An Electrocardiogram Signal Classification Algorithm Based on Improved Deep Residual Shrinkage Networks
-
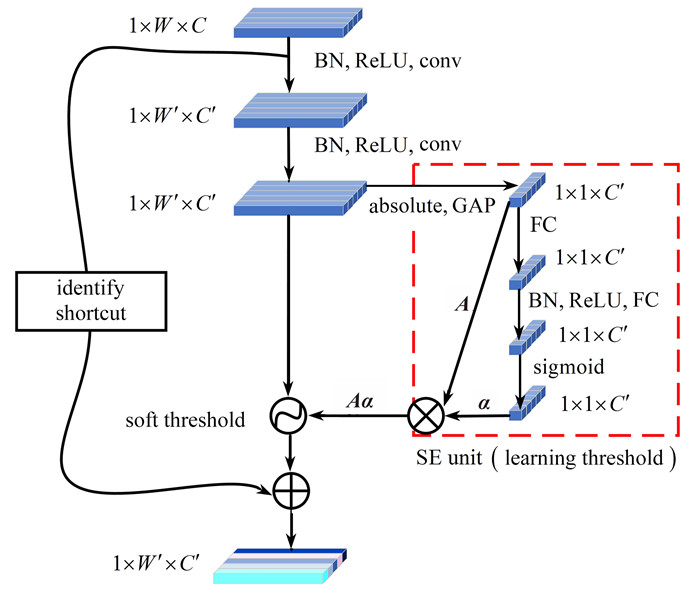
摘要: 心电信号分类是医疗保健领域的重要研究内容. 针对大多数方法不能很好地降低样本数量少的类别漏诊率,以及降低预处理操作的复杂性问题,提出了一种基于改进深度残差收缩网络(IDRSN)的心电信号分类算法(即DRSL算法). 首先,使用合成少数类过采样技术(SMOTE)扩充数量少的类别样本,从而解决了类不平衡问题;其次,利用改进深度残差收缩网络提取空间特征,其残差模块可以避免网络层加深造成的过拟合,压缩激励和软阈值化子网络可以提取重要局部特征并自动去除噪声;然后,通过长短期记忆网络(LSTM)提取时间特征;最后,利用全连接网络输出分类结果. 在MIT-BIH心律失常数据集上的实验结果表明,该算法的分类性能优于IDRSN、DRSN、GAN+2DCNN、CNN+LSTM_ATTENTION、SE-CNN-LSTM分类算法.
-
关键词:
- 心电信号 /
- 合成少数类过采样技术 /
- 深度残差收缩网络 /
- 压缩激励 /
- 长短期记忆网络
Abstract: The electrocardiogram (ECG) signal classification is a significant research topic in the healthcare field. Most existing methods could not effectively reduce the missed diagnosis rate of classification with small-size samples and tackle the complexity of preprocessing operations. An electrocardiogram signal classification algorithm based on the improved deep residual shrinkage networks was proposed, namely the DRSL algorithm. Firstly, the small-size classification samples were augmented with the synthetic minority over-sampling technique to solve the classification imbalance problem. Secondly, the spatial features were extracted by mean of the improved deep residual shrinkage networks, where the residual module can avoid overfitting caused by deepening of network layers, and the squeeze-and-excitation operation with soft threshold subnetwork can extract important local features and remove noises automatically. Then, the time features were extracted with the long short-term memory networks. Finally, the classification results were output with the fully connected neural networks. The experimental results on the MIT-BIH arrhythmia database show that, the proposed algorithm is superior to IDRSN, DRSN, GAN+2DCNN, CNN+LSTM_ATTENTION, SE-CNN-LSTM in terms of classification performances. -
表 1 AAMI标准以及4种心拍类别的样本数量
Table 1. The AAMI standards and the number of heartbeats in the 4 classes
heartbeat category of the AAMI heartbeat category of the MIT-BIH database expert annotation code number normal heartbeat (N) normal beat (N)
left bundle branch block beat (L)
right bundle branch block beat (R)
nodal (junctional) escape beat (j)
atrial escape beat (e)1, 2, 3, 11, 34 90 004 supraventricular ectopic heartbeat (S) aberrated atrial premature beat (a)
nodal (junctional) premature beat (J)
atrial premature beat (A)
supraventricular premature beat (S)4, 7, 8, 9 2 778 ventricular ectopic heartbeat (V) premature ventricular contraction (V)
ventricular escape beat (E)5, 10 7 004 fusion heartbeat (F) fusion of ventricular and normal beat (F) 6 802 total 100 588 表 2 类别平衡前后的数据集
Table 2. Datasets before and after class balancing
N S V F training set 14 000 1 944 4 903 562 balanced training set 14 000 14 000 14 000 14 000 validation set 2 000 278 700 80 test set 4 000 556 1 401 160 表 3 DRSL网络的超参数设置
Table 3. Hyperparameter settings for the DRSL network
layer type network parameter value training parameter value CNN
max pooling
IDRSN(a)+IDRSN(b)
IDRSN(a)+IDRSN(b)
IDRSN(a)+IDRSN(b)
IDRSN(a)+IDRSN(b)
IDRSN(a)+IDRSN(b)
LSTM
global average pooling
dense
denseFfilter=8, Dcs=3, padding=“same”, kernel_regularizer=L2(0.000 1)
pooling_size=(2, 2), strides=(2, 2), a=“tanh”
Cout=8
Cout=16
Cout=32
Cout=64
Cout=128
unit is 32, a=“tanh”
a=“LeakyReLU”
unit is 32
unit is 4, a=“softmax”, kernel_regularizer=L2(0.000 1)epochs is 20
batch_size is 64
optimizer=“Adam”
initial_learning_rate=0.002
each additional 10 epochs,
the learning rate decreased
to 0.1 times表 4 DRSL算法在测试集上的分类结果
Table 4. The classification results of the DRSL algorithm on the test set
δAcc/% δSen/% δSpec/% δPPV/% N 98.53 98.80 98.02 98.95 S 99.17 95.50 99.53 95.33 V 98.92 97.64 99.30 97.64 F 99.30 88.13 99.60 85.45 overall classification performance 98.98 95.02 99.11 94.34 表 5 DRSL算法与其消融实验的总体分类性能比较
Table 5. The overall classification performance comparison between the DRSL algorithm and its ablation experiments
classification algorithm overall classification performance average δAcc/% average δSen/% average δSpec/% average δPPV/% DRSL 98.98 95.02 99.11 94.34 IDRSN 98.94 94.60 99.00 93.93 DRSN 98.79 93.88 98.85 94.71 表 6 DRSL算法与其他算法的总体分类性能比较
Table 6. The overall classification performance comparison between the DRSL algorithm and other algorithms
classification algorithm denoising and sample balancing methods overall classification performance average δAcc/% average δSen/% average δSpec/% average δPPV/% DRSL null+SMOTE 98.98 95.02 99.11 94.34 GAN+2DCNN[9] null+GAN 98.41 93.68 98.85 92.65 CNN+LSTM_ATTENTION[11] wavelet threshold+SMOTE 98.38 95.80 98.58 92.35 SE-CNN-LSTM[12] wavelet threshold+SMOTE 97.69 89.56 97.86 89.27 表 7 DRSL算法与其他算法的S类分类性能比较
Table 7. The classification performance comparison in class S between the DRSL algorithm and other algorithms
classification algorithm class S classification performance δAcc/% δSen/% δSpec/% δPPV/% DRSL 99.17 95.50 99.53 95.33 IDRSN 99.04 92.99 99.64 96.28 DRSN 98.61 92.81 99.19 91.98 GAN+2DCNN[9] 98.05 95.50 98.30 84.69 CNN+LSTM_ATTENTION[11] 98.28 94.24 98.69 87.77 SE-CNN-LSTM[12] 97.47 87.05 98.51 85.36 -
[1] EBRAHIMI Z, LONI M, DANESHTALAB M, et al. A review on deep learning methods for ECG arrhythmia classification[J]. Expert Systems With Applications: X, 2020, 7 : 100033. doi: 10.1016/j.eswax.2020.100033 [2] KLIGFIELD P. The centennial of the einthoven electrocardiogram[J]. Journal of Electrocardiology, 2002, 35 (4): 123-129. doi: 10.1054/jelc.2002.37169 [3] LYNCH R. ECG lead misplacement: a brief review of limb lead misplacement[J]. African Journal of Emergency Medicine, 2014, 4 (3): 130-139. doi: 10.1016/j.afjem.2014.05.006 [4] 李胜蓝, 辛继宾, 莫梅琦, 等. 基于QRS波群的心律失常辅助诊断模型研究[J]. 生物医学工程学进展, 2008, 29 (4): 202-205. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHYC200804006.htmLI Shenglan, XIN Jibin, MO Meiqi, et al. The research of diagnosis model for arrhythmia using QRS complex[J]. Advances in Biomedical Engineering, 2008, 29 (4): 202-205. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHYC200804006.htm [5] LANNOY G D, FRANCOIS D, DELBEKE J, et al. Weighted conditional random fields for supervised interpatient heartbeat classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Bio-Medical Engineering, 2012, 59 (1): 241-247. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2011.2171037 [6] LAGERHOLM M, PETERSON C, BRACCINI G, et al. Clustering ECG complexes using hermite functions and self-organizing maps[J]. IEEE Transactions on Bio-Medical Engineering, 2000, 47 (7): 838-848. doi: 10.1109/10.846677 [7] MINHAS F A, ARIF M. Robust electrocardiogram (ECG) beat classification using discrete wavelet transform[J]. Physiological Measurement, 2008, 29 (5): 555-570. doi: 10.1088/0967-3334/29/5/003 [8] MONDÉJAR-GUERRA V, NOVO J, ROUCO J, et al. Heartbeat classification fusing temporal and morphological information of ECGs via ensemble of classifiers[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2019, 47 : 41-48. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2018.08.007 [9] 陈鹏, 刘子龙. 基于GAN-CNN的心律失常识别[J]. 电子科技, 2022, 35 (3): 45-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKK202203007.htmCHEN Peng, LIU Zilong. Arrhythmia recognition based on GAN-CNN[J]. Electronic Science and Technology, 2022, 35 (3): 45-50. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKK202203007.htm [10] SOWMYA S, JOSE D. Contemplate on ECG signals and classification of arrhythmia signals using CNN-LSTM deep learning model[J]. Measurement: Sensors, 2022, 24 : 100558. doi: 10.1016/j.measen.2022.100558 [11] ZHANG T. Arrhythmias classification based on CNN and LSTM_ATTENTION hybrid model[C]//Proceedings of the 2021 3 rd World Symposium on Artificial Intelligence. Guangzhou, China: IEEE, 2021: 58-63. [12] 郭炜伦, 方钰敏, 徐海蛟, 等. 基于SE-CNN-LSTM的心电识别算法[J]. 电脑知识与技术, 2022, 18 (21): 73-75. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DNZS202221026.htmGUO Weilun, FANG Yumin, XU Haijiao, et al. An ECG recognition algorithm based on SE-CNN-LSTM[J]. Computer Knowledge and Technology, 2022, 18 (21): 73-75. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DNZS202221026.htm [13] HAN C, SHI L. ML-ResNet: a novel network to detect and locate myocardial infarction using 12 leads ECG[J]. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2020, 185 : 105138. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2019.105138 [14] 秦博, 黎明, 黎天翼, 等. 基于注意力残差模型的心律失常分类研究[J]. 湖北师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 42 (3): 18-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBSF202203003.htmQIN Bo, LI Ming, LI Tianyi, et al. Research on arrhythmia classification based on attention residual model[J]. Journal of Hubei Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 42 (3): 18-25. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBSF202203003.htm [15] 刘小靖, 周又和, 王记增. 小波方法及其力学应用研究进展[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2022, 43 (1): 1-13. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.420388LIU Xiaojing, ZHOU Youhe, WANG Jizeng. Research progresses of wavelet methods and their applications in mechanics[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2022, 43 (1): 1-13. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.420388 [16] ZHAO M, ZHONG S, FU X, et al. Deep residual shrinkage networks for fault diagnosis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16 (7): 4681-4690. doi: 10.1109/TII.2019.2943898 [17] HE K, ZHANG X, REN S, et al. Identity mappings in deep residual networks[C]//Proceedings of the Computer Vision ECCV 2016. Cham: Springer, 2016: 630-645. [18] 洪奇峰, 施伟斌, 吴迪, 等. 深度卷积神经网络模型发展综述[J]. 软件导刊, 2020, 19 (4): 84-88. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RJDK202004017.htmHONG Qifeng, SHI Weibin, WU Di, et al. Review of the development of deep convolutional neural network model[J]. Software Guide, 2020, 19 (4): 84-88. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RJDK202004017.htm [19] HU J, SHEN L, SUN G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Washington DC: IEEE, 2018: 7132-7141. [20] 吴爱华, 彭金喜. 基于深度残差收缩网络的信号调制类型识别[J]. 电子信息对抗技术, 2022, 37 (4): 24-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDK202204005.htmWU Aihua, PENG Jinxi. Signal modulation recognition based on deep residual shrinkage network[J]. Electronic Information Countermeasure Technology, 2022, 37 (4): 24-30. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDK202204005.htm [21] HOCHREITER S, SCHMIDHUBER J. Long short-term memory[J]. Neural Computation, 1997, 9 (8): 1735-1780. [22] 张巧灵, 高淑萍, 何迪, 等. 基于时间序列的混合神经网络数据融合算法[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2021, 42 (1): 82-91. doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.410056ZHANG Qiaoling, GAO Shuping, HE Di, et al. A hybrid neural network data fusion algorithm based on time series[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2021, 42 (1): 82-91. (in Chinese) doi: 10.21656/1000-0887.410056 [23] 韦张跃昊, 钱升谊. 基于滤波重构和卷积神经网络的心电信号分类[J]. 电子科技, 2019, 32 (11): 7-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKK201911003.htmWEI Zhangyuehao, QIAN Shengyi. ECG signal classification based on filtering-reconstruction and convolutional neural network[J]. Electronic Science and Technology, 2019, 32 (11): 7-11. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKK201911003.htm [24] LIU F, ZHOU X, WANG T, et al. An attention-based hybrid LSTM-CNN model for arrhythmias classification[C]//Proceedings of the 2019 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. Budapest, Hungary: IEEE, 2019: 1-8. [25] 李兴秀, 唐建军, 华晶. 结合CNN与双向LSTM的心律失常分类[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2021, 15 (12): 2353-2361. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTS202112010.htmLI Xingxiu, TANG Jianjun, HUA Jing. Arrhythmia classification based on CNN and bidirectional LSTM[J]. Computer Science and Exploration, 2021, 15 (12): 2353-2361. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTS202112010.htm [26] 石洪波, 陈雨文, 陈鑫. SMOTE过采样及其改进算法研究综述[J]. 智能系统学报, 2019, 14 (6): 1073-1083. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNXT201906002.htmSHI Hongbo, CHEN Yuwen, CHEN Xin. Summary of research on SMOTE oversampling and its improved algorithms[J]. Journal of Intelligent Systems, 2019, 14 (6): 1073-1083. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNXT201906002.htm [27] 黄莹. 基于深度残差收缩网络的心律失常分类算法研究[D]. 硕士学位论文. 南宁: 广西大学, 2022.HUANG Ying. A research of arrhythmia classification algorithm based on deep residual shrinkage network[D]. Master Thesis. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2022. (in Chinese) -





 下载:
下载:







 渝公网安备50010802005915号
渝公网安备50010802005915号