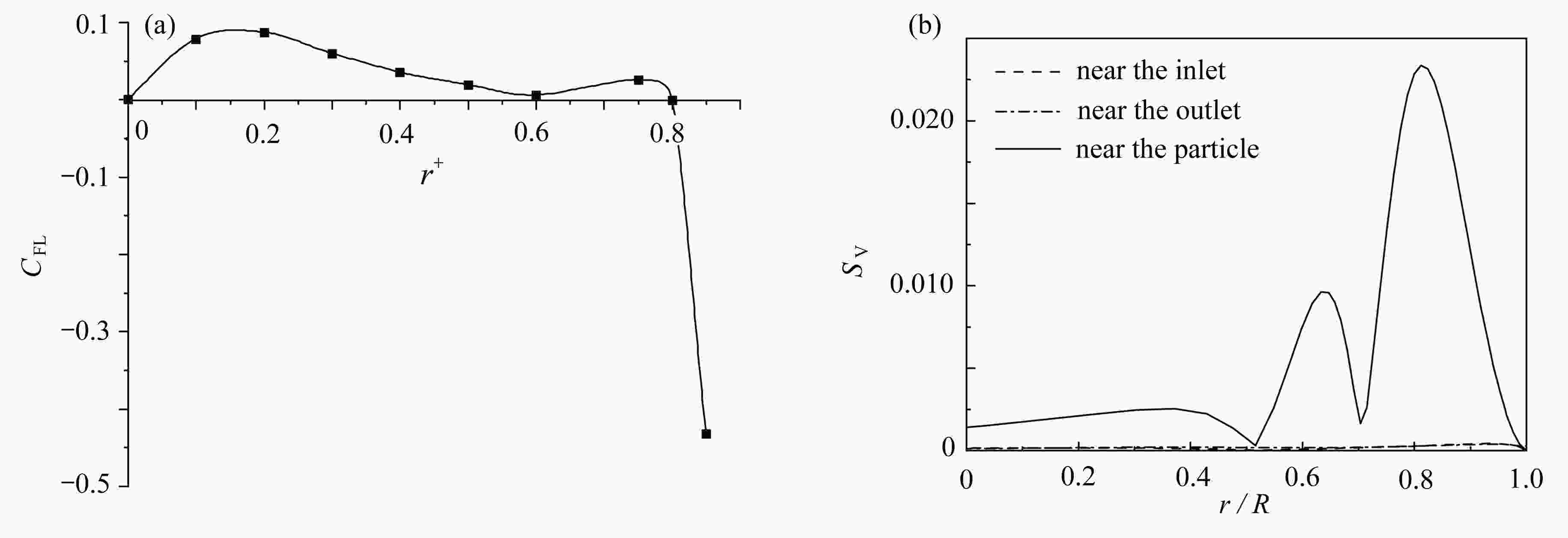
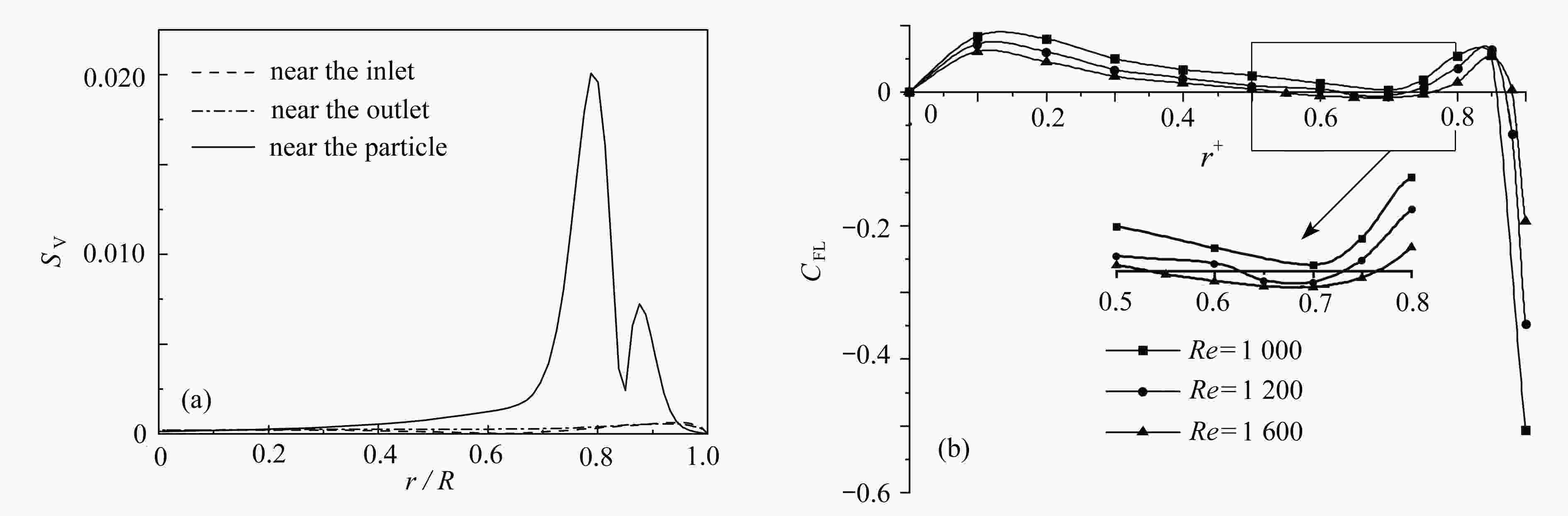
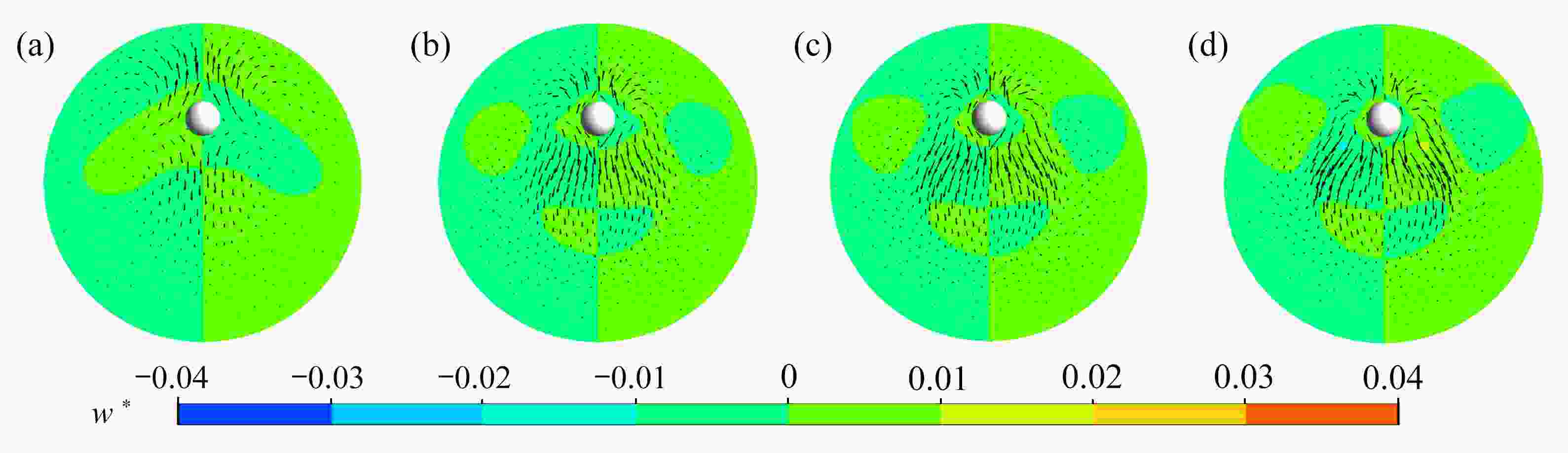
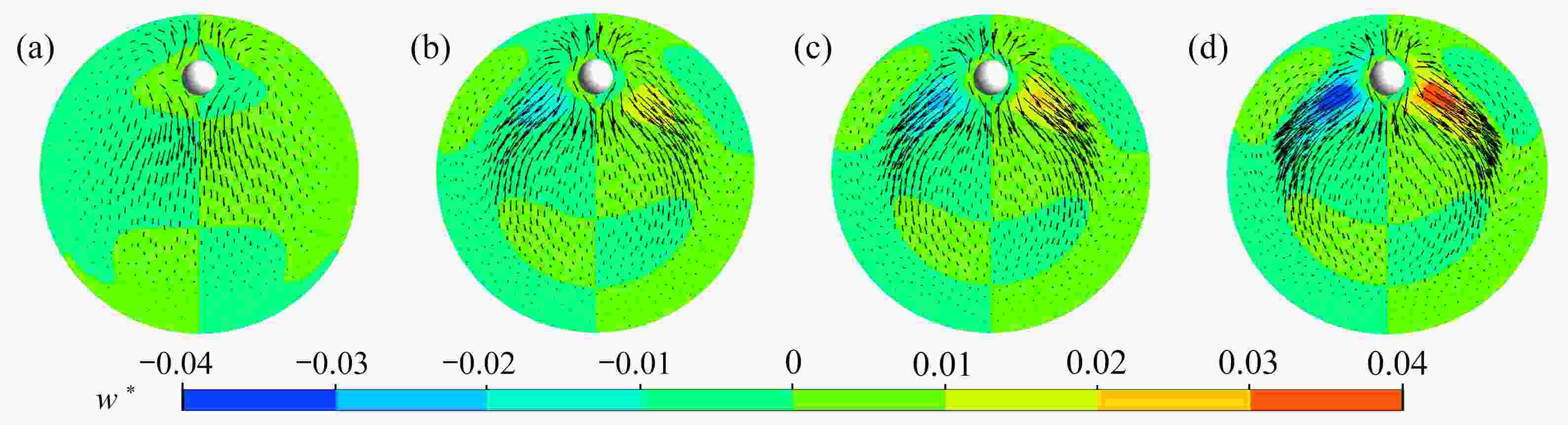
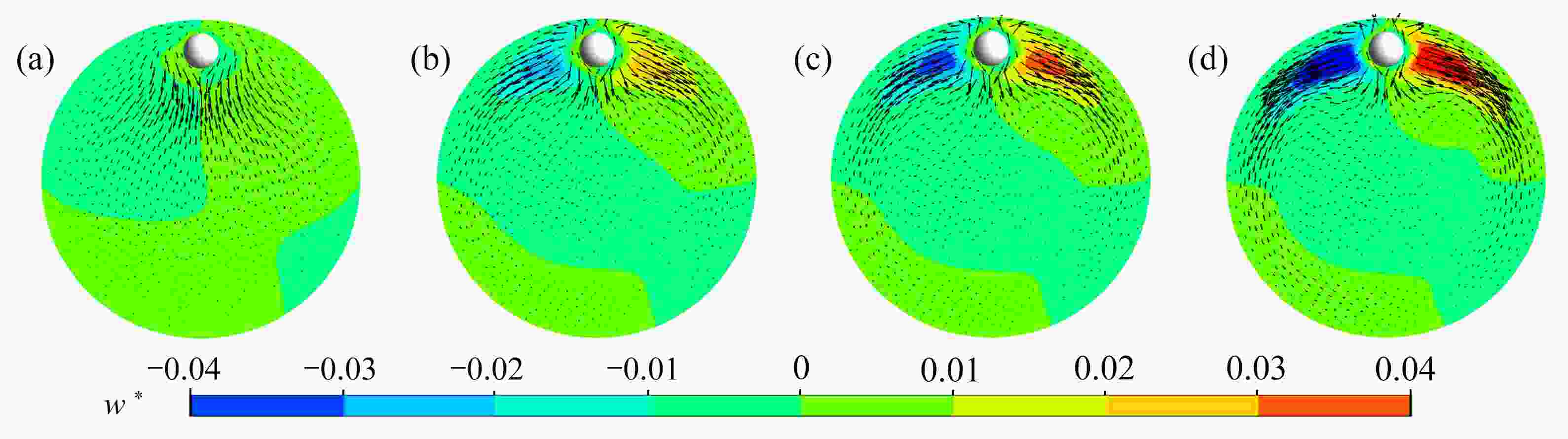
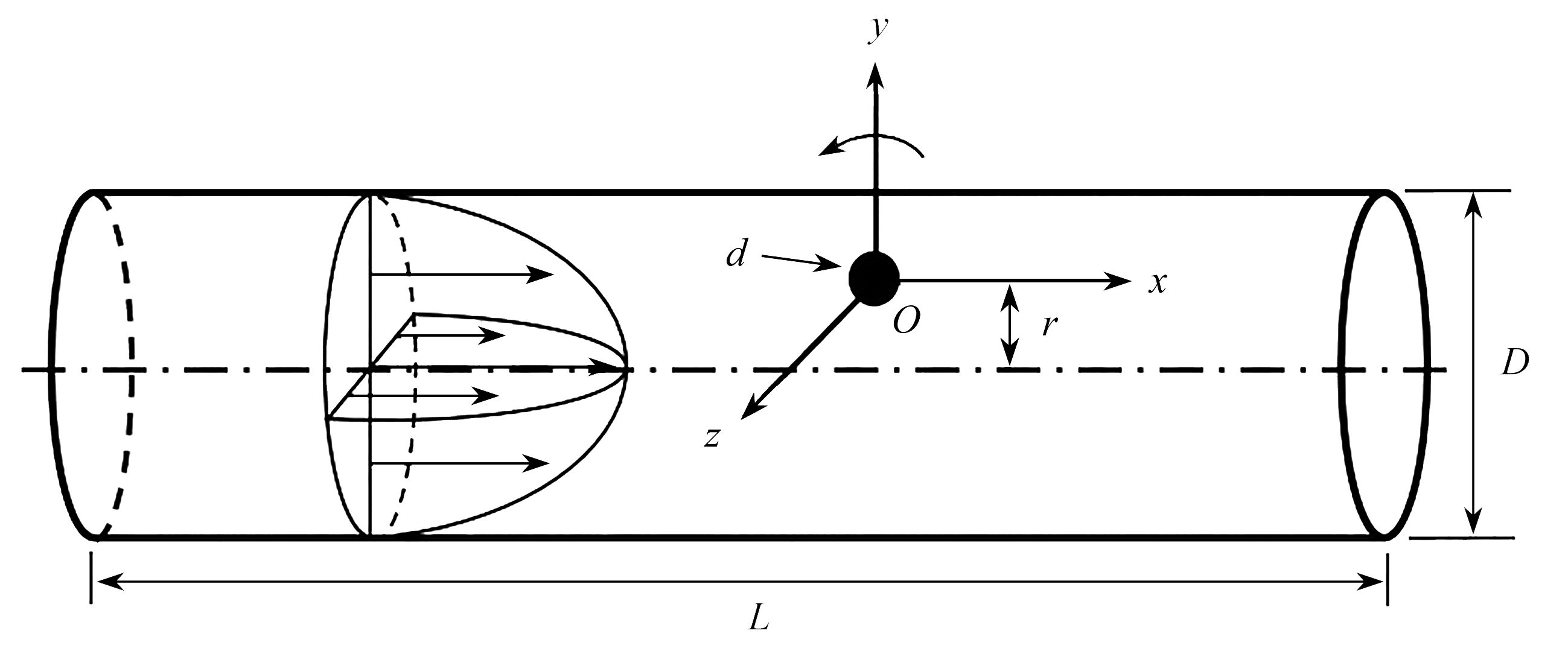
该文基于“相对运动模型”对高Re数层流管道中颗粒的惯性聚集特性进行了数值模拟。为了解决高Re数流长管道问题,对管道进、出口施加了周期性边界条件。研究结果表明,采用周期性边界条件可以有效地减小计算域,选用L=4D的管道便可计算出高Re数管流中颗粒的受力特性。与低Re数不同的是:随着Re数的不断增大,颗粒在径向上的升力不再呈类抛物线分布,升力曲线在r + =0.5 ~ 0.7之间出现一个下凹的区域,在这个区域内有出现新聚集点的趋势,并且用a + =1/17的颗粒在Re>1 000时得到了这个新聚集点的位置。此外,通过对流场进行分析,发现颗粒的周围有二次流产生,其强度随着Re数的增大以及颗粒向壁面靠近逐渐增强,而二次流的产生影响了颗粒升力空间分布。
Abstract:The inertial focusing characteristics of particles in laminar flow pipes with high Re numbers were studied based on the “relative motion model”. In order to solve the problem of long pipes with high Re number flow, periodic boundary conditions were imposed on the inlet and outlet of the pipe. The research results show that the use of periodic boundary conditions can effectively reduce the computational, and the mechanical properties of particles in high Re flow can be calculated by using L=4D pipe. The difference from the low Re number is that as the Re number continues to increase,the lift force of the particles in the radial direction is no longer distributed as a parabola. The lift curve has a concave area between r+ =0.5 ~ 0.7, and there is a tendency for a new inertial focus point to appear in this section. By means of particles of a+ =1/17 for Re > 1 000, this new focus point position is solvable. In addition, in the analysis of the flow field, a secondary flow occurs around the particle, and its intensity gradually increases with the Re number and the closeness of the particle to the wall. The generation of the secondary flow affects the spatial distribution of the particle lift.
-
-
[1] SEGRE G, SILBERBERG A. Radial particle displacements in poiseuille flow of suspension[J]. Nature, 1961, 189(4760): 209-210. doi: 10.1038/189209a0 [2] DI CARLO D. Inertial microfluidics[J]. Lab on a Chip, 2009, 9(21): 3038-3046. doi: 10.1039/b912547g [3] 王企鲲, 李海军, 孙仁, 等. 颗粒惯性聚集中惯性升力的特性研究[J]. 水动力学研究与进展, 2014, 29(5): 530-535WANG Qikun, LI Haijun, SUN Ren, et al. Investigation on the behaviors of inertial lift inducing inertial focus of particles[J]. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 2014, 29(5): 530-535.(in Chinese) [4] MATAS J P, MORRIS J F, GUAZZELLI É. Inertial migration of rigid spherical particles in Poiseuille flow[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2004, 515: 171-195. doi: 10.1017/S0022112004000254 [5] MORITA Y, ITANO T, SUGIHARA-SEKI M. Equilibrium radial positions of neutrally buoyant spherical particles over the circular cross-section in Poiseuilleflow[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2017, 813: 750-767. doi: 10.1017/jfm.2016.881 [6] 陈亚飞, 郑云英. 不可压缩黏性流体的二维Navier-Stokes方程的间断有限元模拟[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2020, 41(8): 844-852CHEN Yafei, ZHENG Yunying. A discontinuous Galerkin FEM for 2D Navier-Stokes equations of incompressible viscous fluids[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2020, 41(8): 844-852.(in Chinese) [7] 王金城, 齐进, 吴锤结. 不可压缩Navier-Stokes方程最优动力系统建模和分析[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2020, 41(1): 1-15 doi: 10.1007/s10483-020-2560-6WANG Jincheng, QI Jin, WU Chuijie. Analysis and modelling of optimal dynamical systems of incompressible Navier-Stokes equations[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2020, 41(1): 1-15.(in Chinese) doi: 10.1007/s10483-020-2560-6 [8] 熊英, 关晖, 吴锤结. 基于有限体积法的非结构网格大涡模拟离散方法研究[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2016, 37(11): 1129-1144XIONG Ying, GUAN Hui, WU Chuijie. LES discretization methods for unstructured meshes based on the finite volume method[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2016, 37(11): 1129-1144.(in Chinese) [9] SHAO Xueming, ZHAO Shengyu, SUN Bo. Inertial migration of spherical particles in circular Poiseuille flow at moderately high Reynolds numbers[J]. Physics of Fluids, 2008, 20(10): 103307. doi: 10.1063/1.3005427 [10] NAKAGAWA N, YABU T, OTOMO R. Inertial migration of a spherical particle in laminar square channel flows from low to high Reynolds numbers[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2015, 779: 776-793. doi: 10.1017/jfm.2015.456 [11] CARLO D D, EDD J F, HUMPHRY K J, et al. Particle segregation and dynamics in confined flows[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2009, 102(9): 094503. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.102.094503 [12] 王企鲲. 微通道中颗粒所受惯性升力特性的数值研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2014, 50(2): 165-170 doi: 10.3901/JME.2014.02.165WANG Qikun. Numerical investigation on mechanism for inertial lift on particles in micro-channel[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2014, 50(2): 165-170.(in Chinese) doi: 10.3901/JME.2014.02.165 [13] WANG Qikun, YUAN Dan, LI Weihua. Analysis of hydrodynamic mechanism on particles focusing in micro-channel flows[J]. Micromachines, 2017, 8(7): 197. doi: 10.3390/mi8070197 [14] 陶文铨. 数值传热学[M]. 2版. 西安: 西安交通大学出版社, 2001: 489.TAO Wenquan. Numerical Heat Transfer[M]. 2nd ed. Xi’an: Xi’an Jiaotong University Press, 2001: 489. (in Chinese) [15] ZOU He, WANG Qikun, XUE Zhuangzhuang. Characteristics of lift and resistance of spherical wall in semi-unbounded flow field[J]. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 2022, 14(3): 1-13. -





 下载:
下载:



 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号